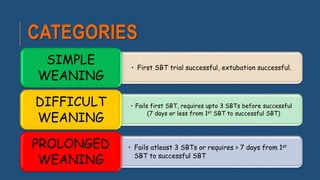
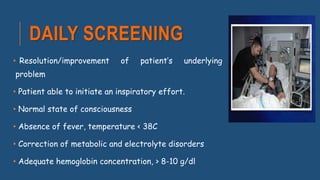
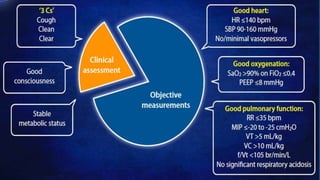
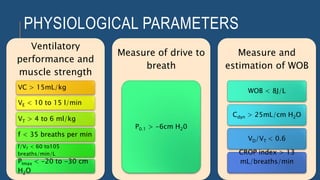
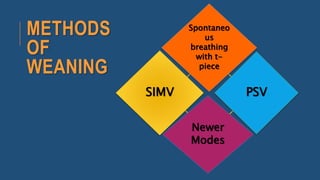
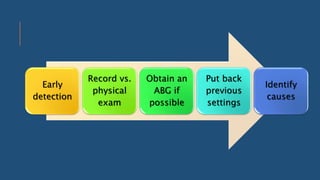
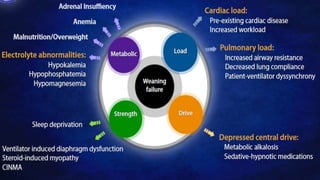
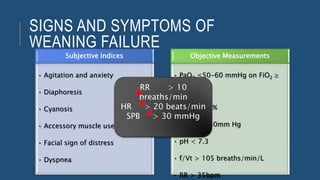
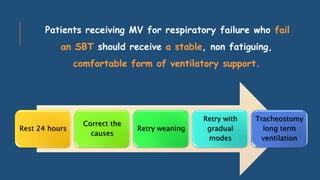
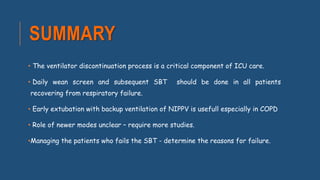
The document discusses weaning patients off mechanical ventilation. It defines weaning as the transition from full ventilator support to spontaneous breathing. Patients can have simple, difficult, or prolonged weaning depending on how many spontaneous breathing trials they require. Daily screening checks if patients meet criteria for an initial spontaneous breathing trial. Successful trials are then followed by extubation. Patients who fail trials should have their causes investigated and corrected before retrying weaning.