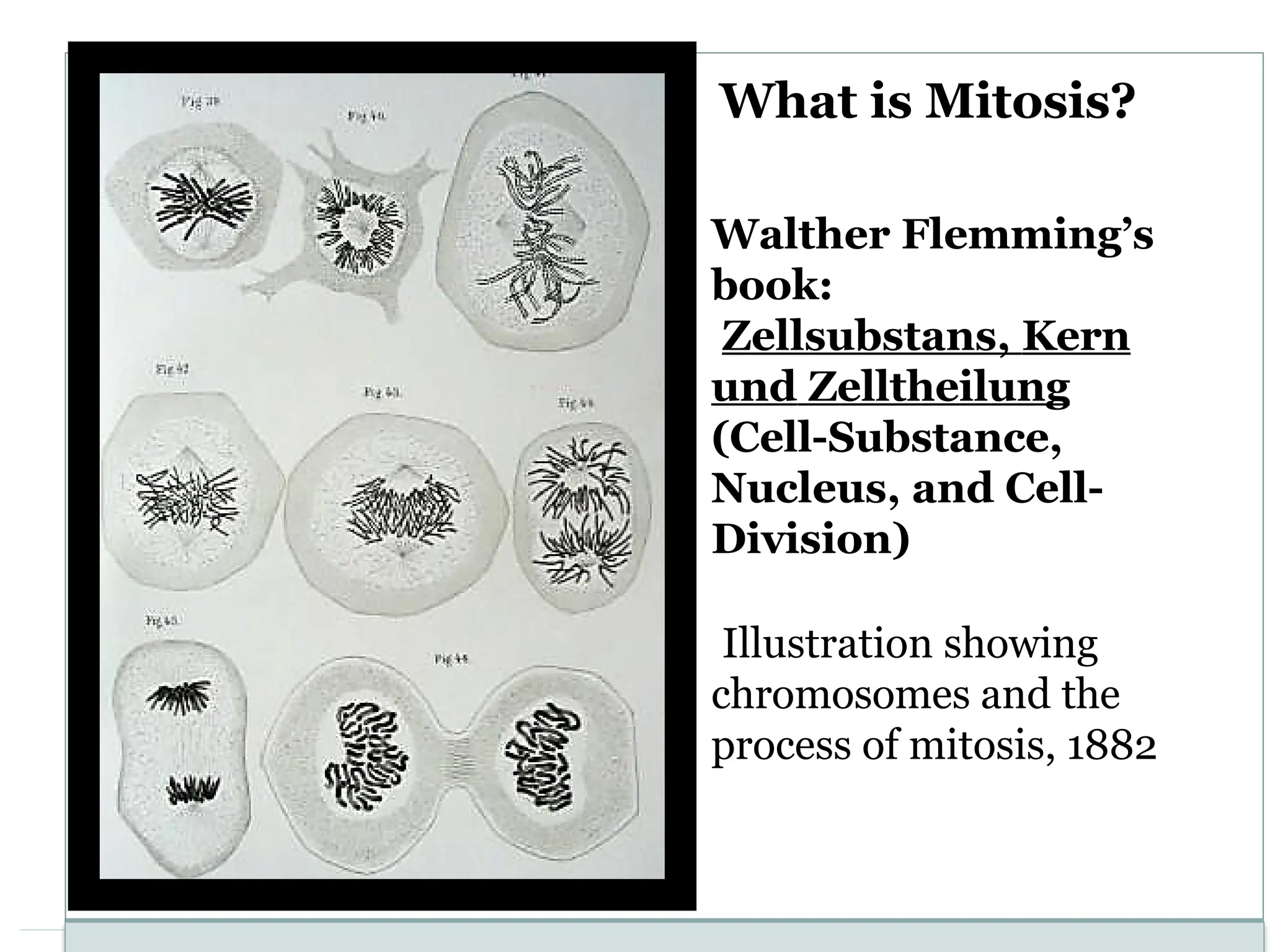
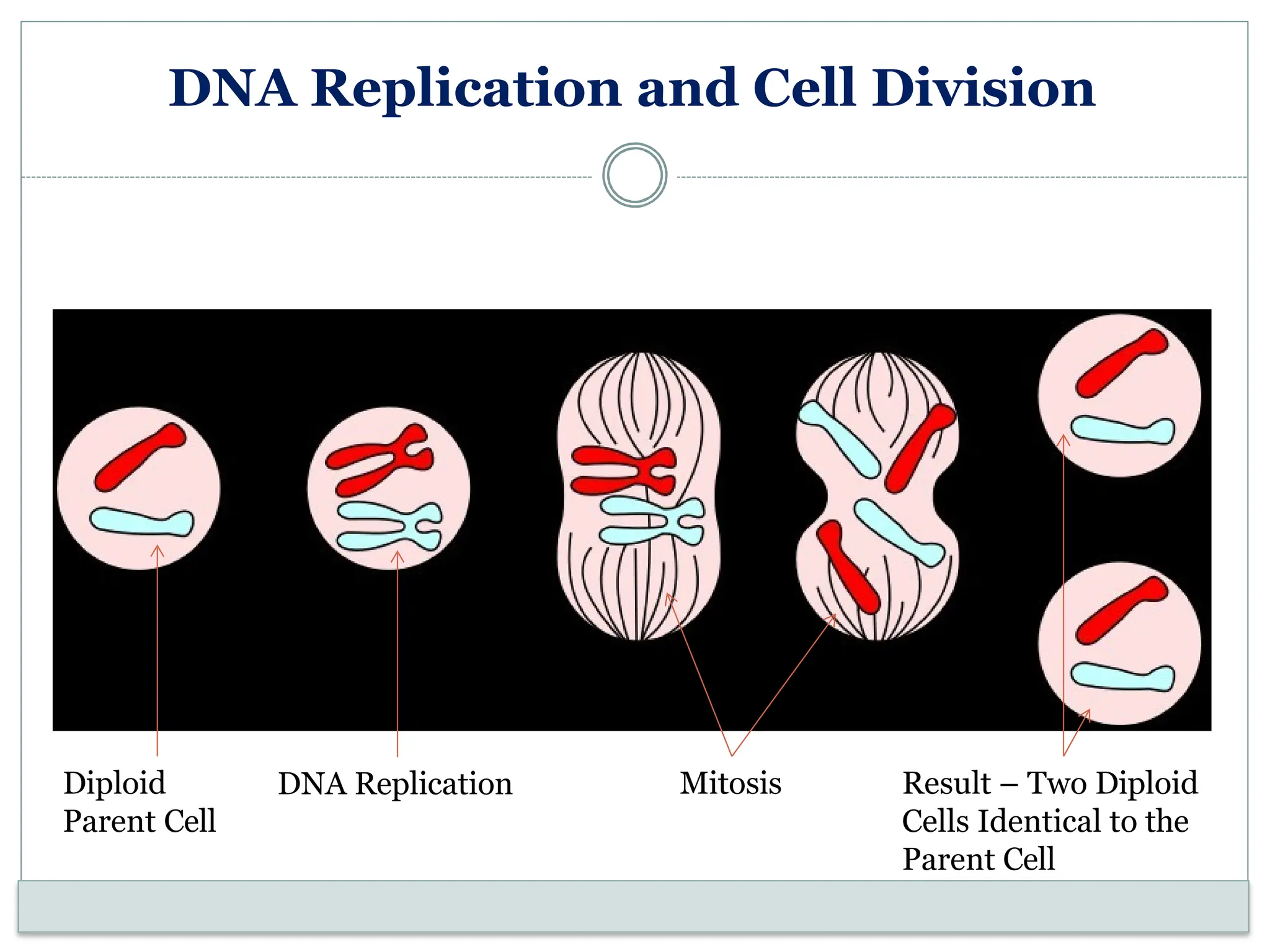
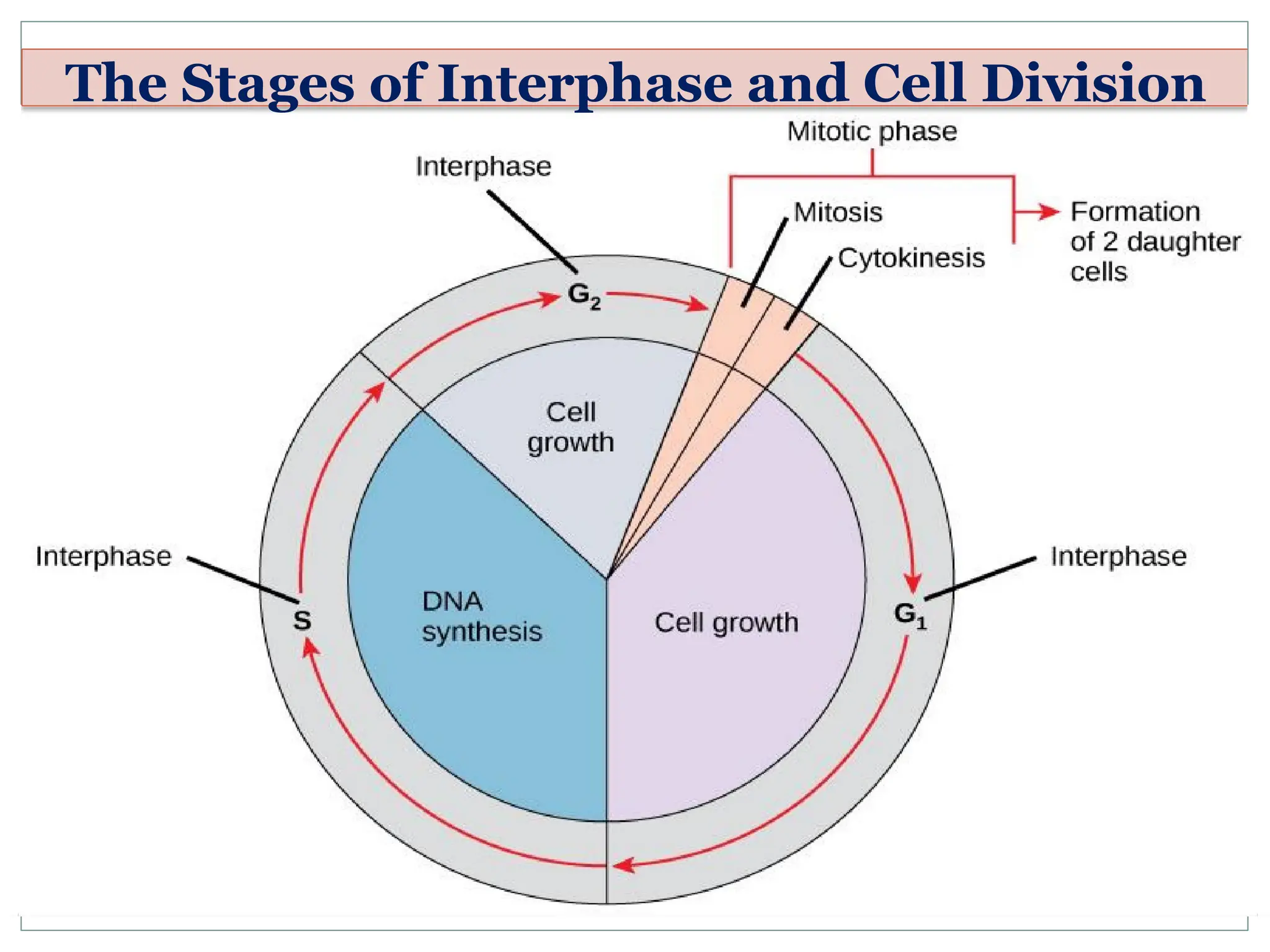
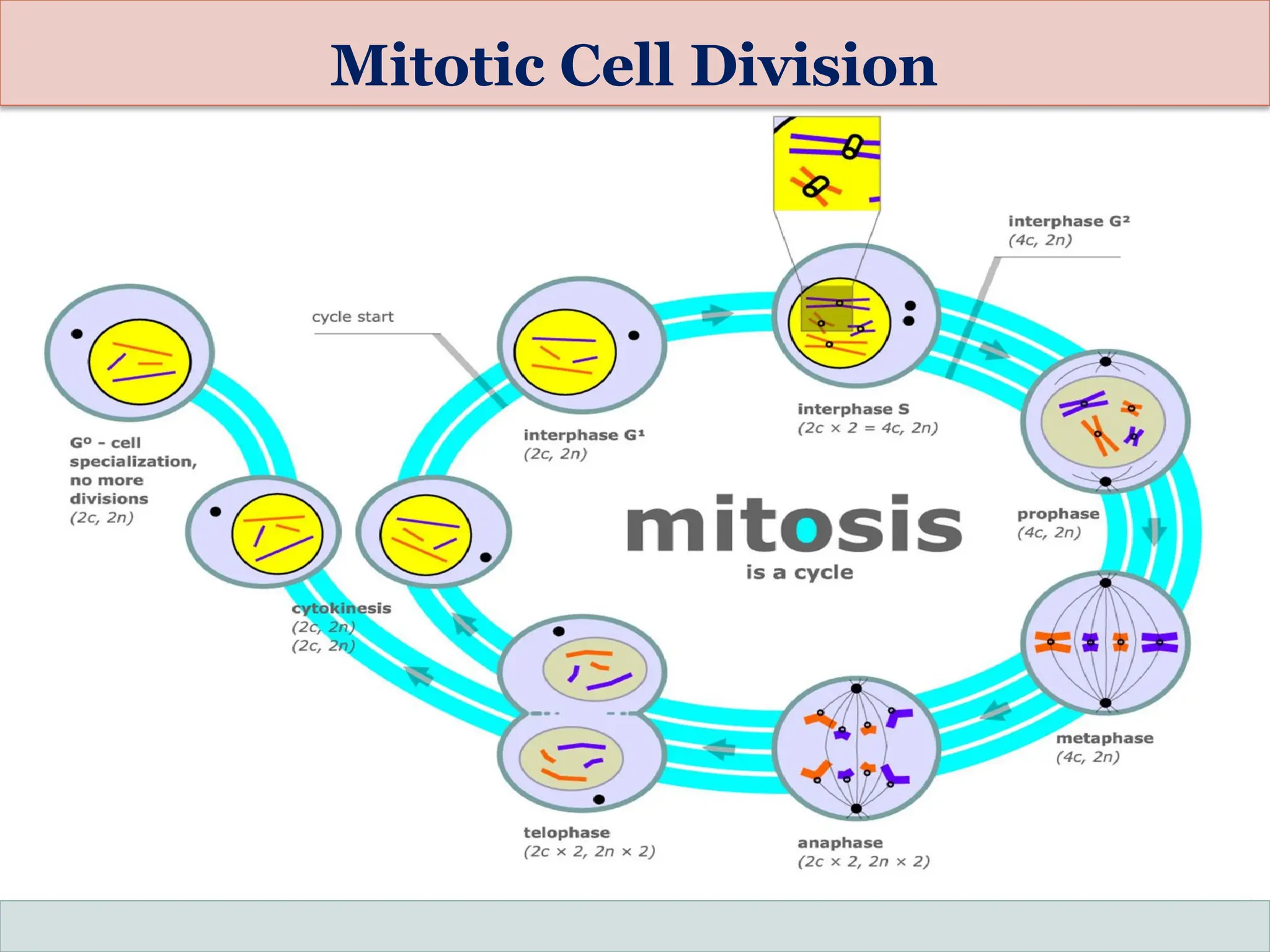
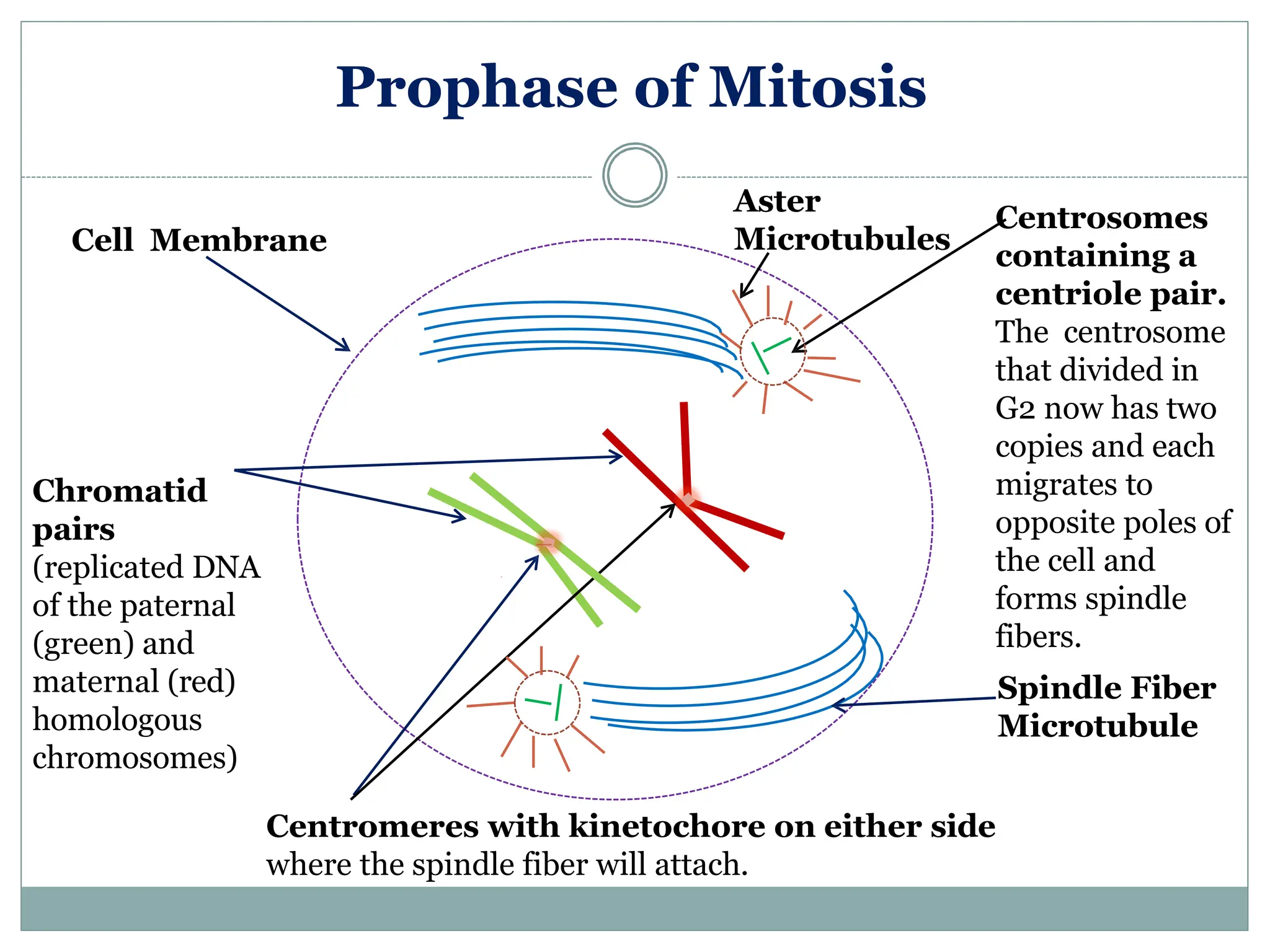
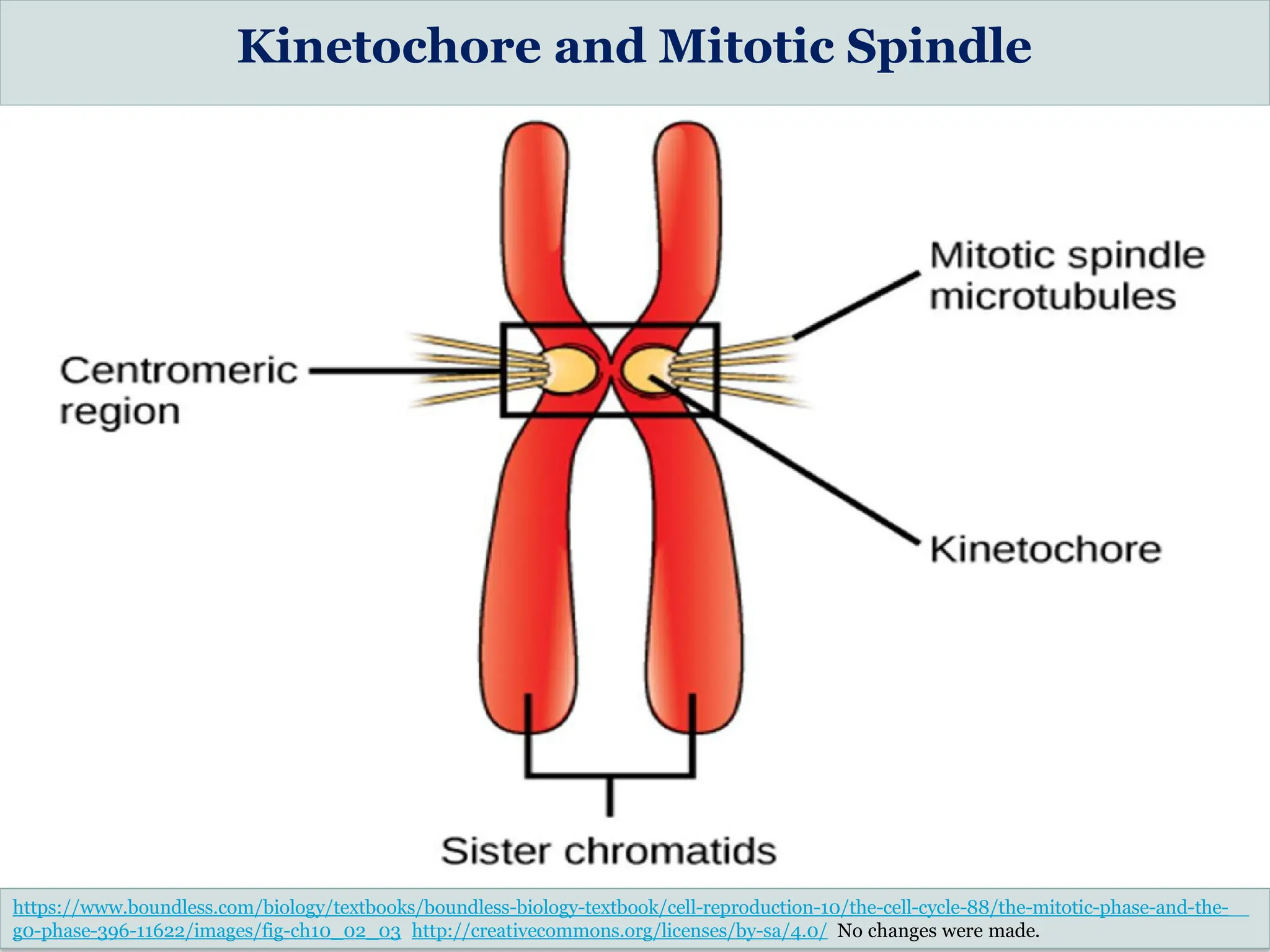
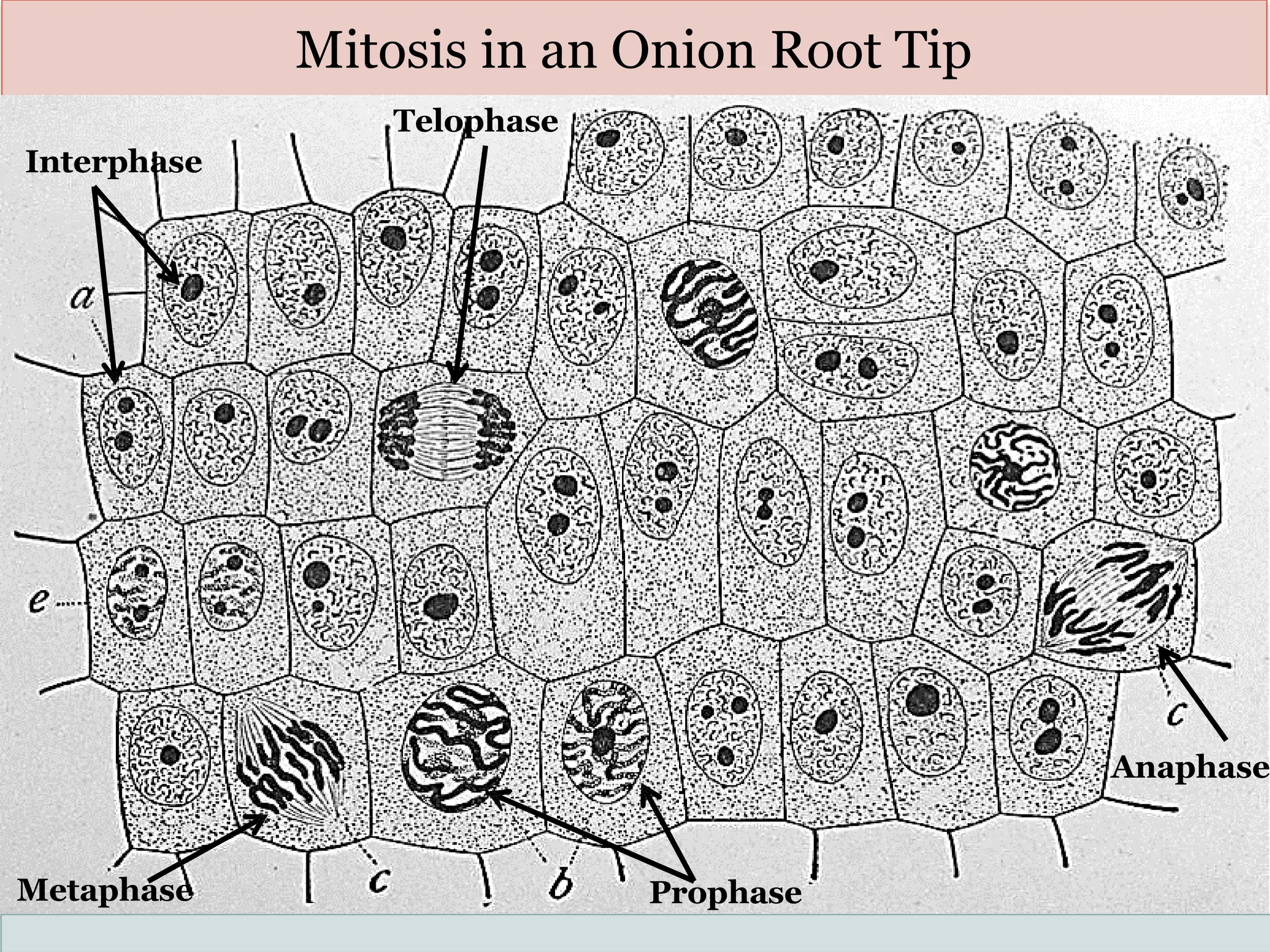
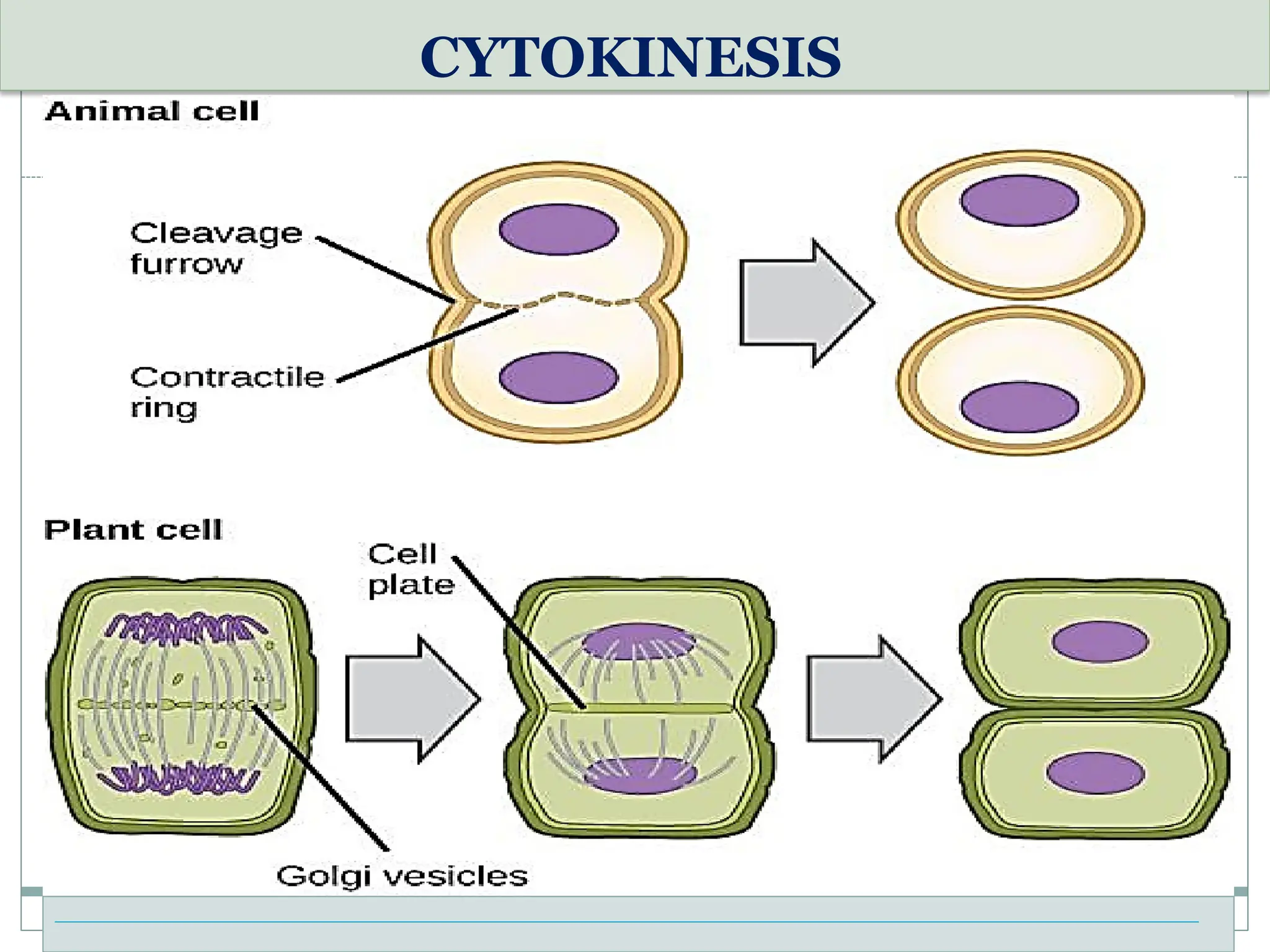
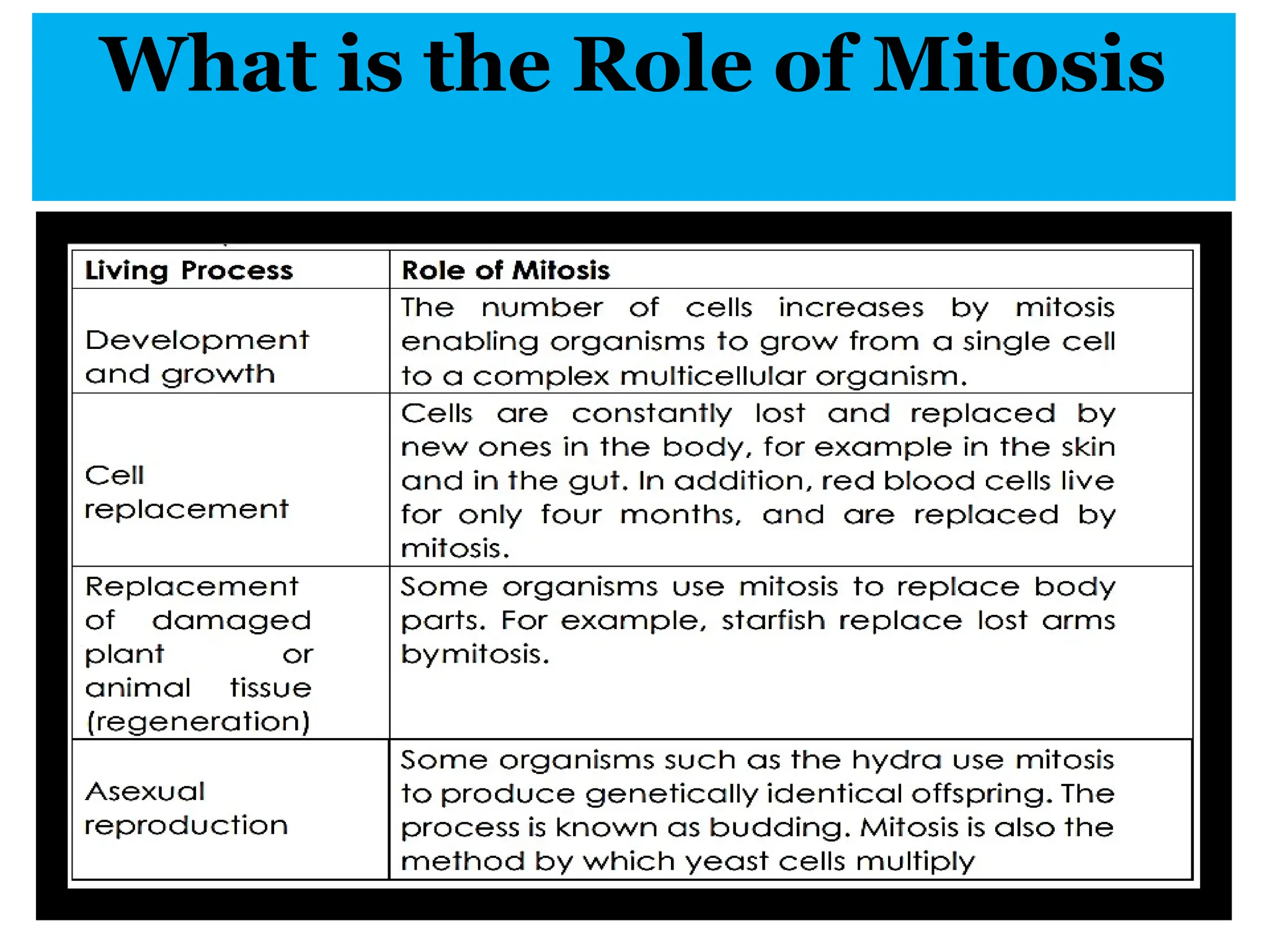
The document discusses mitosis, including its significance and stages, as well as its historical context in understanding cell division and cancer. It describes the process of mitosis, the role of key historical figures in its study, and explains how it results in genetically identical daughter cells. Additionally, it outlines the importance of mitosis in maintaining cellular function and nutrient absorption, highlighting the significance of understanding normal cell division.