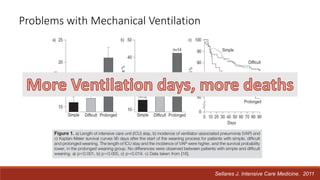
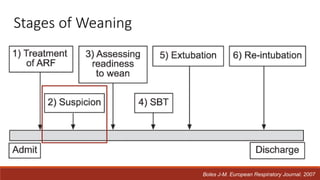
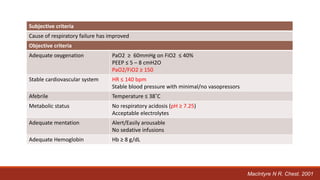
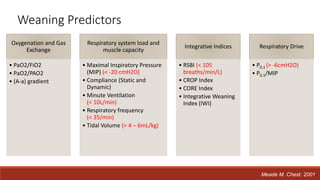
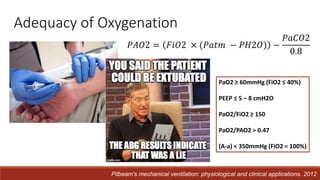
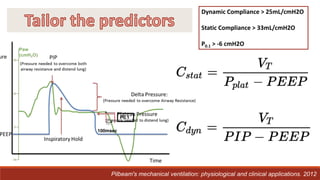
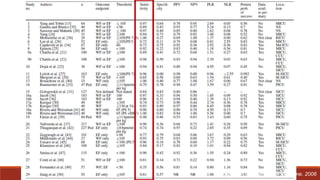
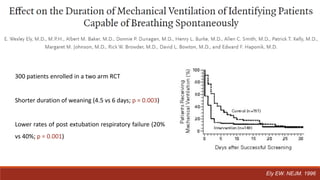
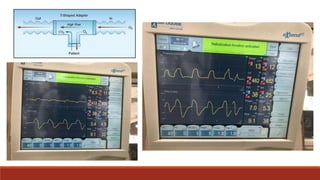
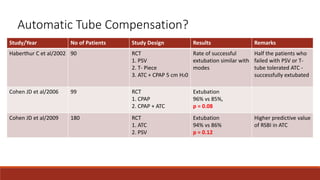
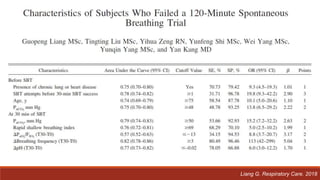
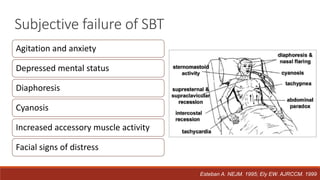
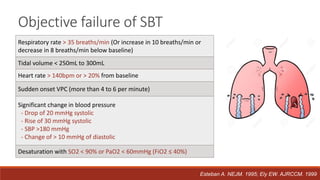
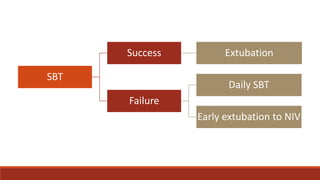
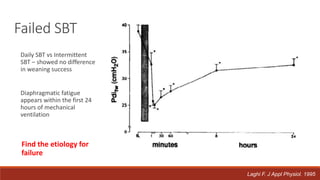
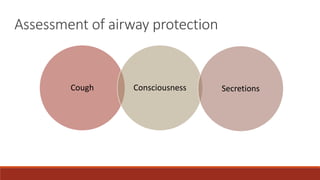
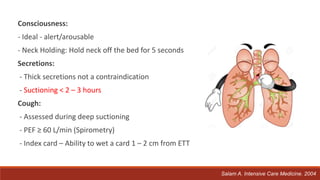
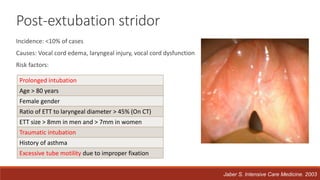
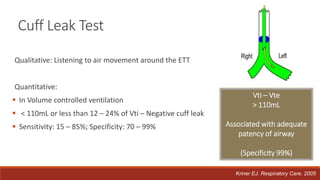
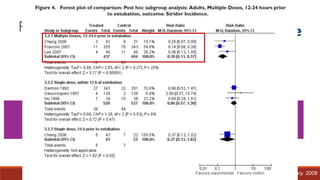
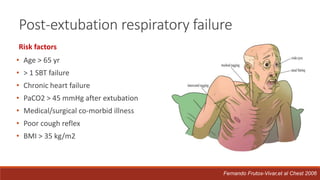
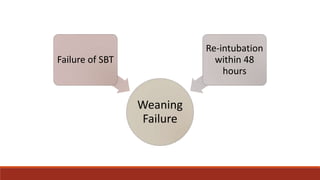
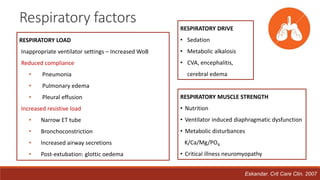
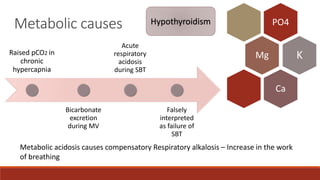
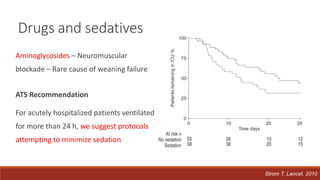
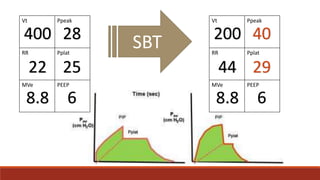
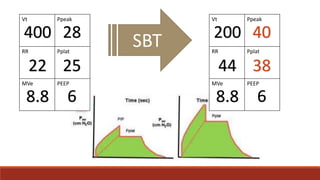
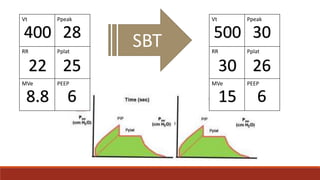
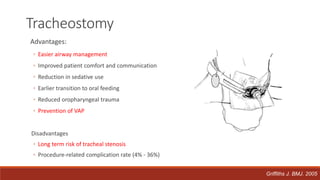
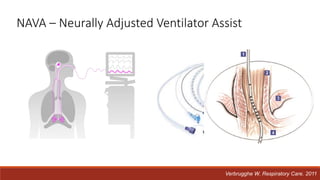
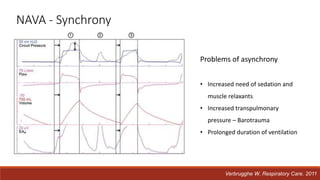
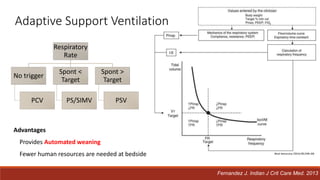
Dr. Sujay Halkur Shankar presented on the topic of weaning patients from mechanical ventilation. The presentation covered assessing patient readiness, different weaning methods like spontaneous breathing trials, factors that can cause difficulty weaning like respiratory, cardiac and neuromuscular issues, and post-extubation care. Spontaneous breathing trials are the preferred method of weaning and have higher rates of success than pressure support or intermittent mandatory ventilation. Factors that can contribute to weaning failure include increased respiratory load or drive, decreased respiratory muscle strength, and cardiac dysfunction induced by weaning.