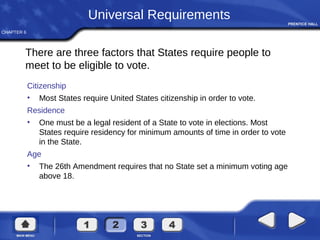
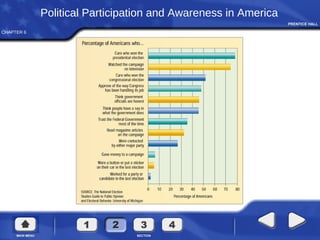
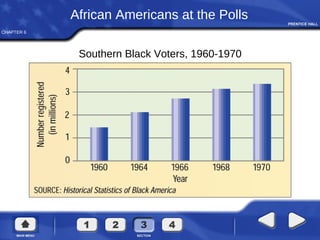
The document summarizes key aspects of voting rights and political participation in the United States. It discusses how voting rights have expanded over time from only allowing white male property owners to vote to all citizens over 18. It also outlines the 15th, 19th, 24th, and 26th amendments that prohibit denying the right to vote based on race, sex, failure to pay a poll tax, and minimum age of 18. The document also examines factors that affect voter turnout and behavior such as socioeconomic characteristics, party affiliation, and how candidates and issues can influence voting decisions.