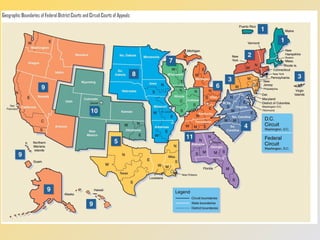
The federal court system is established by Article III of the Constitution. The federal courts have jurisdiction over cases involving the Constitution, federal law, disputes between states or citizens of different states, and disputes involving foreign governments. The lower federal courts include district courts and courts of appeals. District courts handle most cases and have original jurisdiction, while courts of appeals only hear appeals from lower courts. The highest court is the Supreme Court, which has the power of judicial review to determine the constitutionality of laws and final authority on interpreting the Constitution.