1. Traps are devices installed on drains and waste pipes to prevent foul gases from entering homes. They work by providing a water seal barrier between the drain and the house.
2. Different types of traps include P, Q, and S traps (named for their shapes), gully traps, intercepting traps, anti-D traps, and anti-siphon traps.
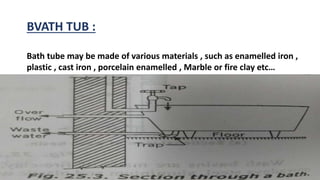
3. Proper plumbing and sanitary fittings in buildings are required, including wash basins, sinks, bath tubs, flushing cisterns, water closets, and urinals which are available in various standard sizes and materials.