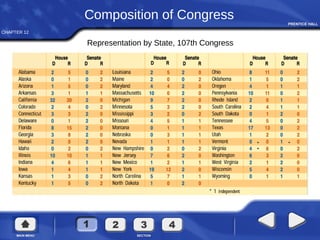
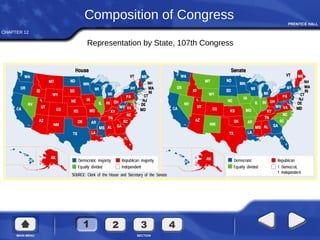
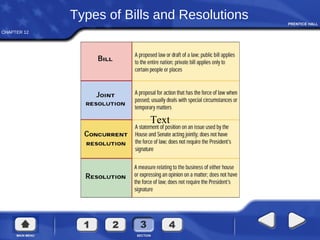
Congress organizes at the beginning of each new term. The House and Senate establish committees and leadership positions. In the House, the Speaker of the House presides, while in the Senate the Vice President presides as President of the Senate. Bills are introduced and may be amended as they pass through committees before coming to a floor vote. If differences exist between House and Senate versions, a conference committee works to create a single bill to pass both chambers. Finally, the President may sign the bill, veto it, or do nothing and allow it to become law.