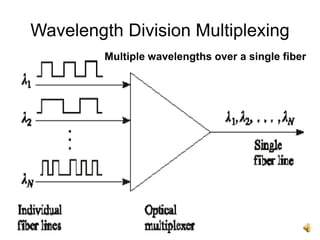
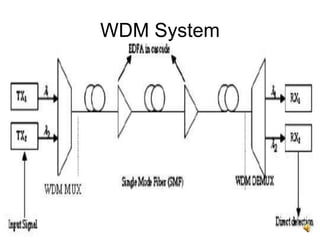
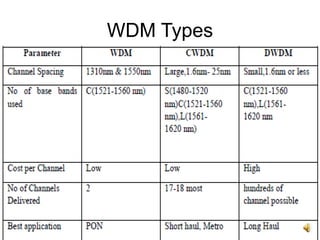
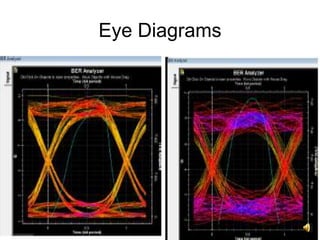
The document provides an overview of Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM), highlighting its features, benefits, and performance parameters. It describes how WDM allows for multiple optical signals to be transmitted over a single fiber, increasing network capacity and security while ensuring efficient bandwidth utilization. Key performance metrics such as bit error rate, optical signal to noise ratio, and eye height are also discussed.