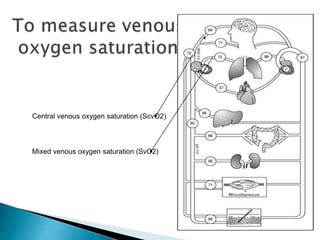
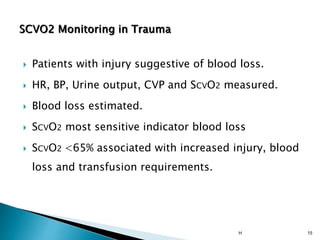
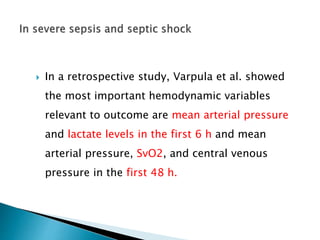
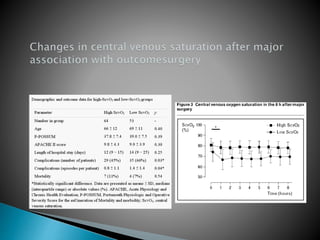
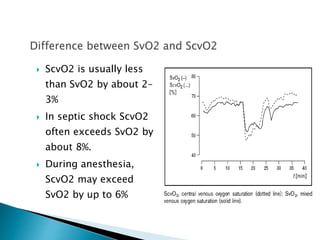
1. Mixed venous blood is a mixture of blood from the systemic veins that has undergone gas exchange in the tissues, excluding shunted blood. It provides information on the balance between oxygen delivery and consumption on a systemic level.
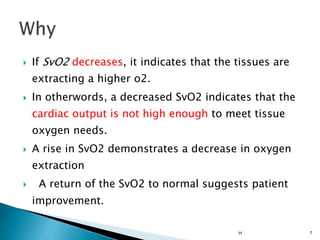
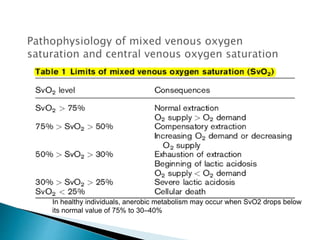
2. The mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) reflects this balance, with a normal value around 75%. A low SvO2 indicates oxygen delivery is not meeting tissue demands, while a high SvO2 suggests impaired tissue extraction of oxygen.
3. The central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) approximates SvO2 but is usually a few points higher. Both can help guide resuscitation in shock states like sepsis when used as targets for















![ Factors affecting mixed venous O2 tension
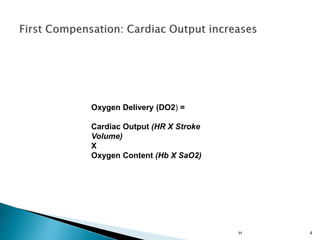
From Fick equation
VO2 = Q x (CaO2 - CvO2)
CvO2 = CaO2 - VO2/Q
SvO2 = SaO2 - VO2/(Q x 1.34 x [Hb])
NB:SvO2 is derived so O2 dissociation curve (which is
SpO2 vs PO2) can be used
H 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vso2venousoximetrymixedvenouso2sat-150122161856-conversion-gate01/85/Vso2-venous-oximetry-mixed-venous-o2-sat-26-320.jpg)
![ Firstly When O2 dissociation curve is fixed:
SvO2 = SaO2 - VO2/(Qx1.34x[Hb])
SvO2 is increased when:
• SaO2 is increased
• O2 consumption (VO2) is decreased
• cardiac output (Q) is increased
• Hb concentration is increased
As SvO2 increase, PO2 is increased.
H 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vso2venousoximetrymixedvenouso2sat-150122161856-conversion-gate01/85/Vso2-venous-oximetry-mixed-venous-o2-sat-27-320.jpg)
![ However, at mixed venous blood level of PO2
(40mmHg), changes in SvO2 doesn't have as great
an effect on PvO2 as it would at higher level of PO2.
PvO2 will increase when ODC moves to the right
due to:• increased PvCO2;• increased [H+] (i.e. drop
in pH);• increased temperature;increased red cell
2,3 DPG
H 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vso2venousoximetrymixedvenouso2sat-150122161856-conversion-gate01/85/Vso2-venous-oximetry-mixed-venous-o2-sat-28-320.jpg)

![ Mixed venous O2 tension is increased by:
increased SaO2
decreased O2 consumption
increased cardiac output
increased Hb concentration
right shift in ODC, due to:
* increased PvCO2
* increased [H+]
* increased temperature
* increased red cell 2,3DPG
1/22/2015 30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vso2venousoximetrymixedvenouso2sat-150122161856-conversion-gate01/85/Vso2-venous-oximetry-mixed-venous-o2-sat-30-320.jpg)



