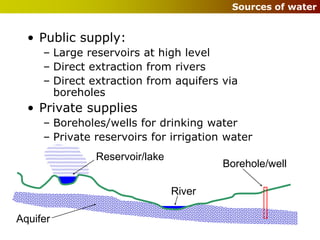
Wet services provide water supply and drainage for public health. Water supply comes from public mains, private boreholes, or reservoirs. Drainage includes domestic and public sewer systems. Water is distributed through pipes from sources like reservoirs, rivers, or aquifers and is treated before local distribution to buildings. Internal plumbing uses copper pipes with compression or soldered joints to distribute cold and hot water.