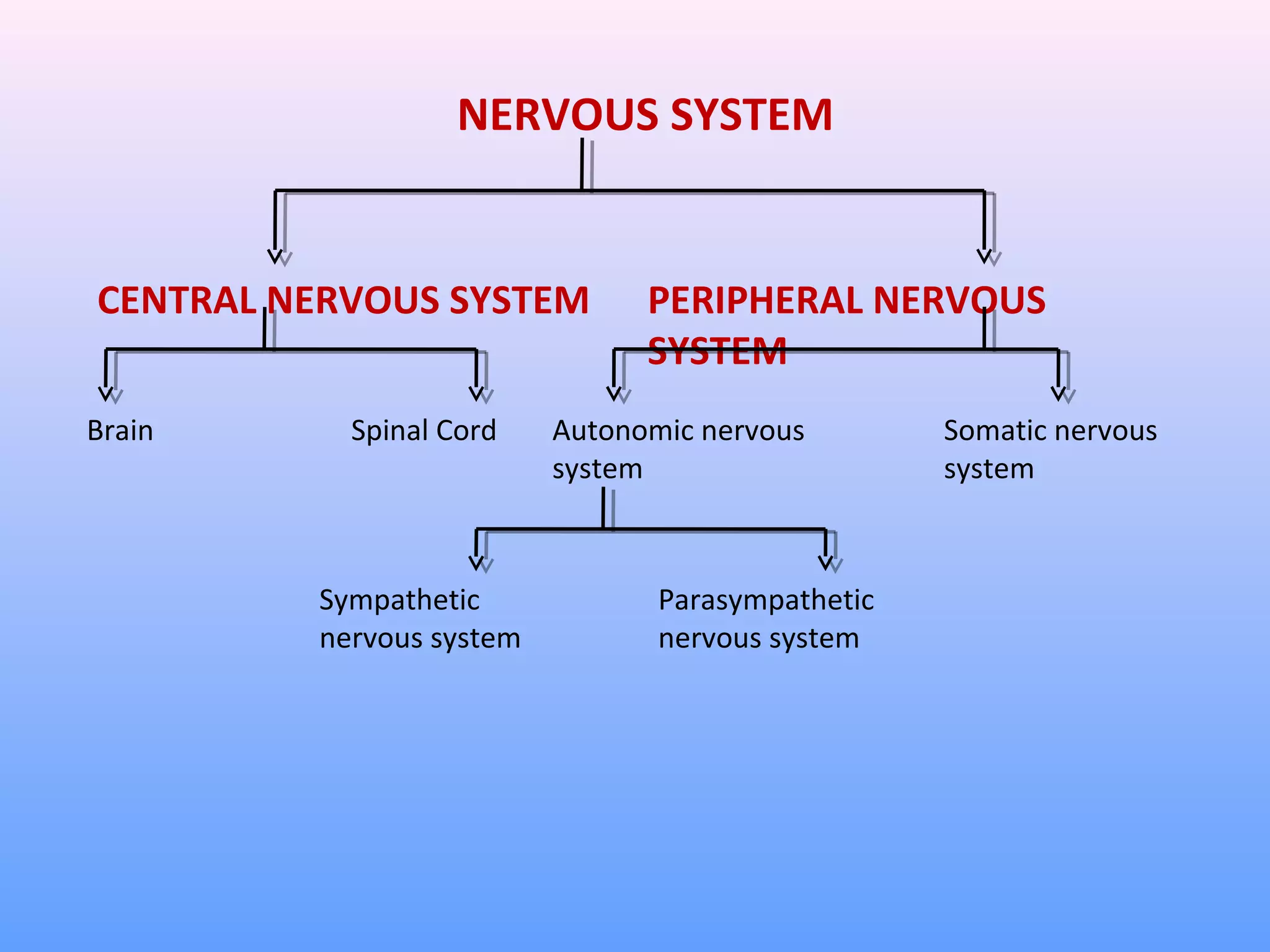
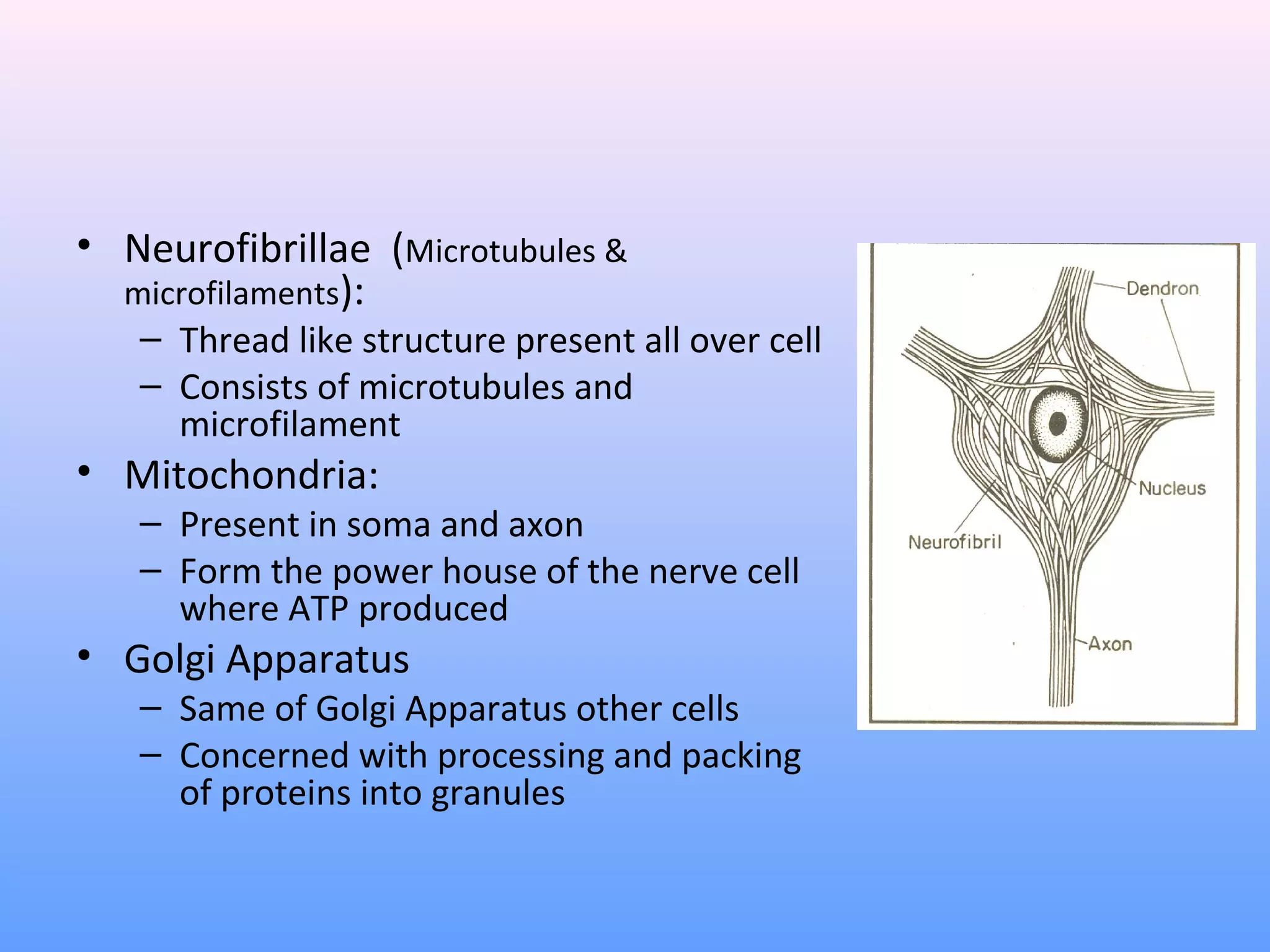
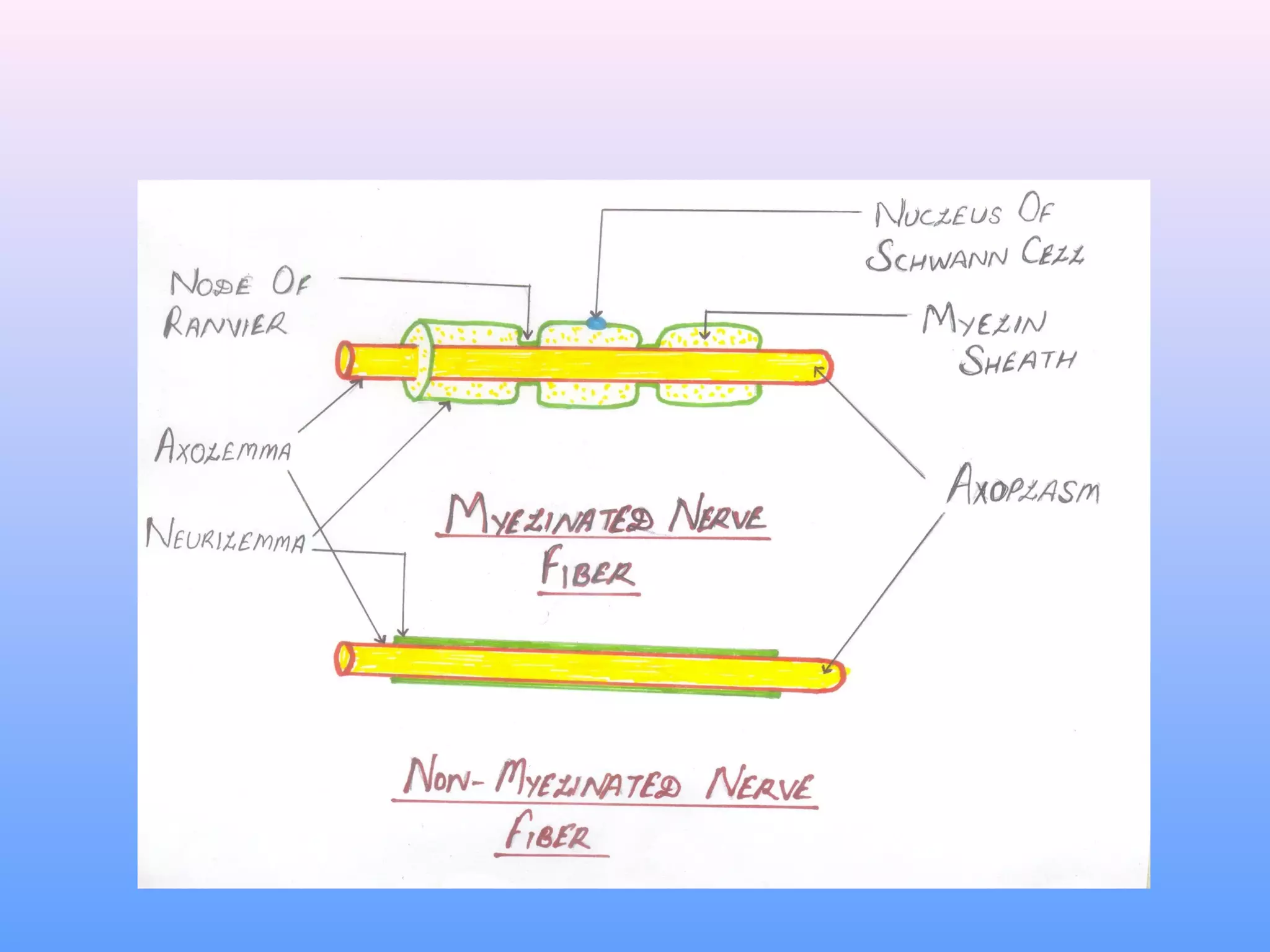
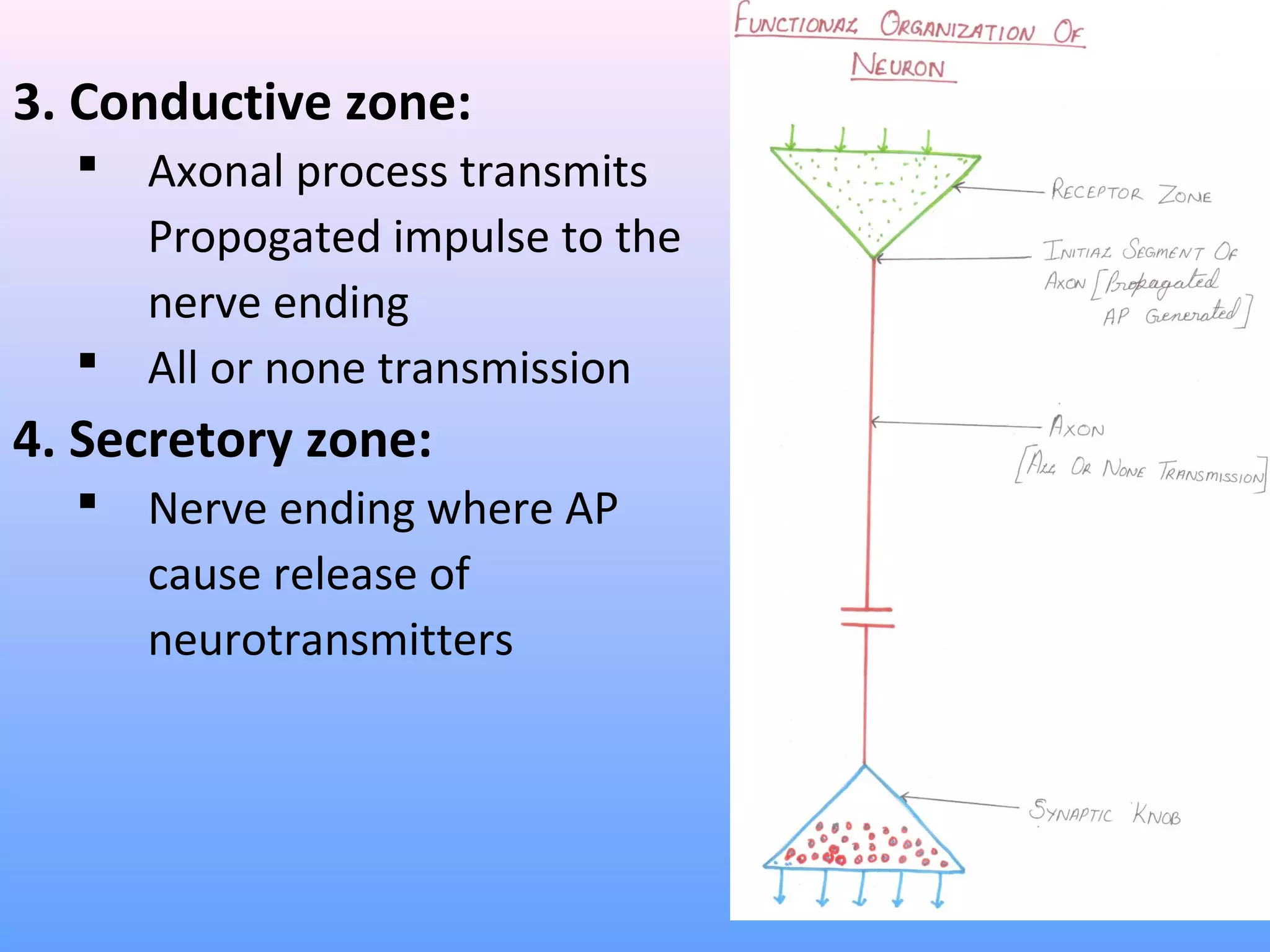
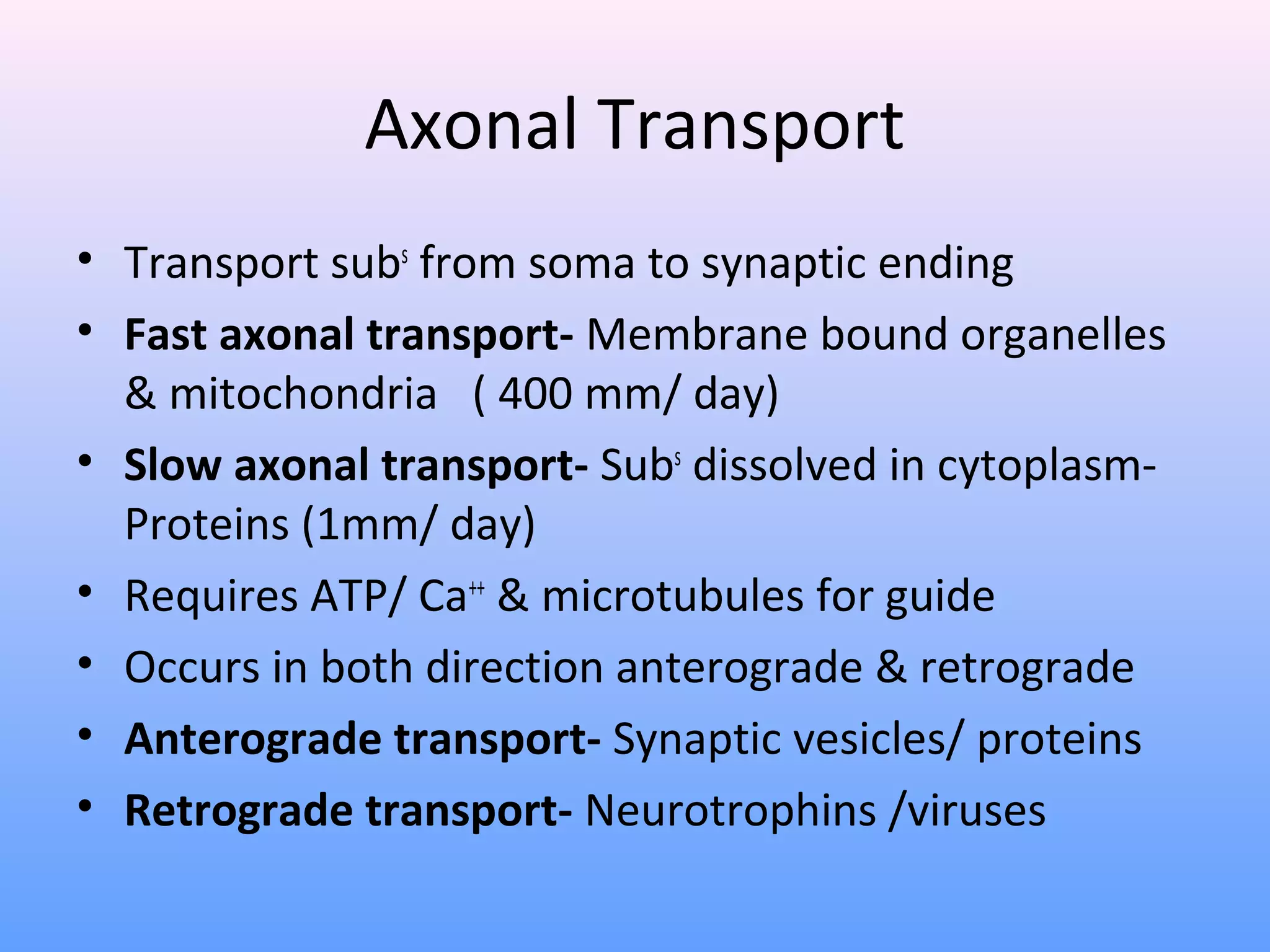
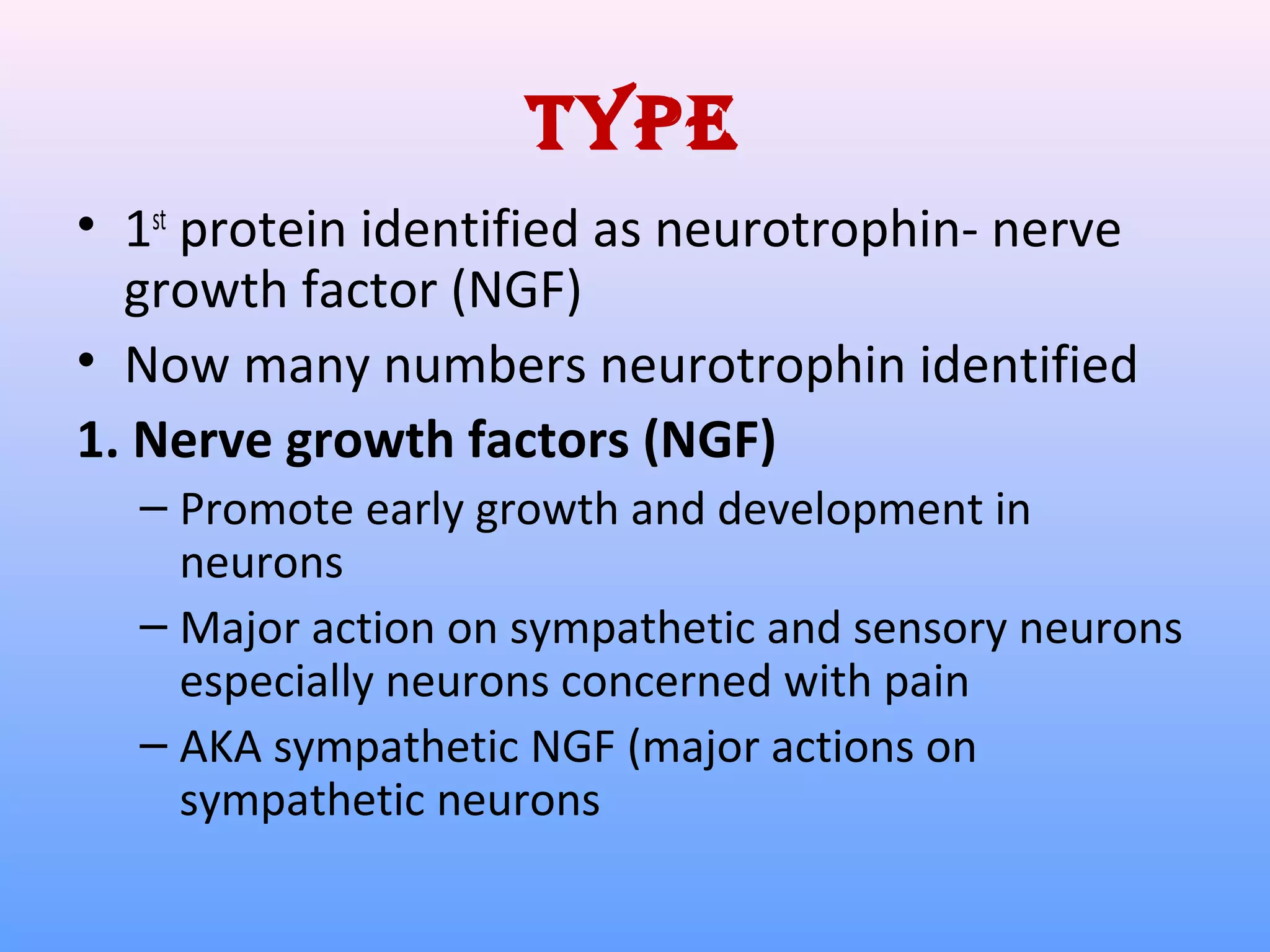
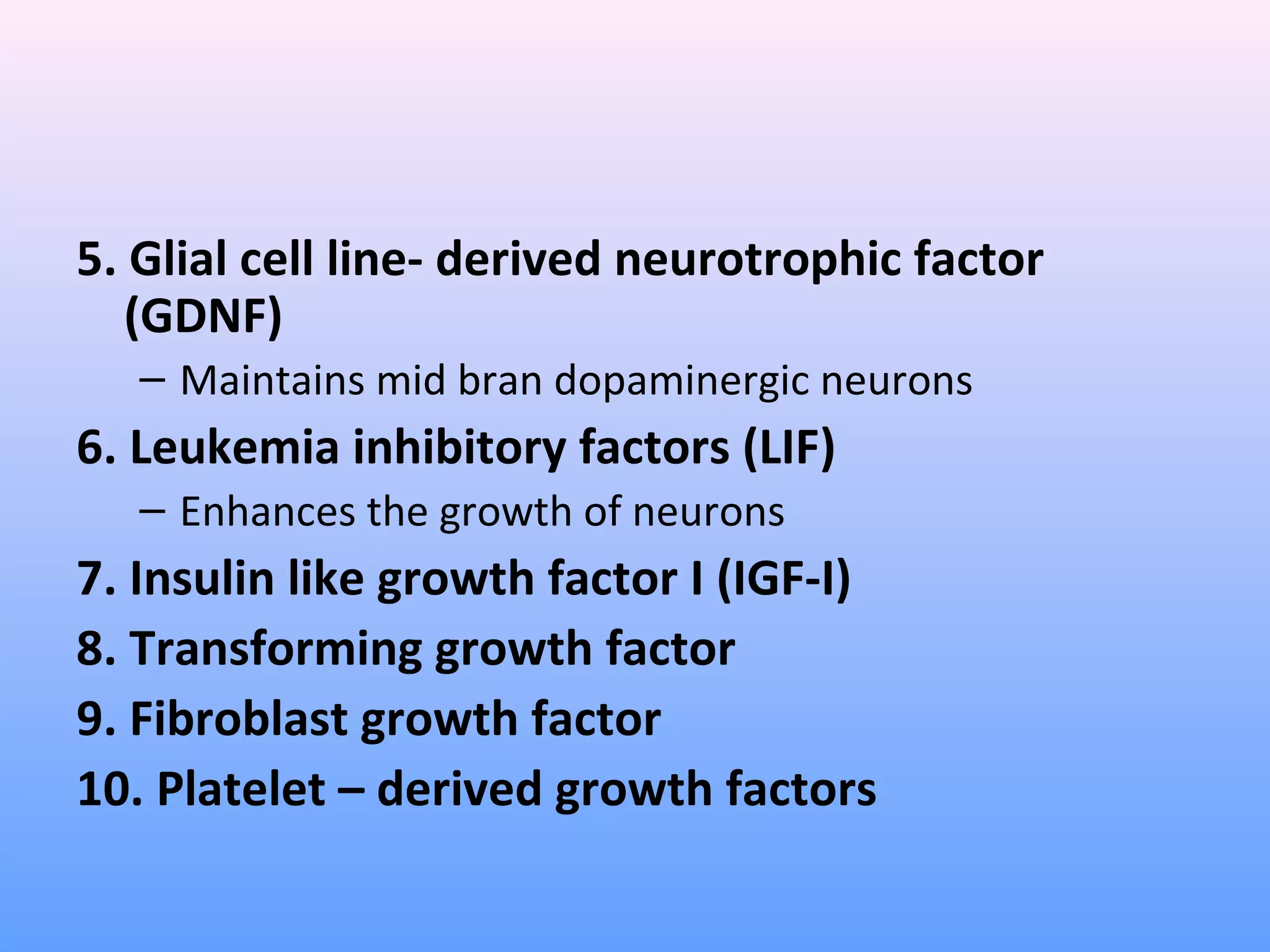
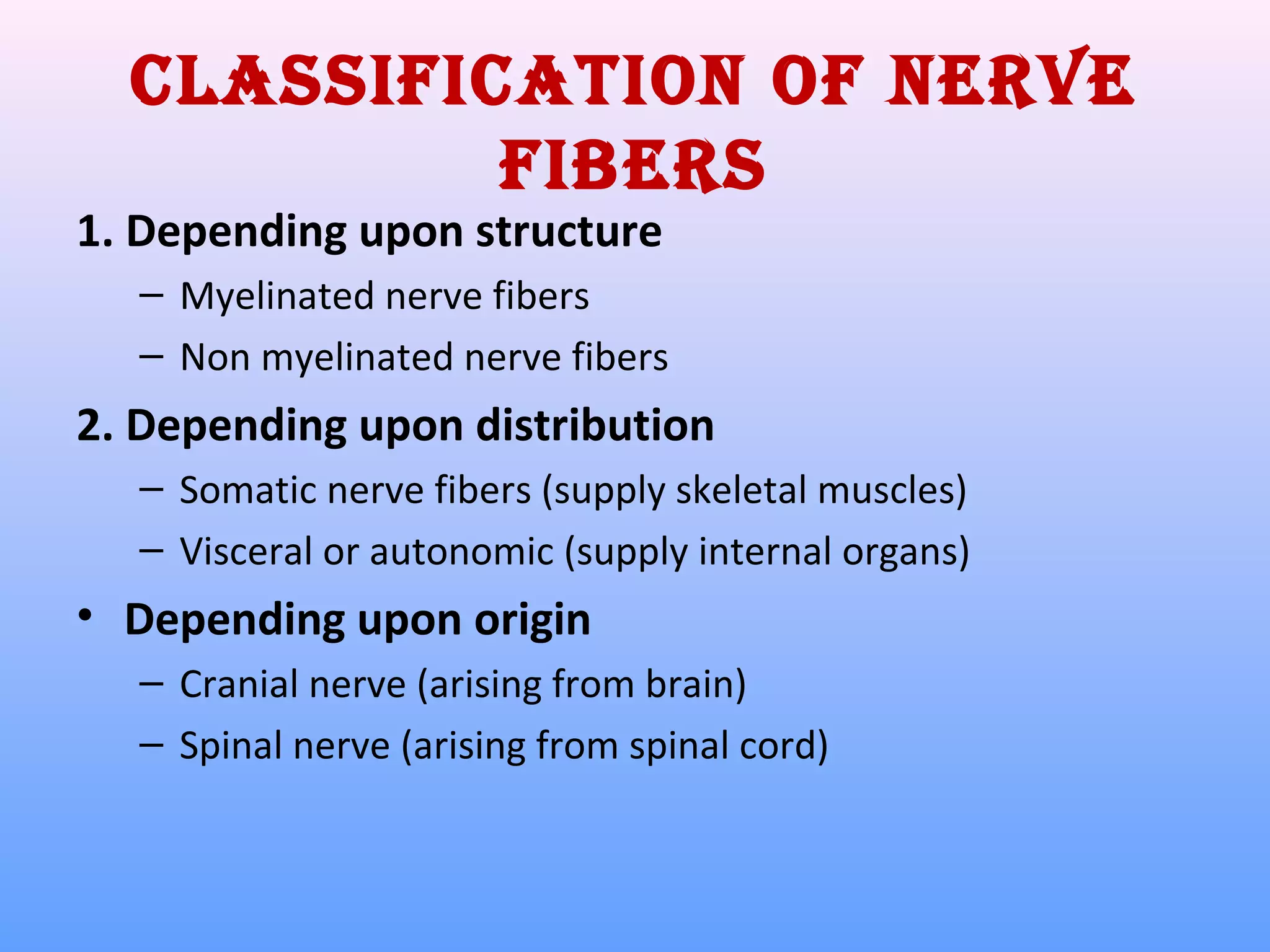
This document provides information on nerve muscle physiology. It discusses the structure and function of neurons, including their classification based on number of poles and length of axon. Key parts of the neuron are described, including the cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, and neurofibrils. The roles of the myelin sheath and Schwann cells in insulation and myelination are covered. Neurotrophic factors that promote neuronal growth and survival are also summarized.