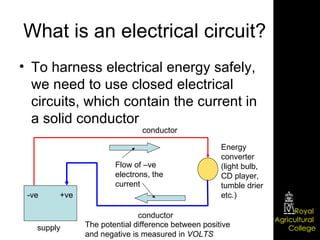
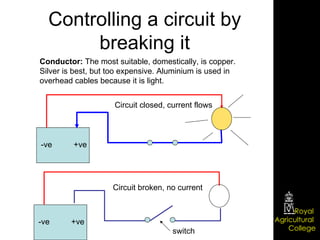
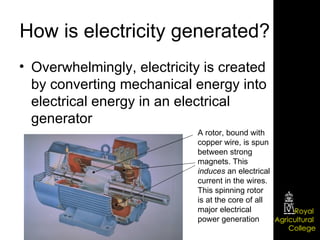
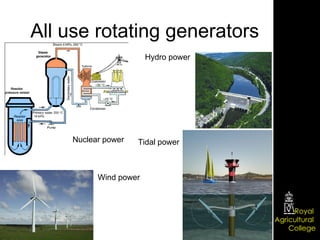
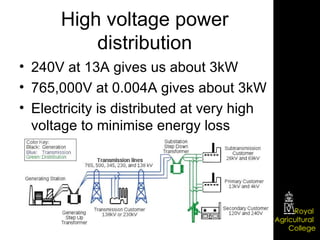
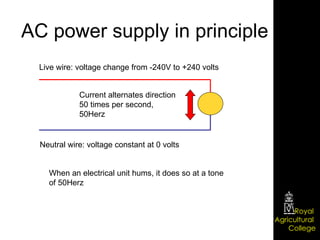
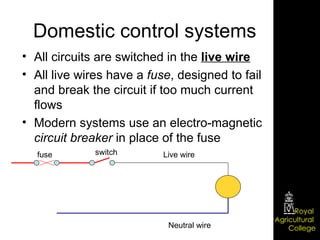
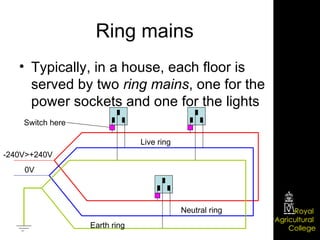
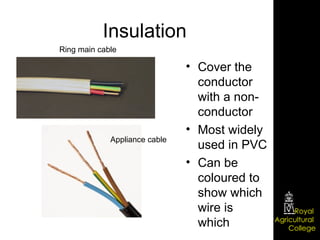
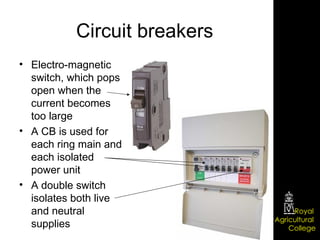
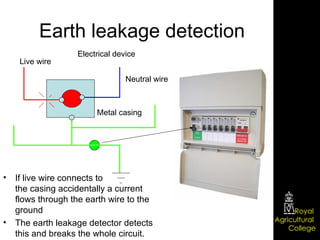
Domestic electrical systems provide a core source of energy in modern societies. Electricity is generated through converting mechanical energy to electrical energy in generators, then distributed through high-voltage power lines to minimize energy loss. In homes, electricity is delivered through ring main wiring systems at 240 volts and 50 Hertz, with safety features like fuses, circuit breakers, and grounding to prevent electric shocks.