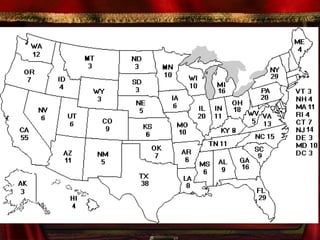
The document outlines the US electoral process for selecting a president. It describes the two-part process of first nominating candidates through state primaries and caucuses from February to June. Then the general election in November where the nominees from the two major parties compete for the presidency. It explains how candidates earn delegates at state conventions to win their party's nomination at the national convention. Finally, it discusses how the president is indirectly elected through the electoral college system rather than a popular vote.