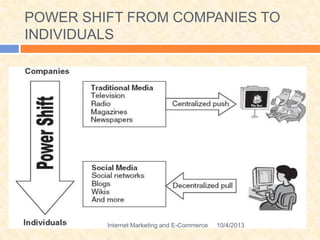
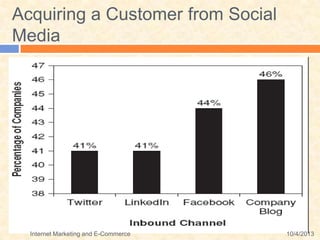
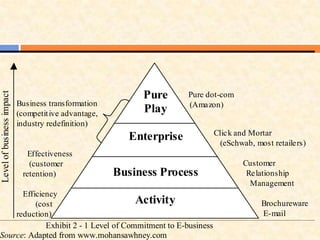
This document defines various terms related to internet marketing and e-commerce. It discusses the evolution of online marketing from early Web 1.0 technologies which focused on one-way communication, to today's Web 2.0 which enables social media and user-generated content. Web 2.0 has shifted power to consumers and created new opportunities for customer acquisition through social media. The future Web 3.0 is predicted to be driven by semantic applications across mobile and smart devices.