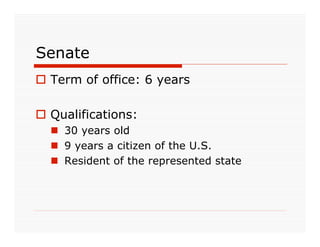
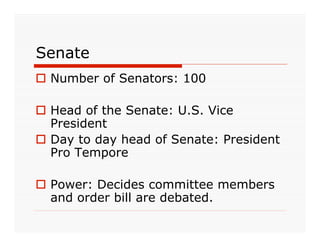
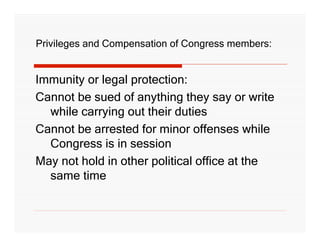
The document outlines the structure and powers of the United States Legislative Branch. It describes the two chambers of Congress - the House of Representatives and the Senate. It details the terms, qualifications, numbers of members, leadership roles, and special powers of each chamber. It also summarizes Congress's shared powers and privileges, as well as powers granted to and denied from Congress by the Constitution.