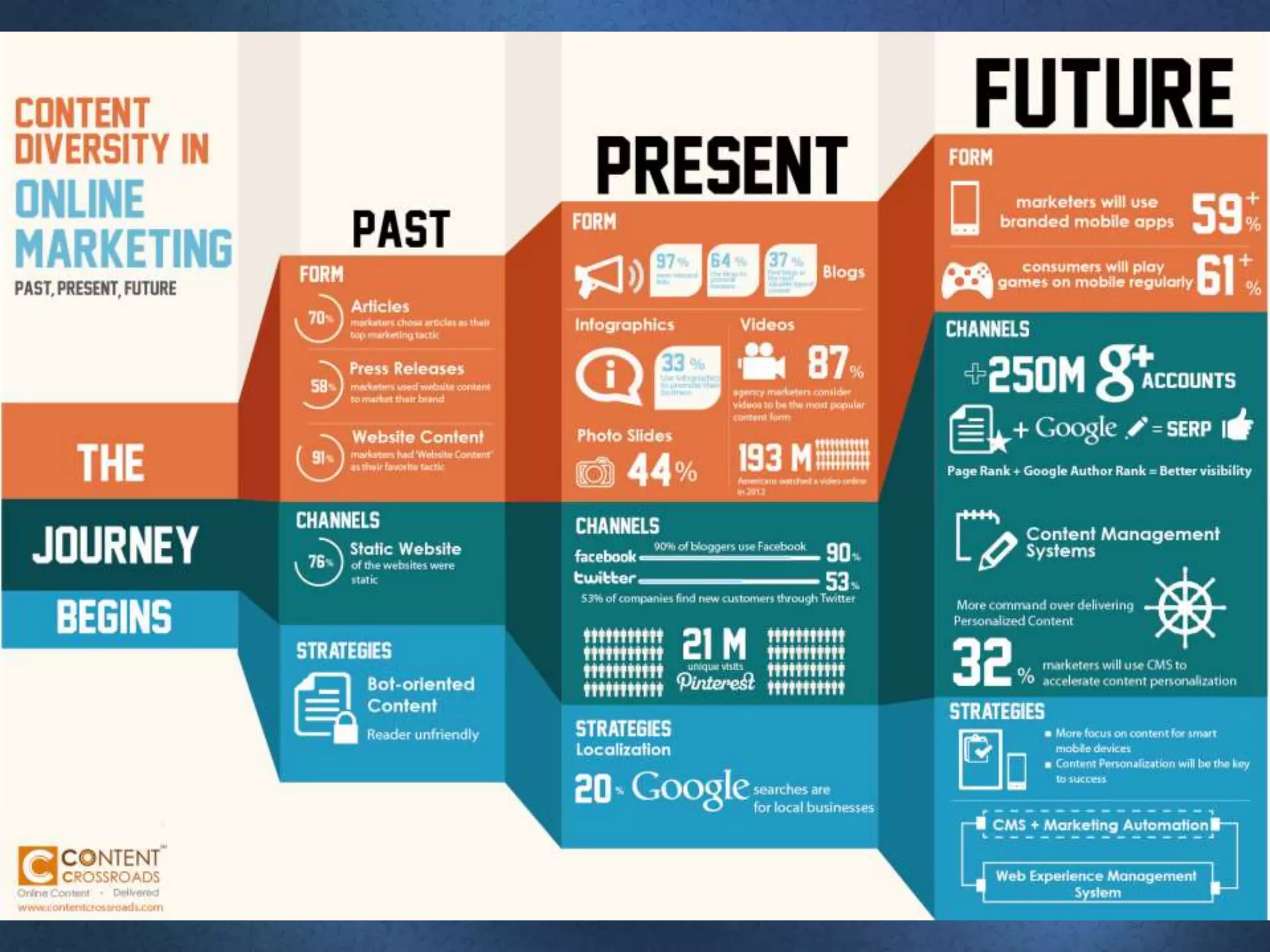
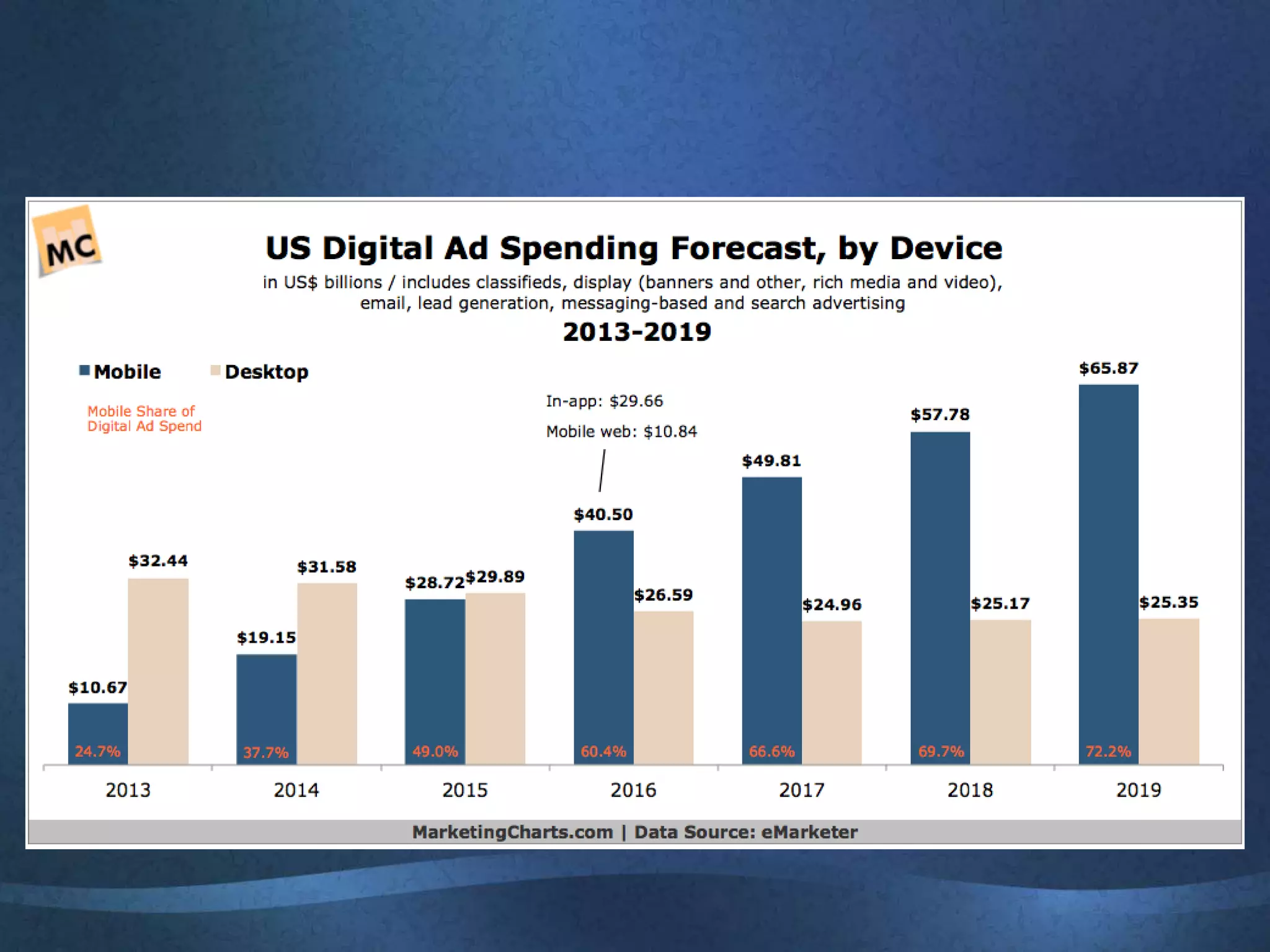
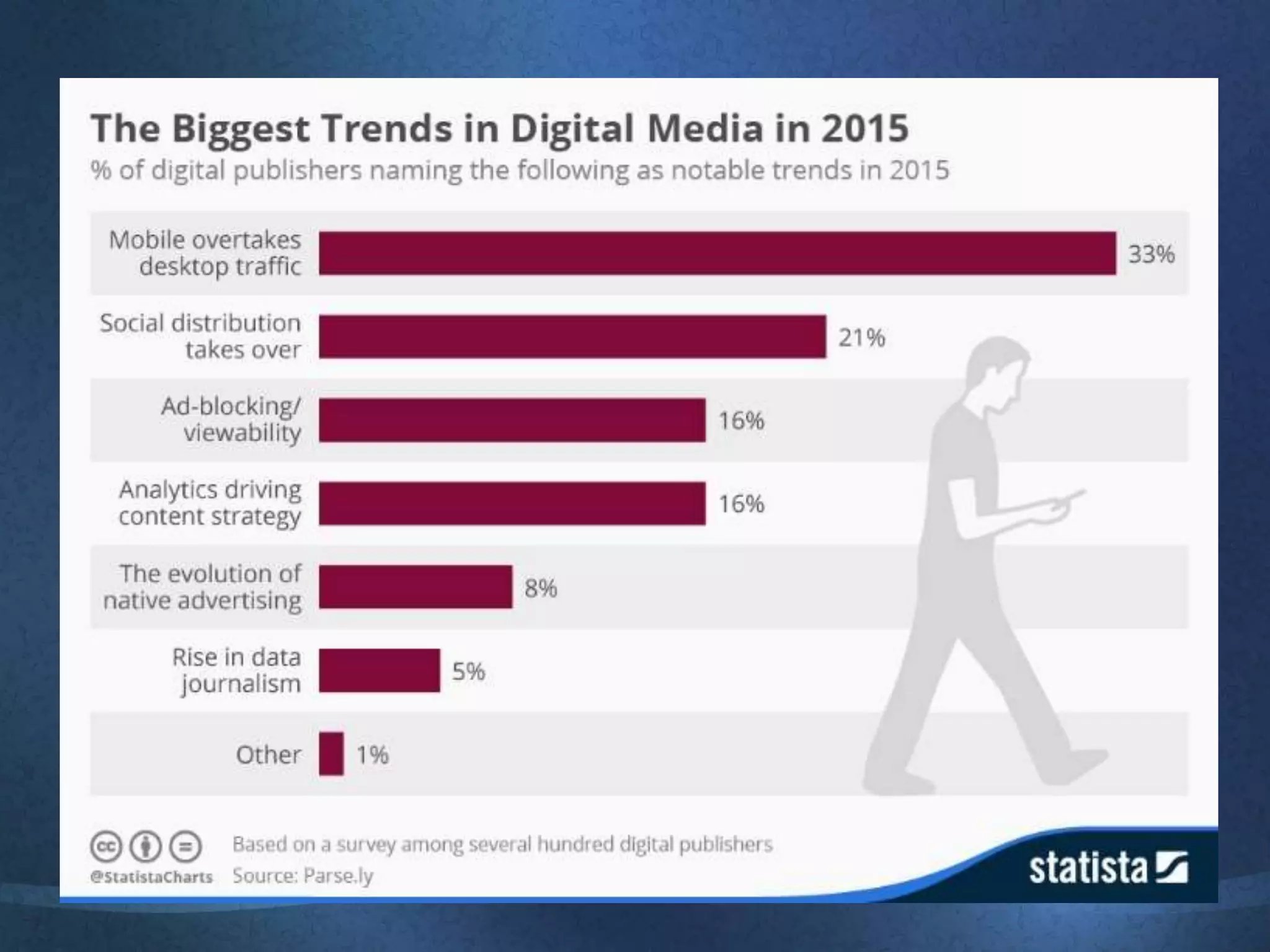
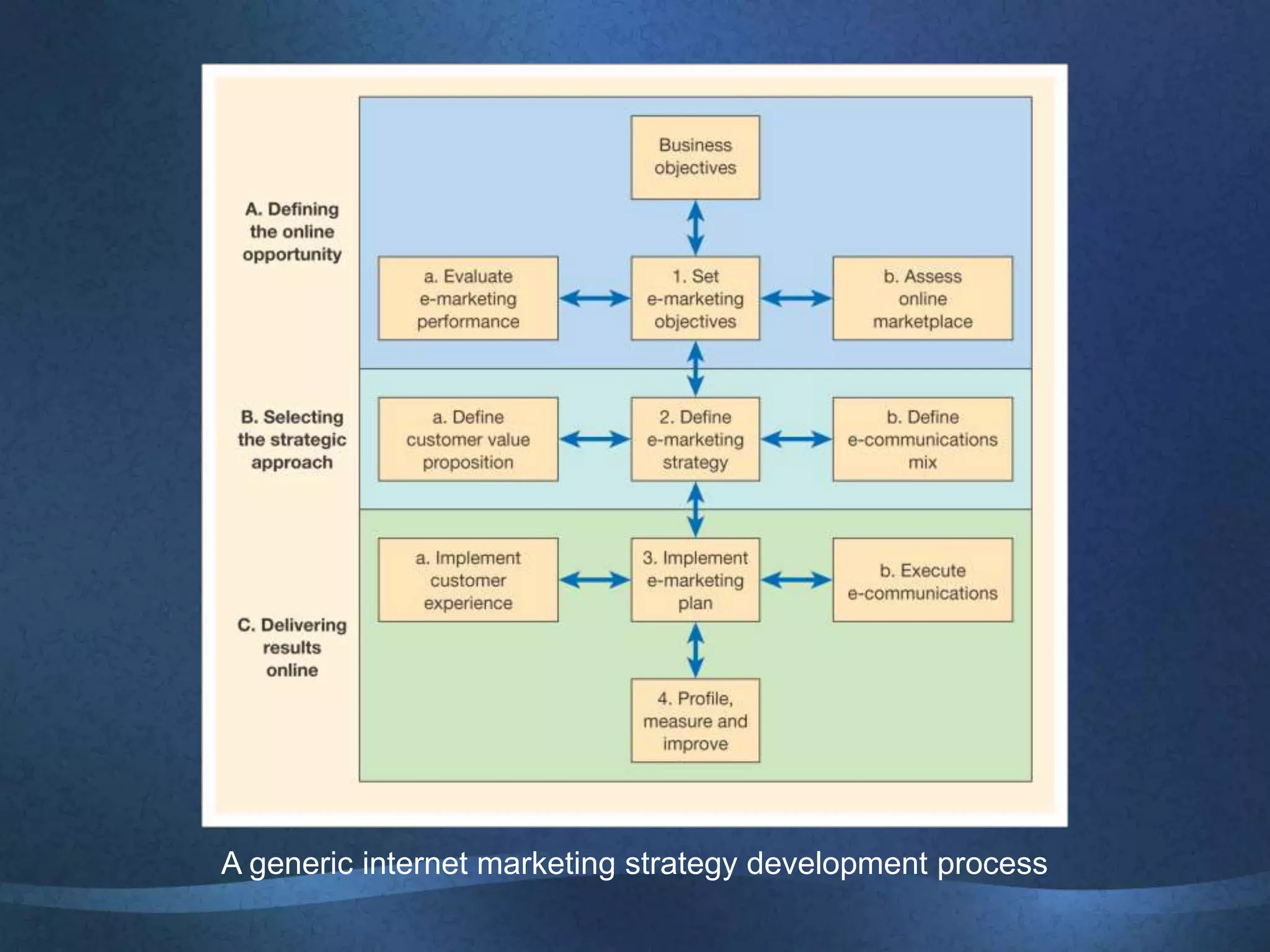
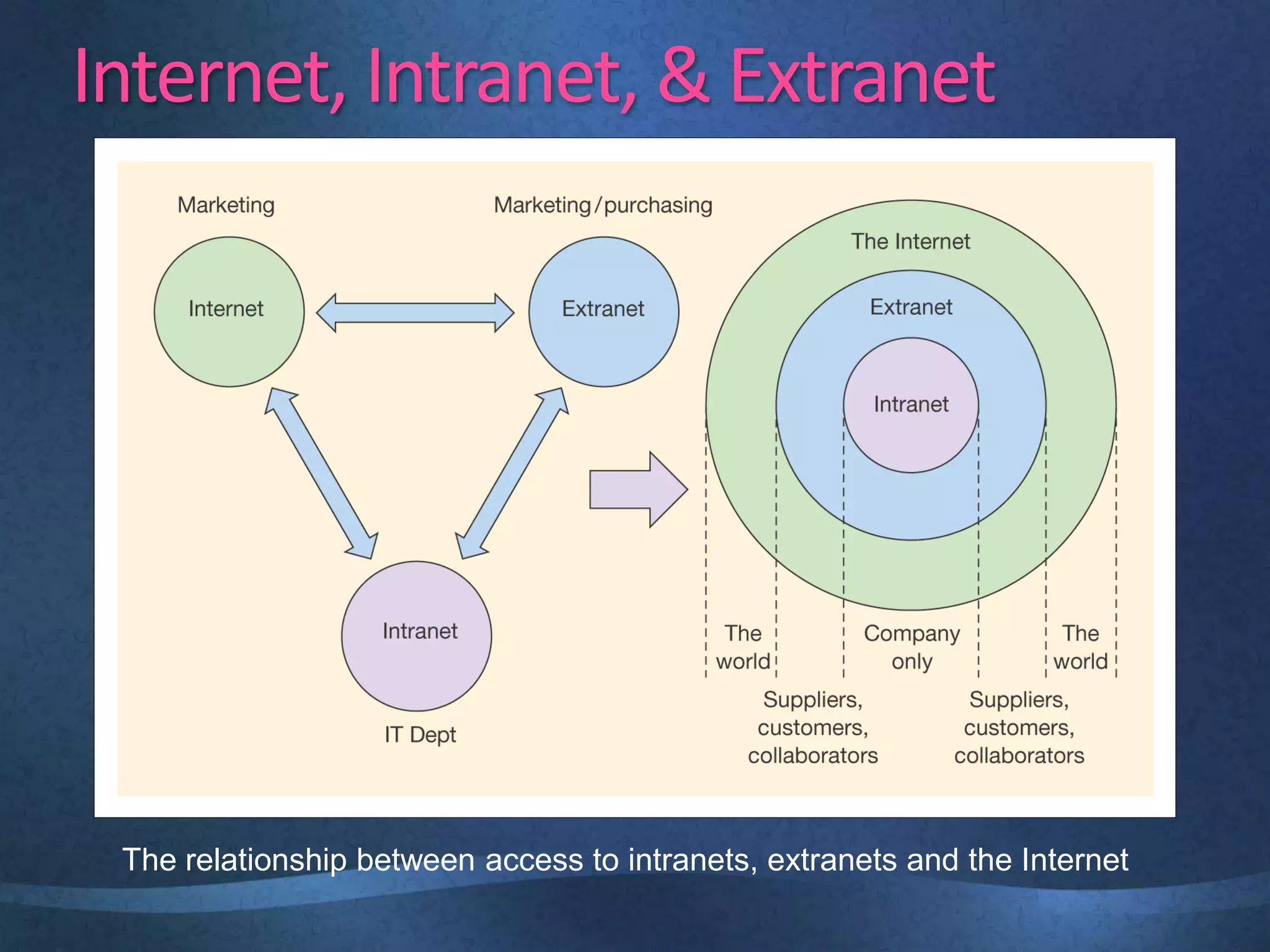
The document discusses the growing importance of online advertising as a key channel for businesses, emphasizing the need for active management and the shift in consumer attention from traditional media to the internet. It outlines advantages such as increased reach and targeted marketing, while also highlighting concerns regarding costs and measurement. Additionally, the document covers various advertising methods, the implications of e-commerce, and the importance of creating engaging content to maintain customer interest.