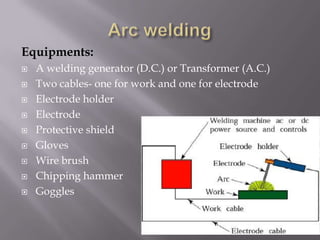
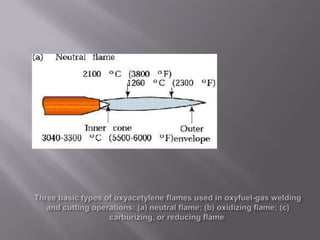
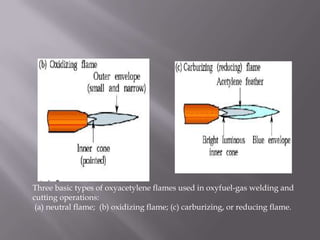
Welding is a process that joins materials by heating them to melt and fuse together. It is used to make permanent joints in manufacturing processes like automobiles, aircraft, machinery, and shipbuilding. There are two main types of welding - plastic welding which uses heat and pressure, and fusion welding which melts the materials. Fusion welding includes arc welding, gas welding, and other processes that use heat sources like electric arcs, oxy-acetylene gas, plasma arcs, or lasers, and may add filler material. Arc welding specifically uses an electric arc to melt metals and can use direct or alternating current along with consumable or non-consumable electrodes.