This document provides information about integrated circuit voltage regulators, including:
1) It defines an IC voltage regulator as an integrated circuit that regulates an unregulated input voltage to provide a constant, regulated output voltage.
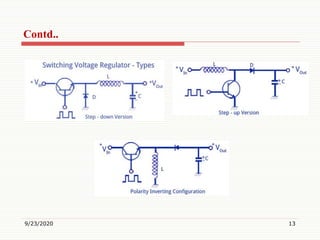
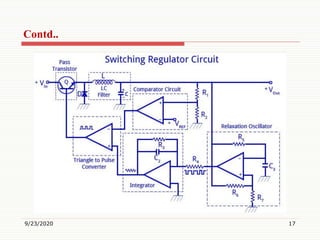
2) It classifies IC voltage regulators as either linear or switching regulators, and also as fixed voltage, adjustable voltage, positive voltage, or negative voltage regulators.
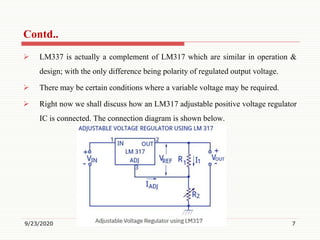
3) It provides examples of common IC voltage regulators like the 7805 and LM317, and explains how they regulate voltage.