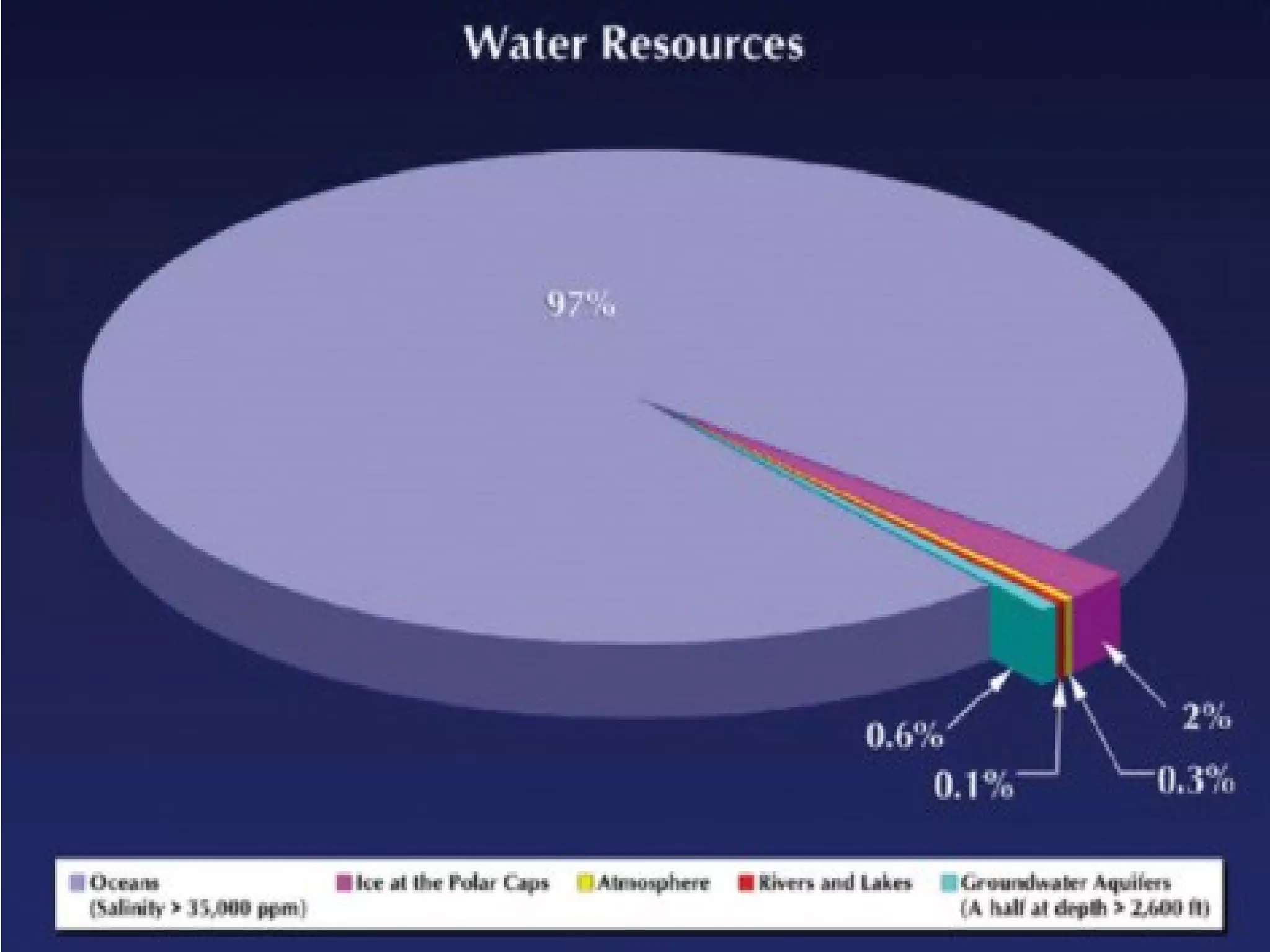
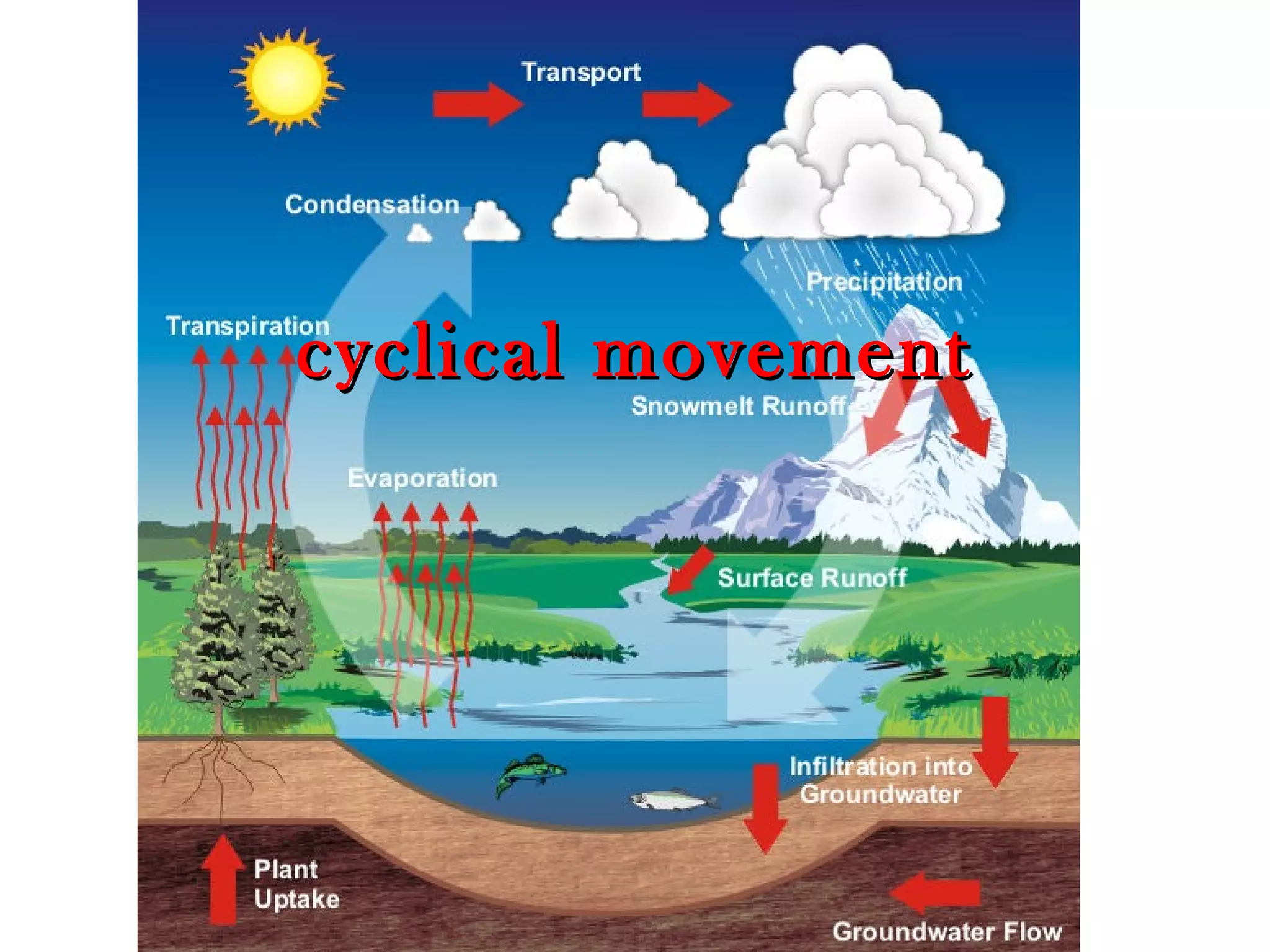
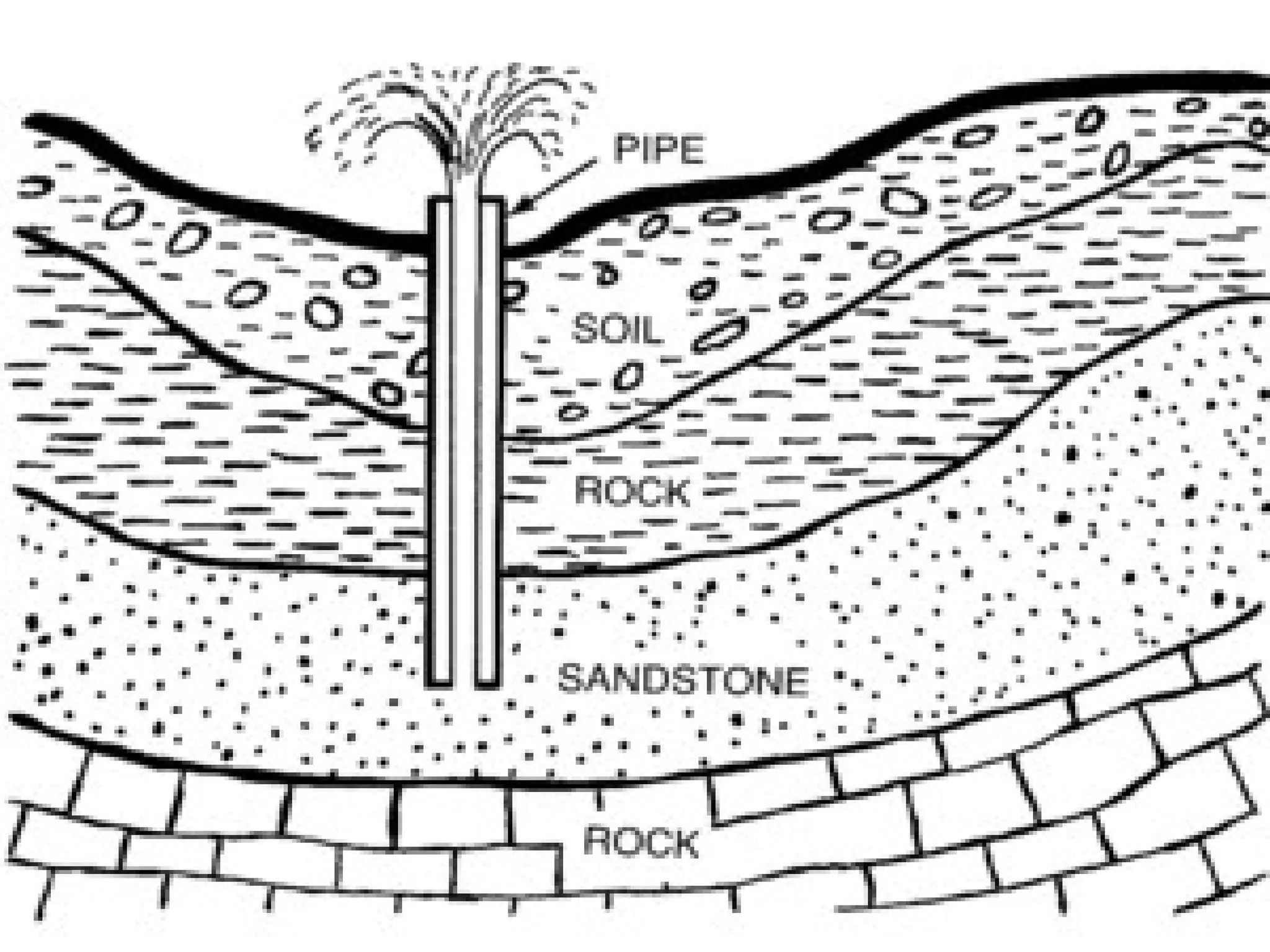
Water is essential for life on Earth. It covers about 2/3 of the planet's surface and is found naturally in three states: liquid, gas and solid. Most water on Earth is saline and located in oceans, while only 3% is freshwater found in rivers, lakes, ice caps and underground aquifers. The total quantity of water on Earth remains relatively constant due to the water cycle, in which water evaporates from oceans and land into the atmosphere, condenses into clouds, and falls back to the surface as precipitation.