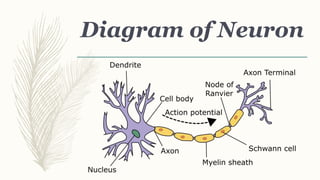
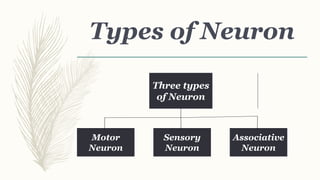
Neurons are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system. They transmit electrochemical signals throughout the body and have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. There are about 100 billion neurons in the human brain that come in three main types - motor neurons carry signals from the brain to muscles and glands, sensory neurons carry signals from receptors to the brain, and associative neurons connect neurons within the brain and spinal cord. Neurons transmit information via an electrochemical process where electrical signals travel through the neuron and chemical signals are used to transmit between neurons at synapses.