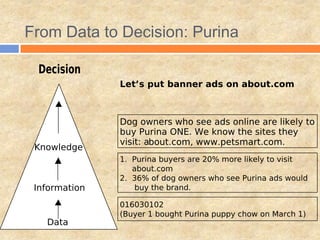
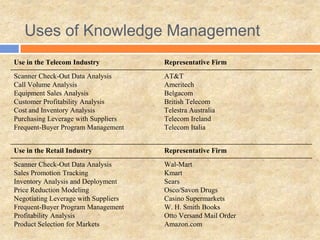
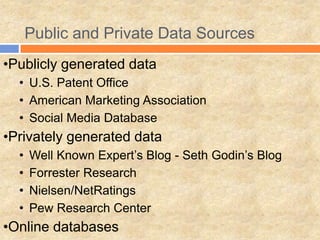
Nestle Purina PetCare wanted to understand the impact of their online advertising and websites on offline sales. They analyzed online and offline panel data and found that (1) banner clickthrough was low at 0.06% but (2) 31% of subjects exposed to both online and offline ads mentioned Purina, and (3) those with high exposure mentioned Purina more. Companies are using vast amounts of online and offline data through marketing information systems and knowledge management to guide business decisions.