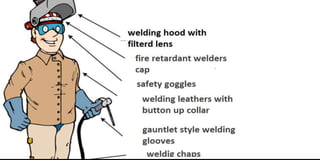
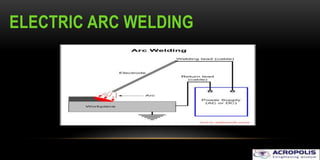
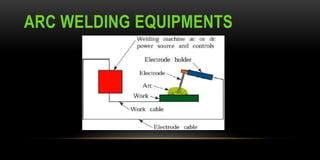
The document discusses arc welding, including its basics and principles. Arc welding involves striking an electric arc between an electrode and the metal workpiece to melt and join the metals. The key steps are preparing the materials, selecting the welding process and filler material, assessing safety requirements, and inspecting the final weld. Arc welding is commonly used in construction and fabrication due its portability, low equipment cost, and ability to weld steels and other alloys.