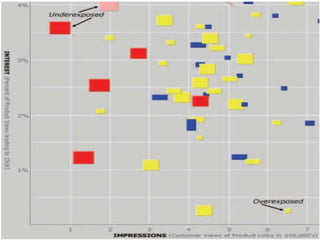
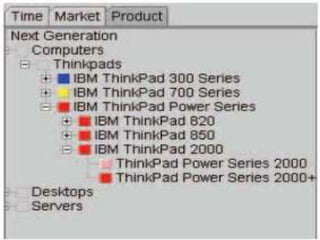
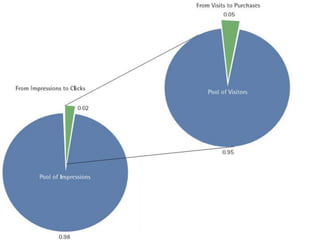
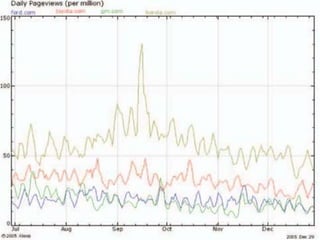
This document discusses search engine marketing (SEM) and strategies for building web traffic. It begins by explaining what SEM is and some key terms. It then discusses the challenges of gaining web traffic and different sources of traffic like branding, affiliate programs, online promotions, and search engines. Next, it covers analyzing traffic patterns, volume, and costs. The document concludes by providing goals for traffic building and strategies like search engine optimization, online promotions, and evaluating keyword advertising.