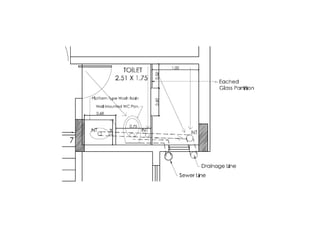
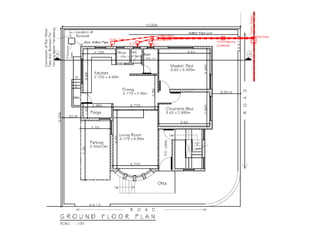
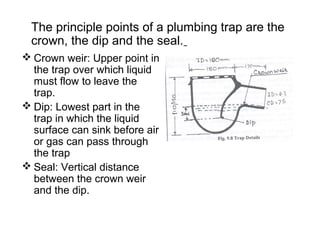
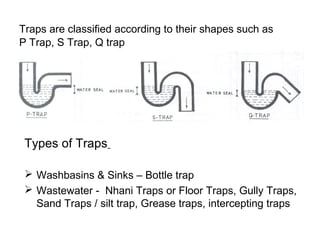
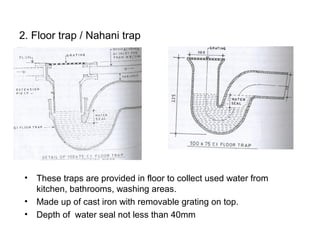
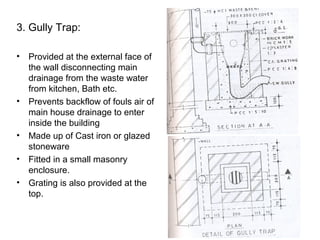
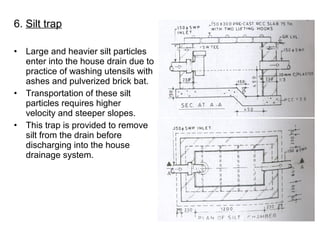
The document discusses building drainage systems and traps. It explains that a building drainage system is the system of pipes that collects waste water from sanitary fixtures and discharges it to the public sewer via gravity. It also discusses general design principles for drainage systems, such as laying pipes along walls for maintenance and providing proper ventilation and slopes. The document then focuses on traps, explaining that traps hold water to prevent foul gases and vermin from entering rooms. It describes different types of traps used in drainage systems and their purposes.