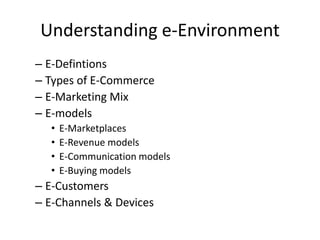
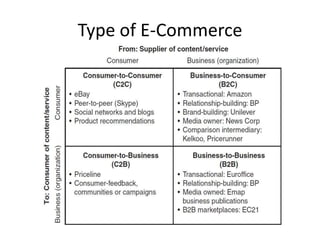
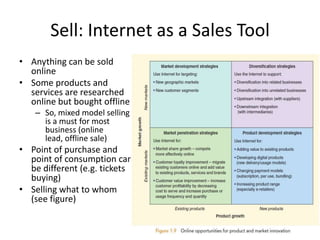
This document provides an overview of e-marketing from a textbook. It defines key terms like e-business, e-commerce, and e-marketing. It discusses how the internet continues to grow globally and the implications for businesses and customers. It outlines the objectives of e-marketing using the 5S model: sell, serve, speak, save, and sizzle. It also covers e-definitions, types of e-commerce sites, the dynamic dialog with customers, and using the internet as a sales, customer service, communication, cost reduction, and brand building tool.