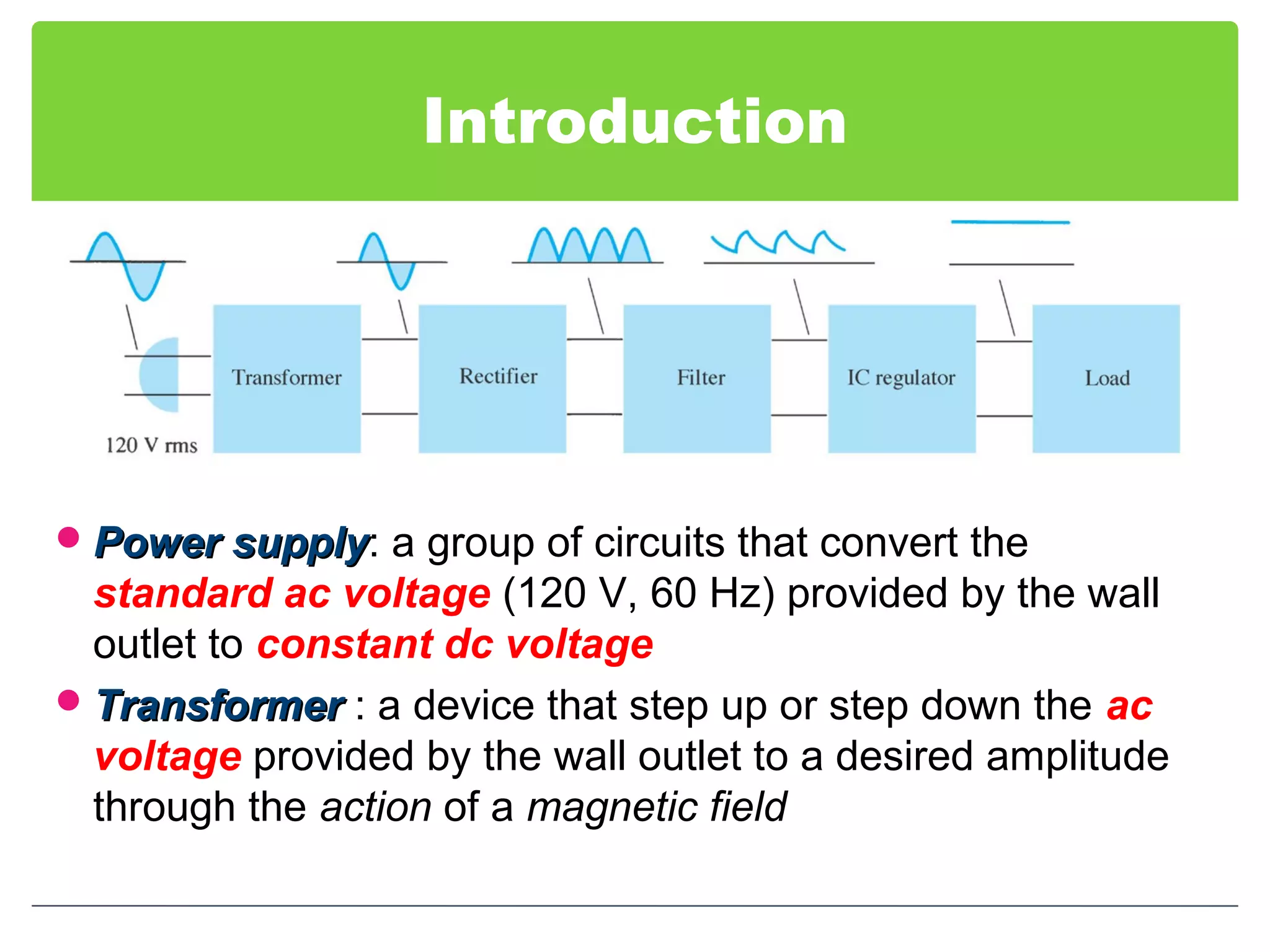
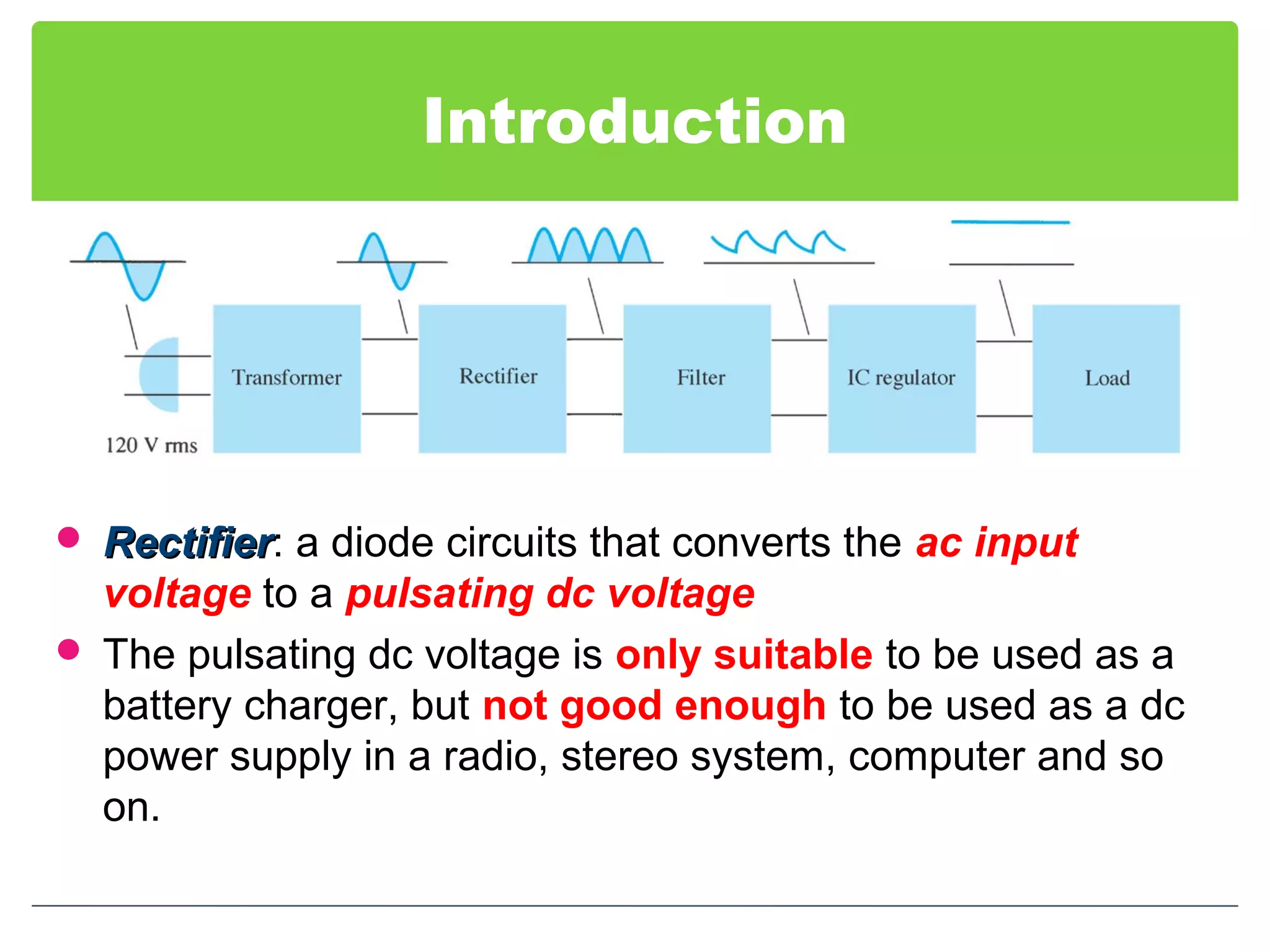
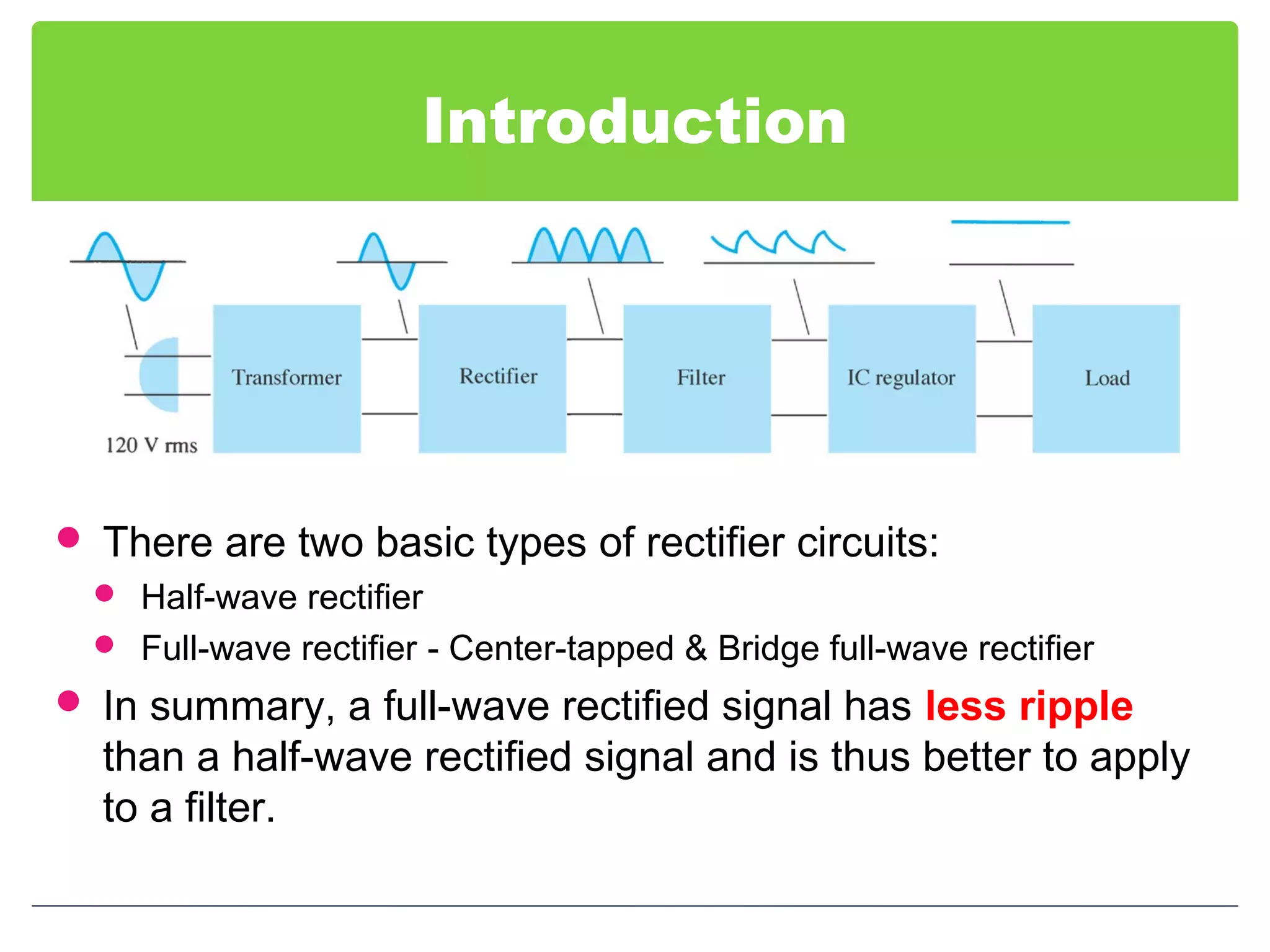
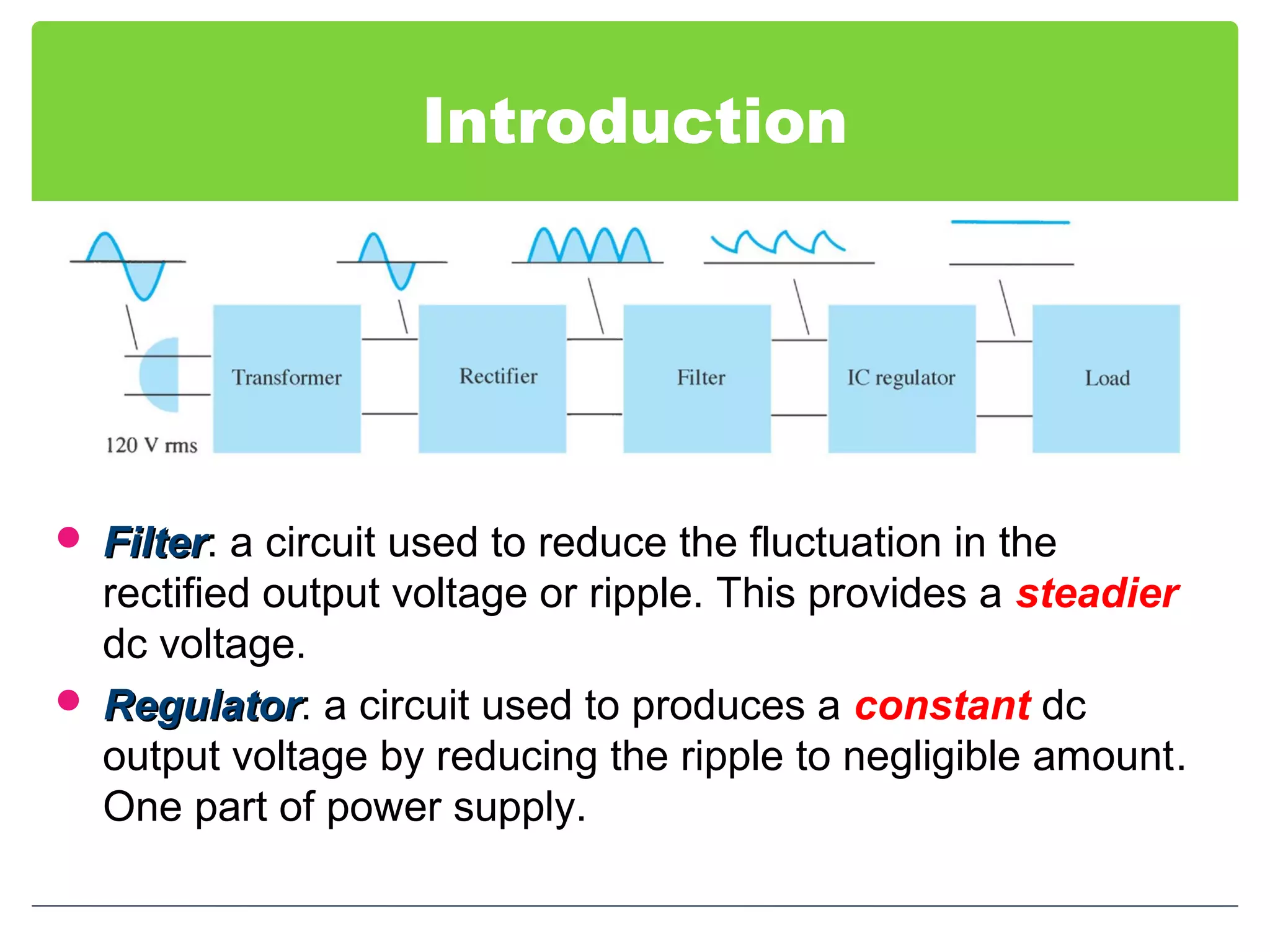
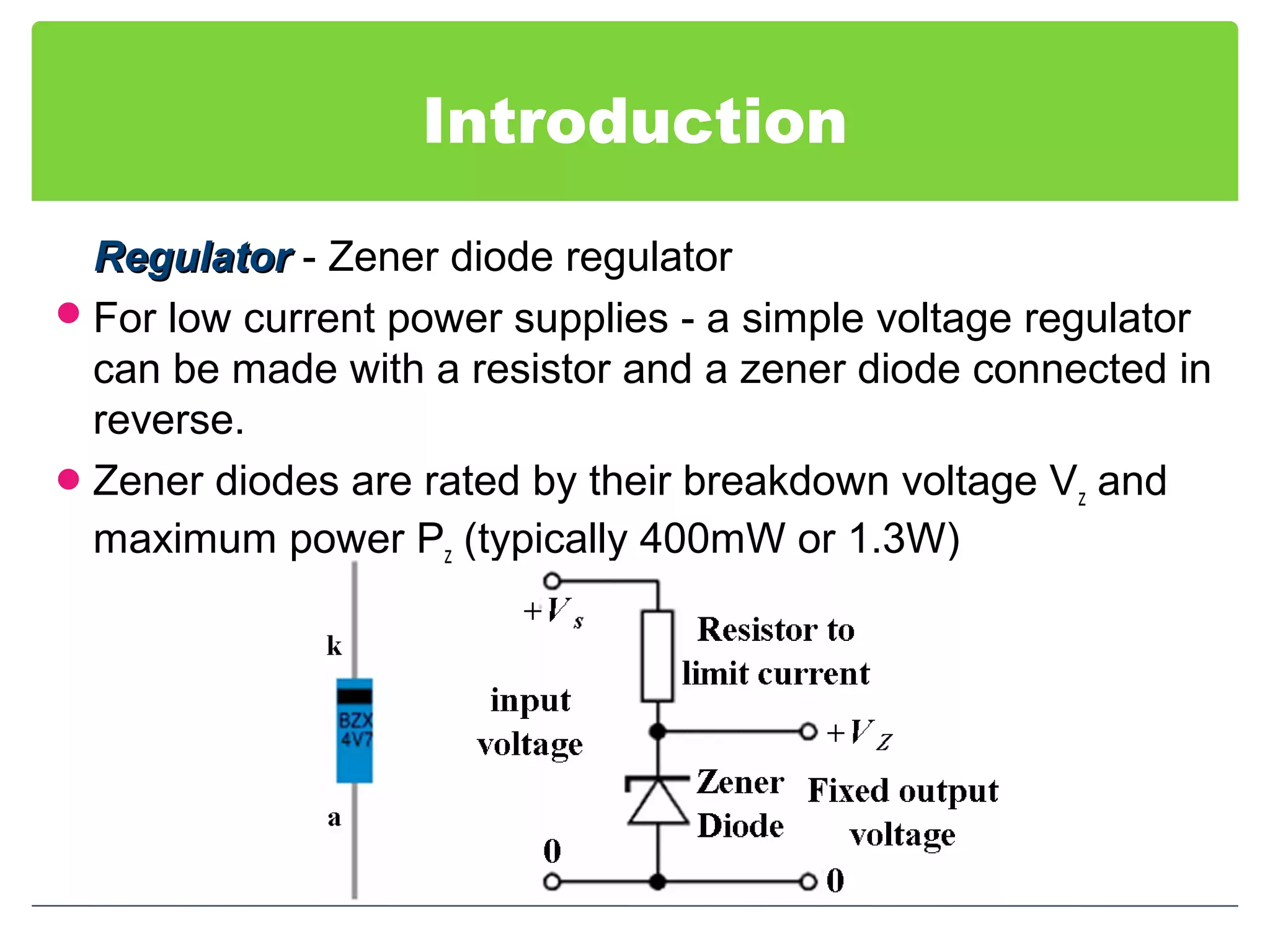
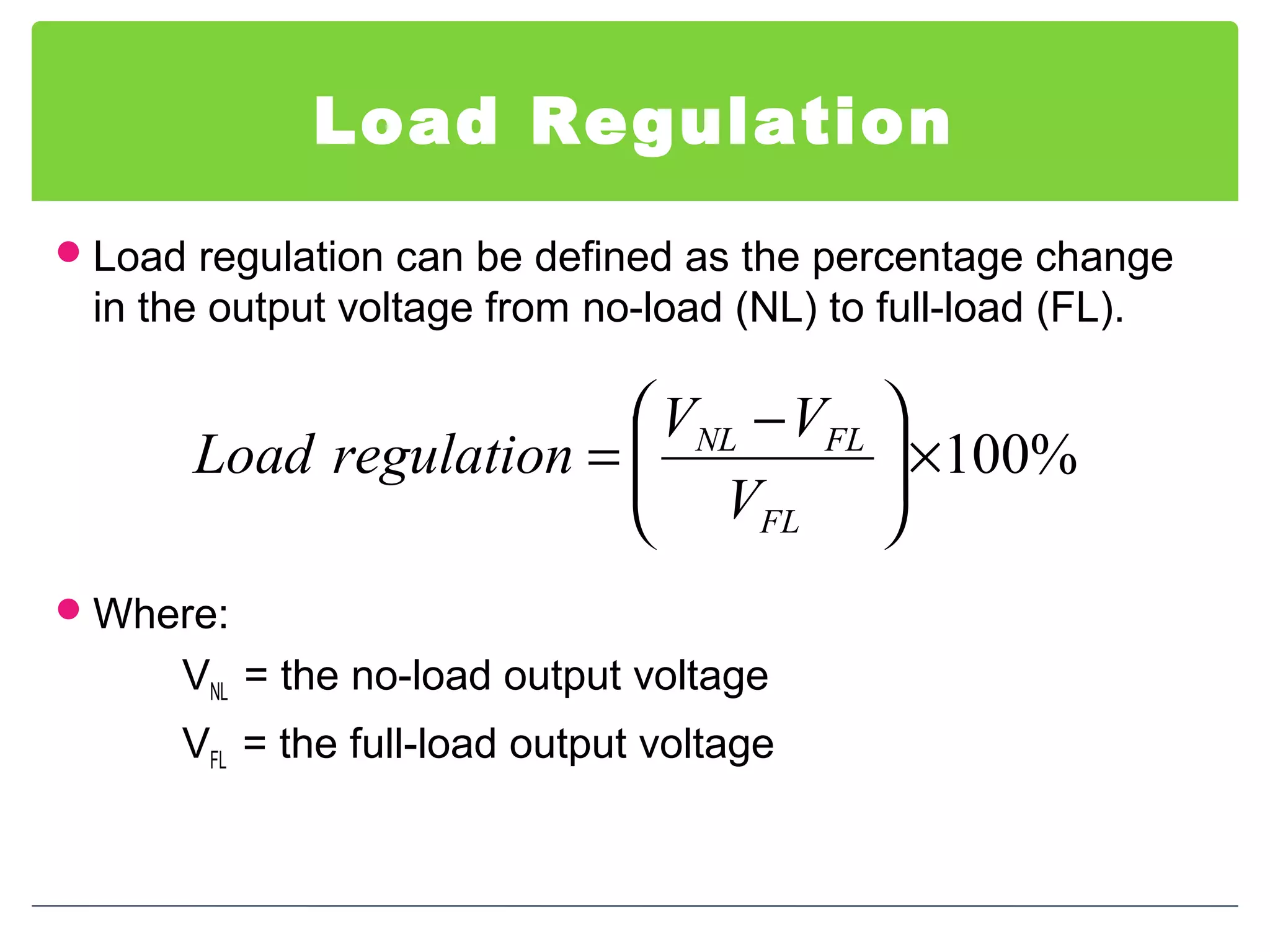
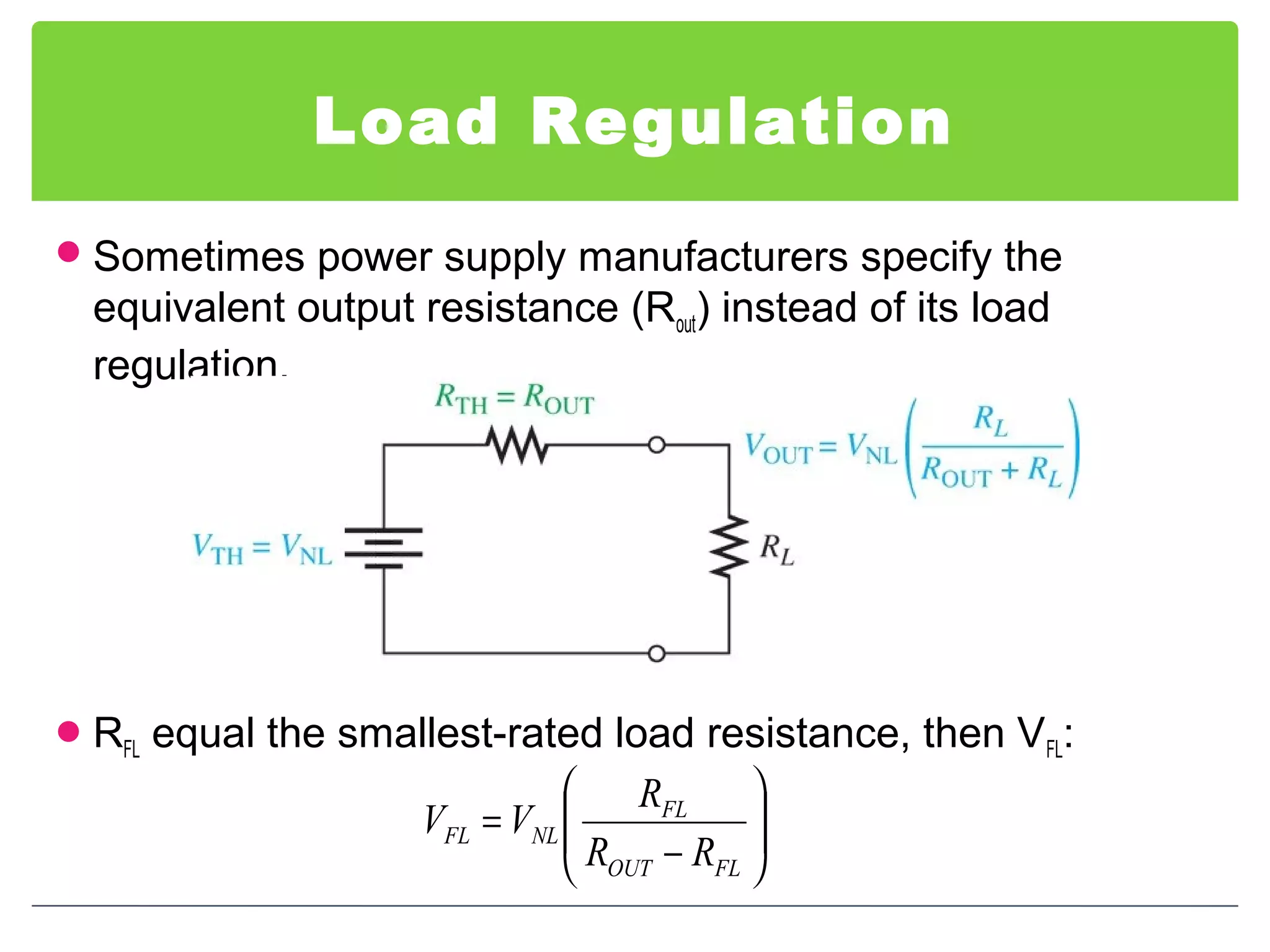
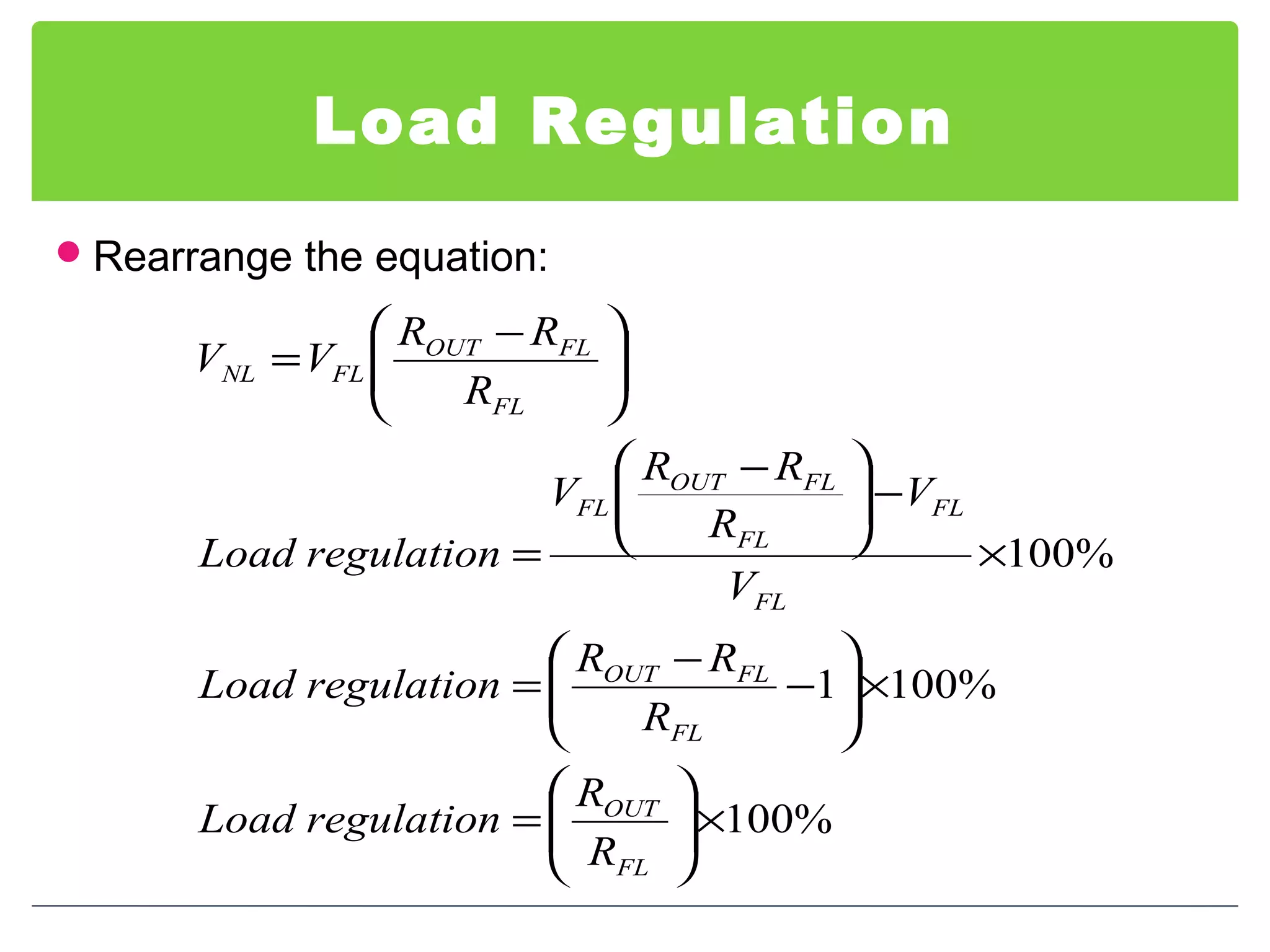
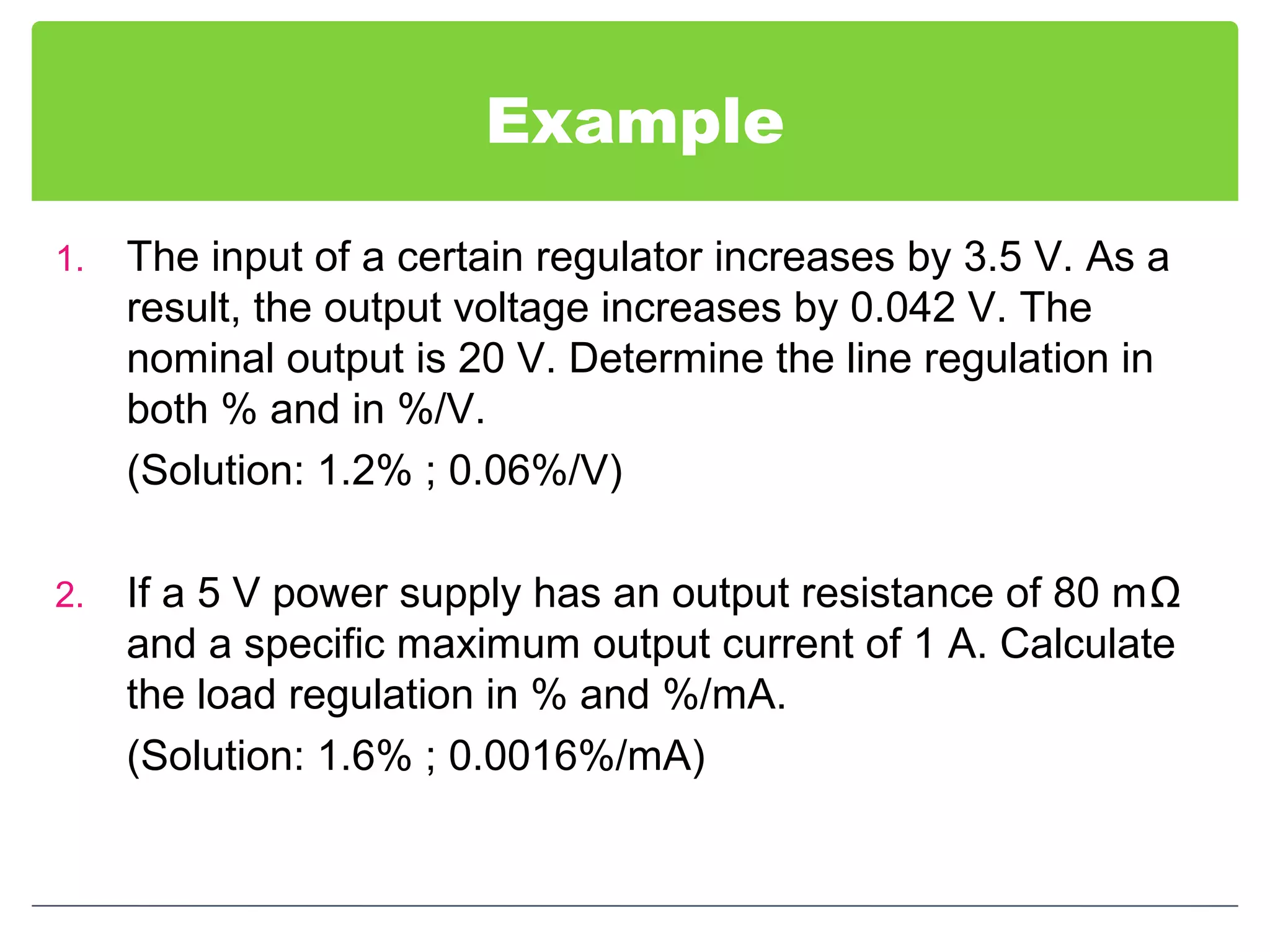
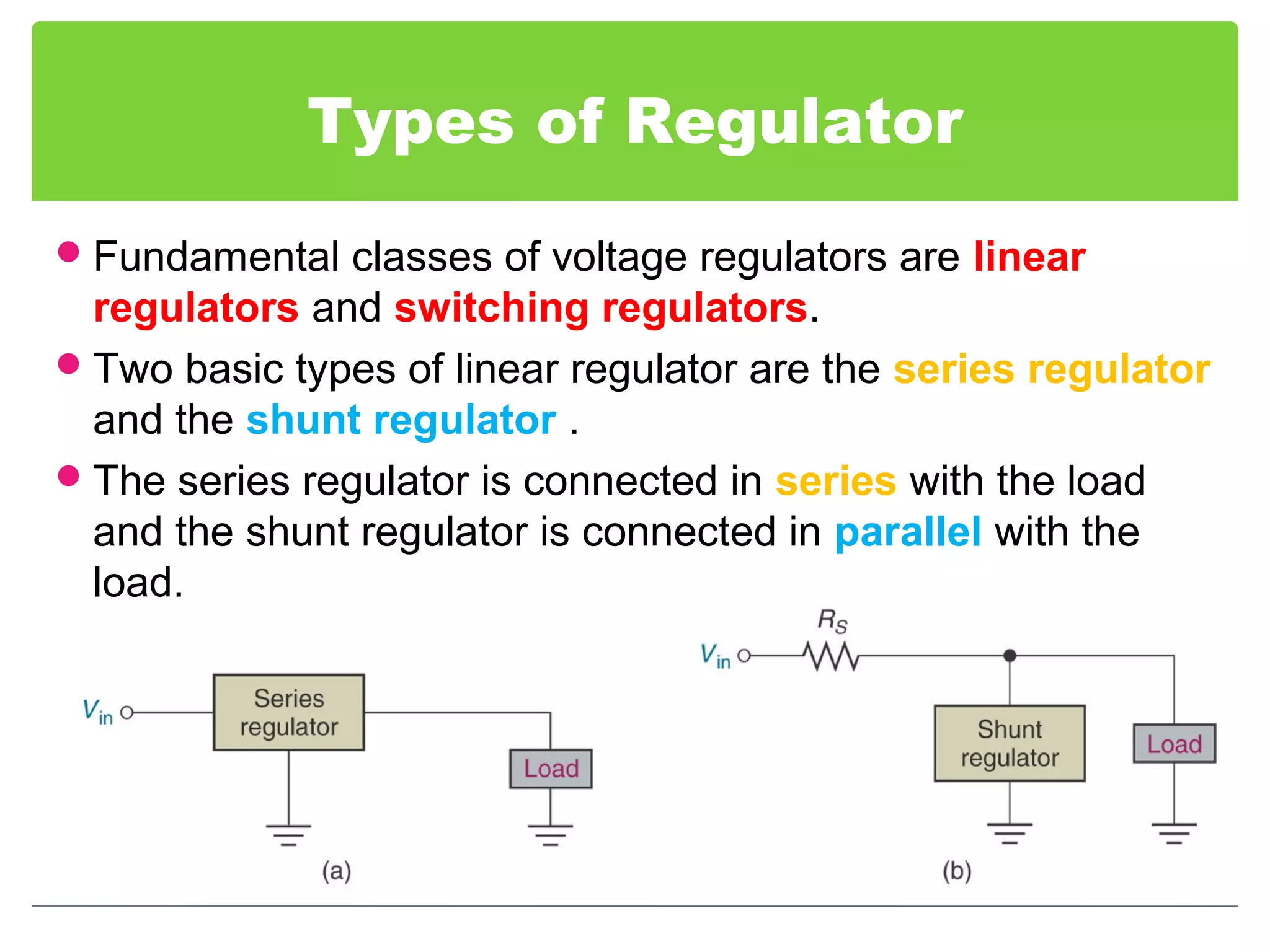
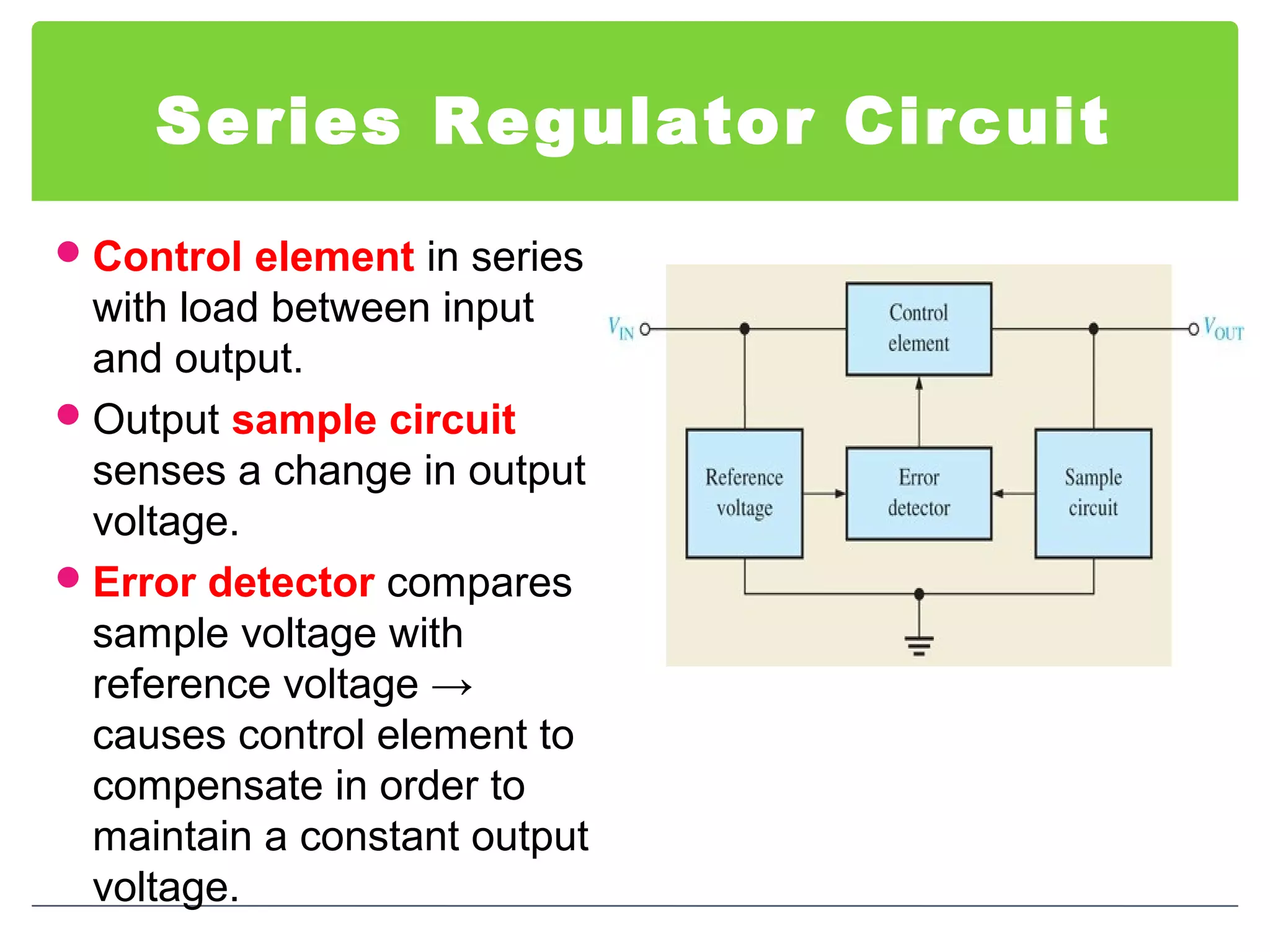
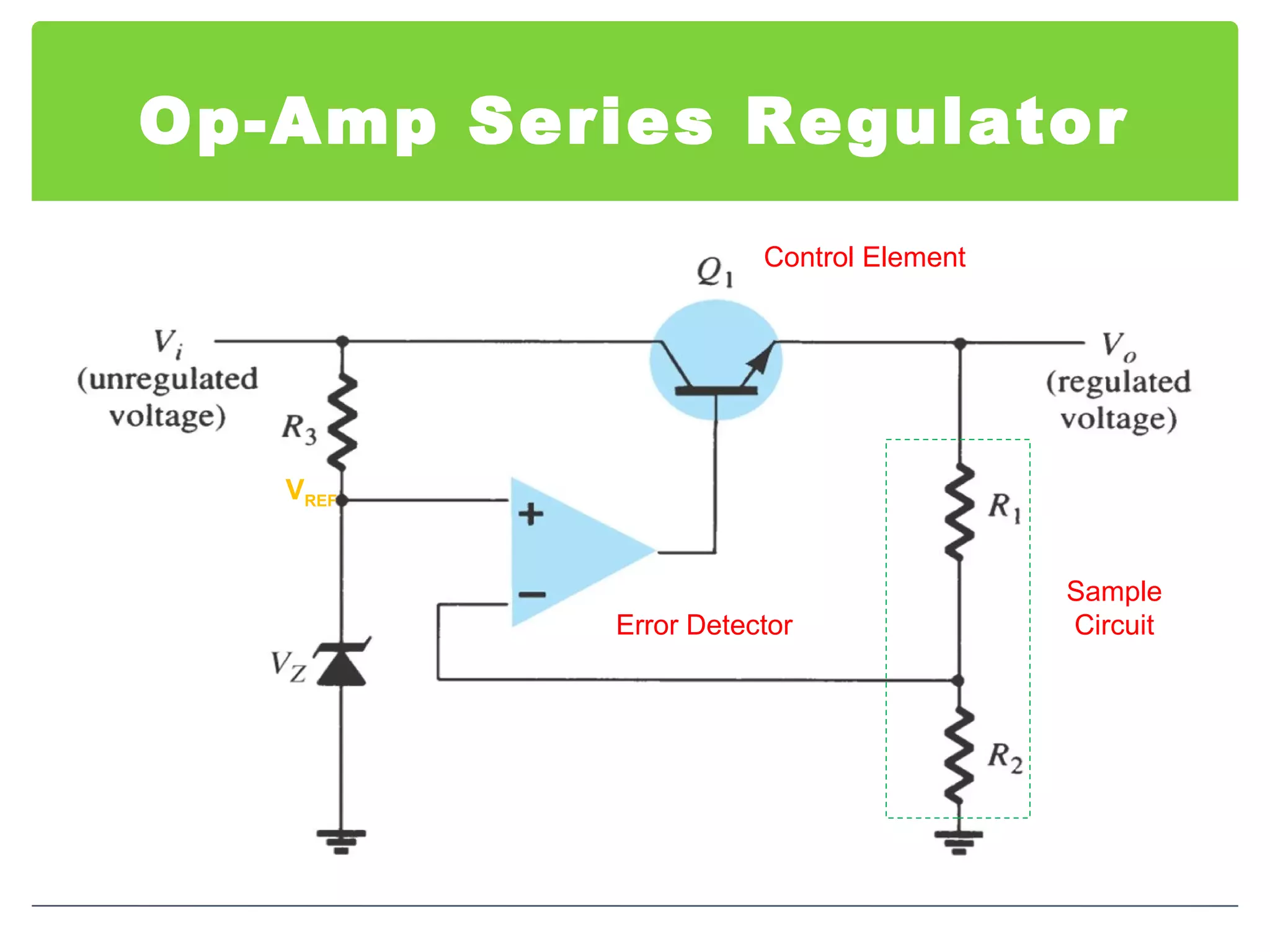
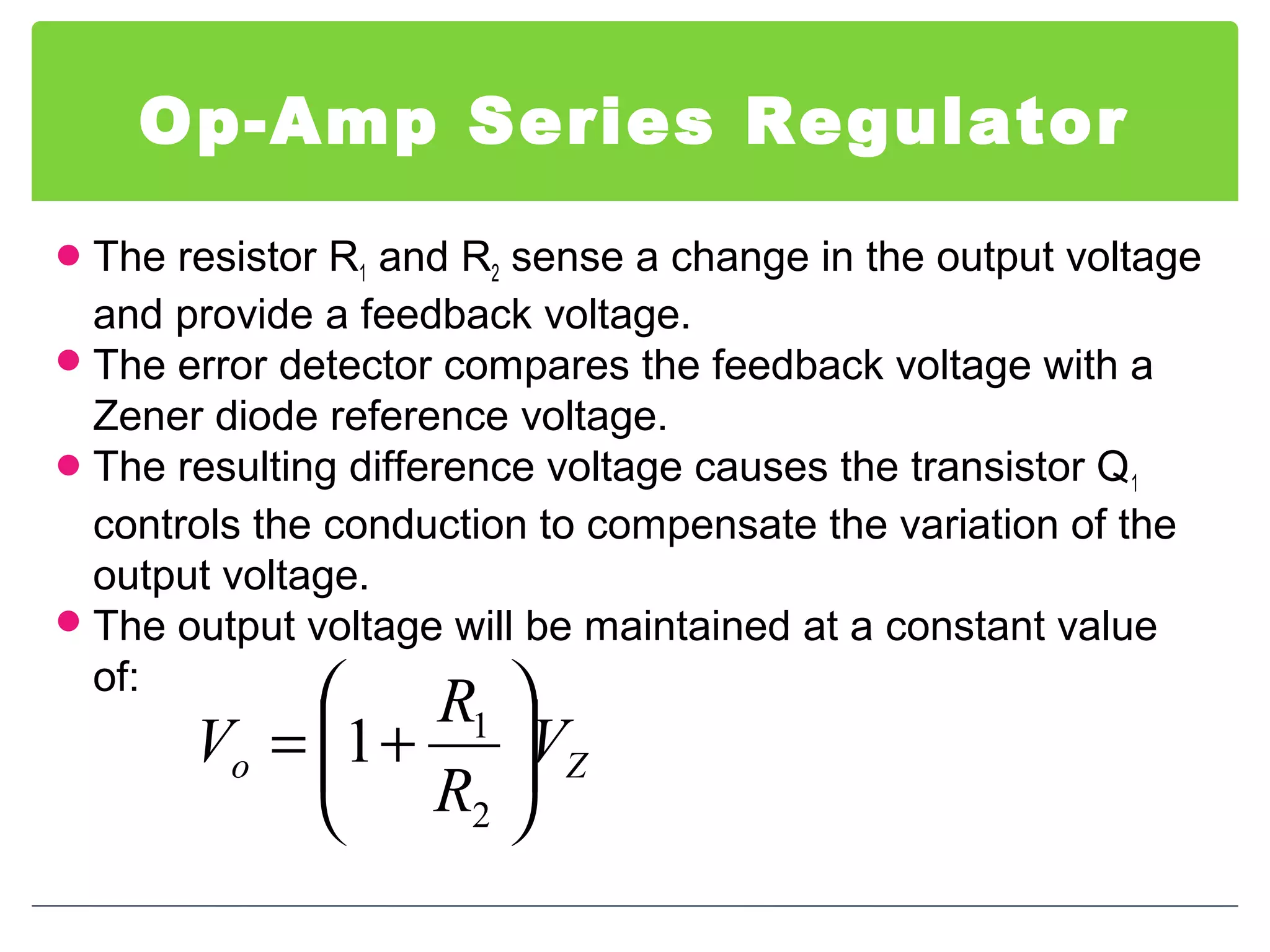
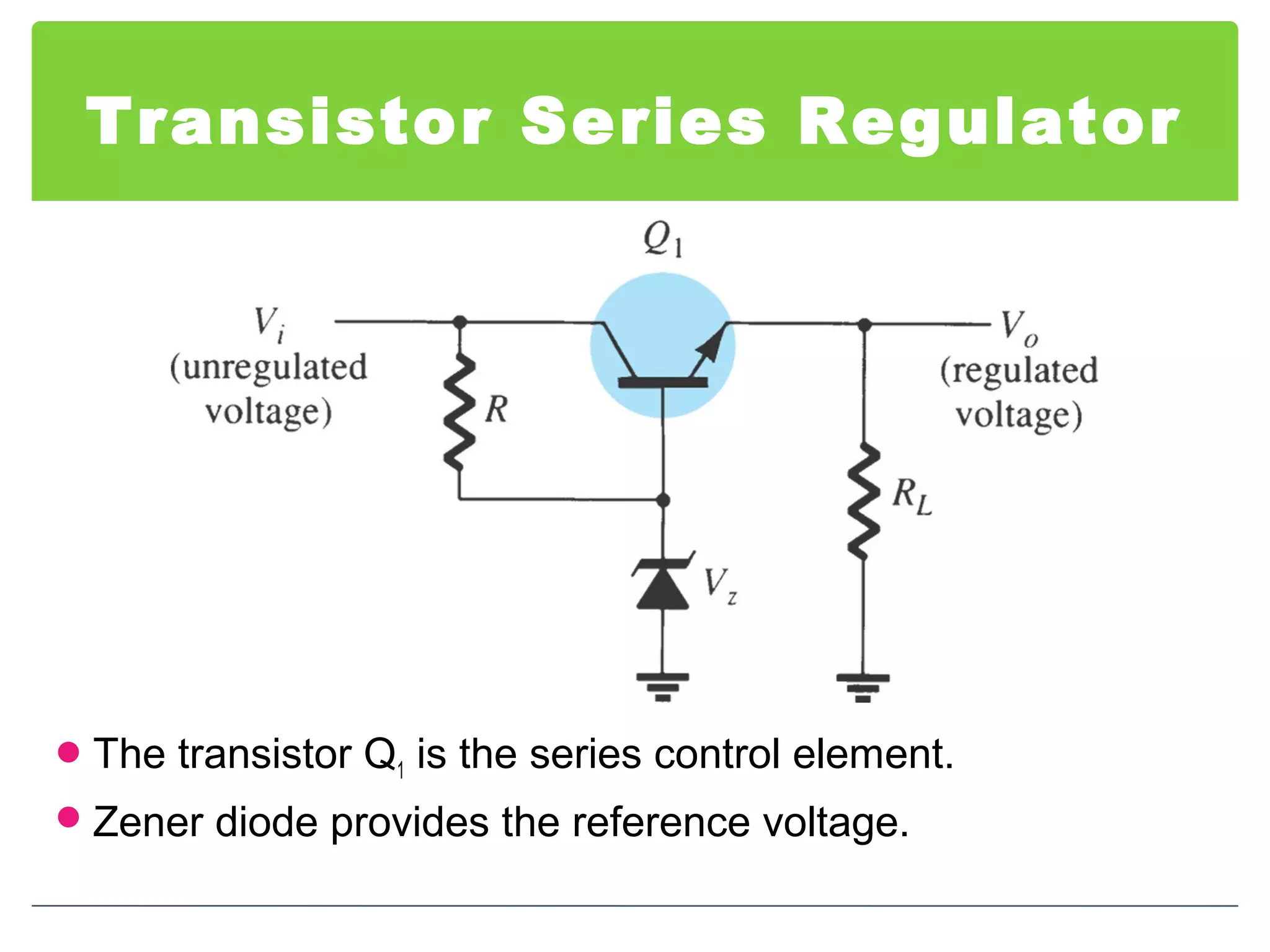
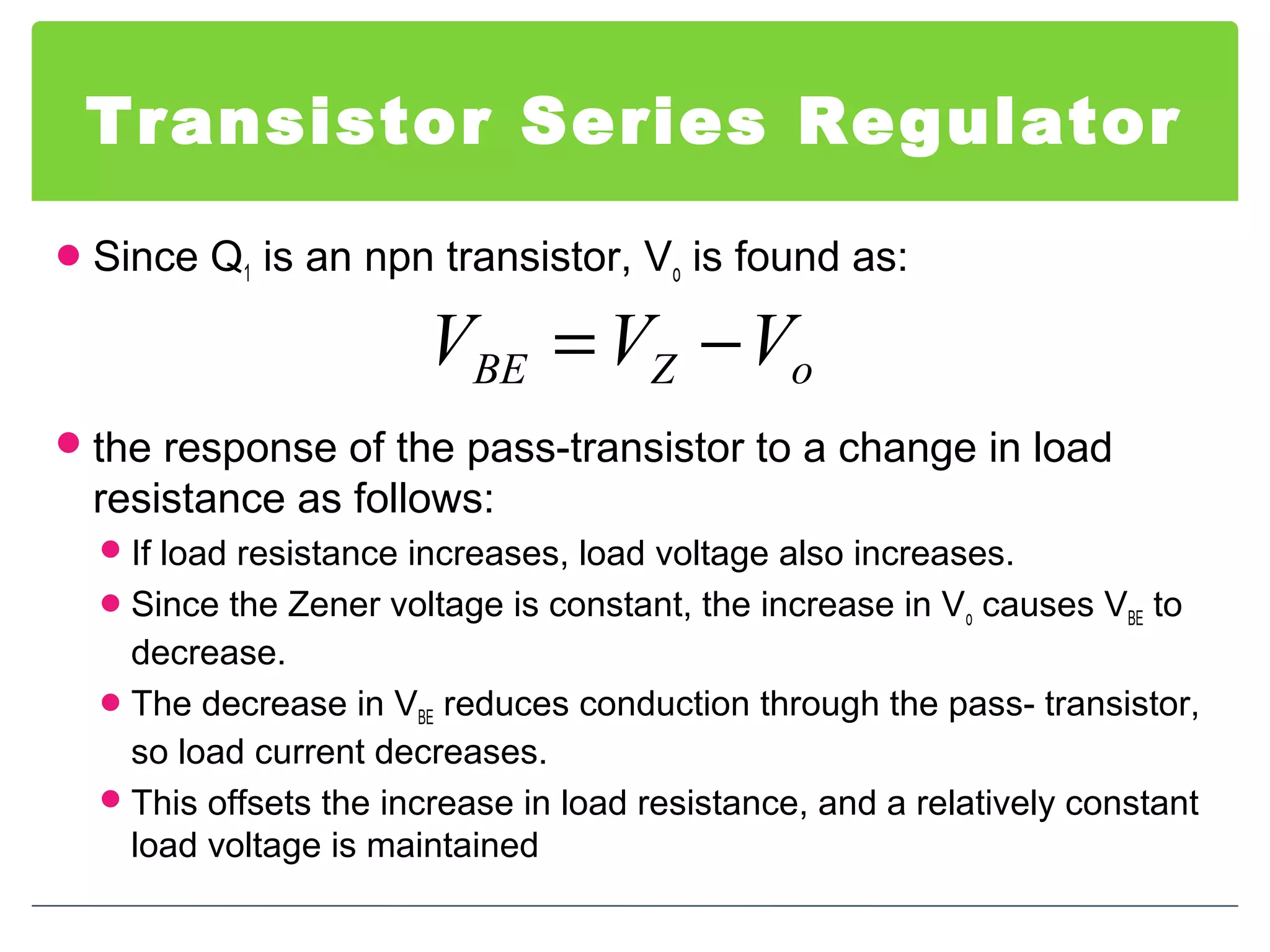
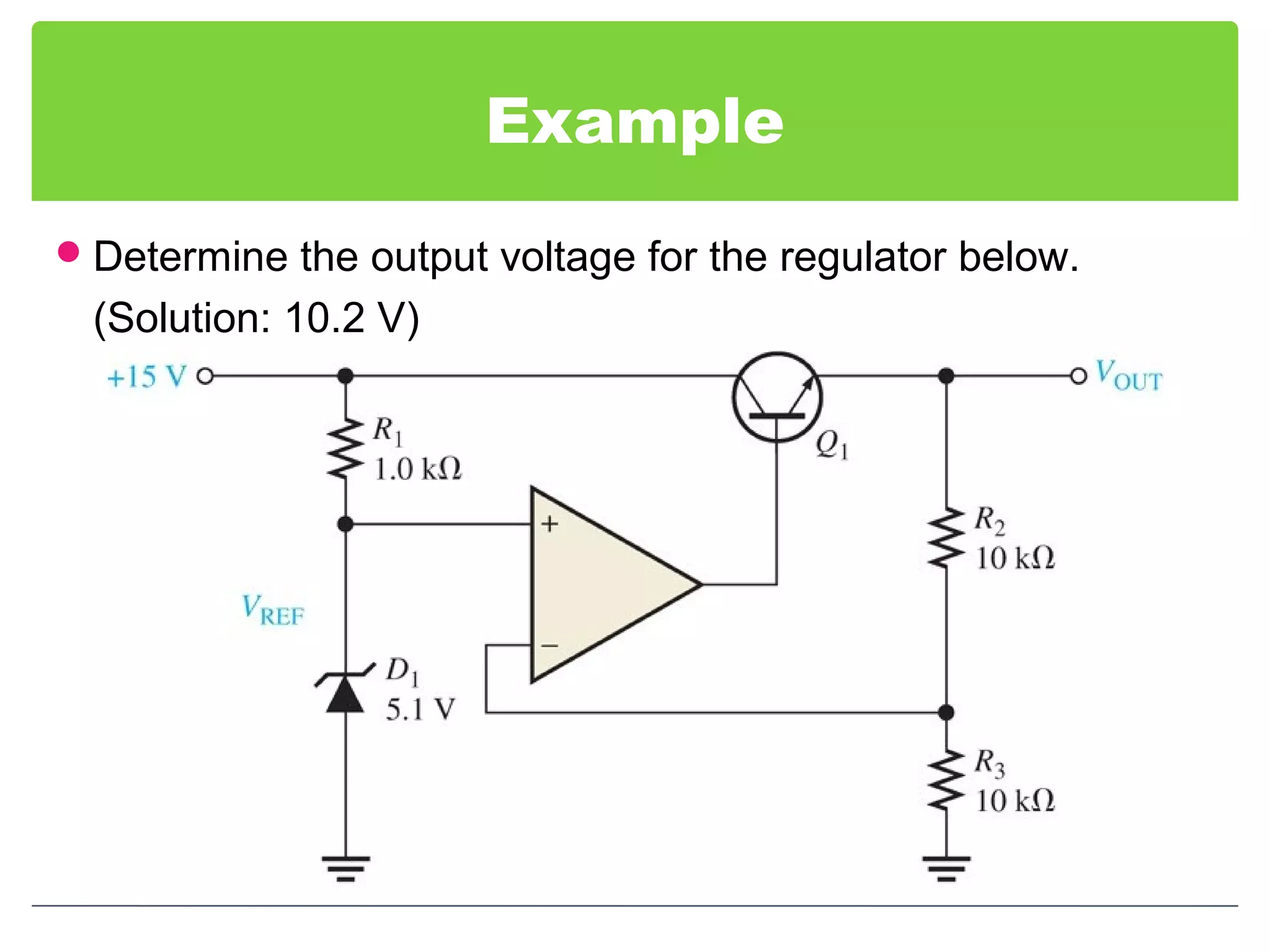
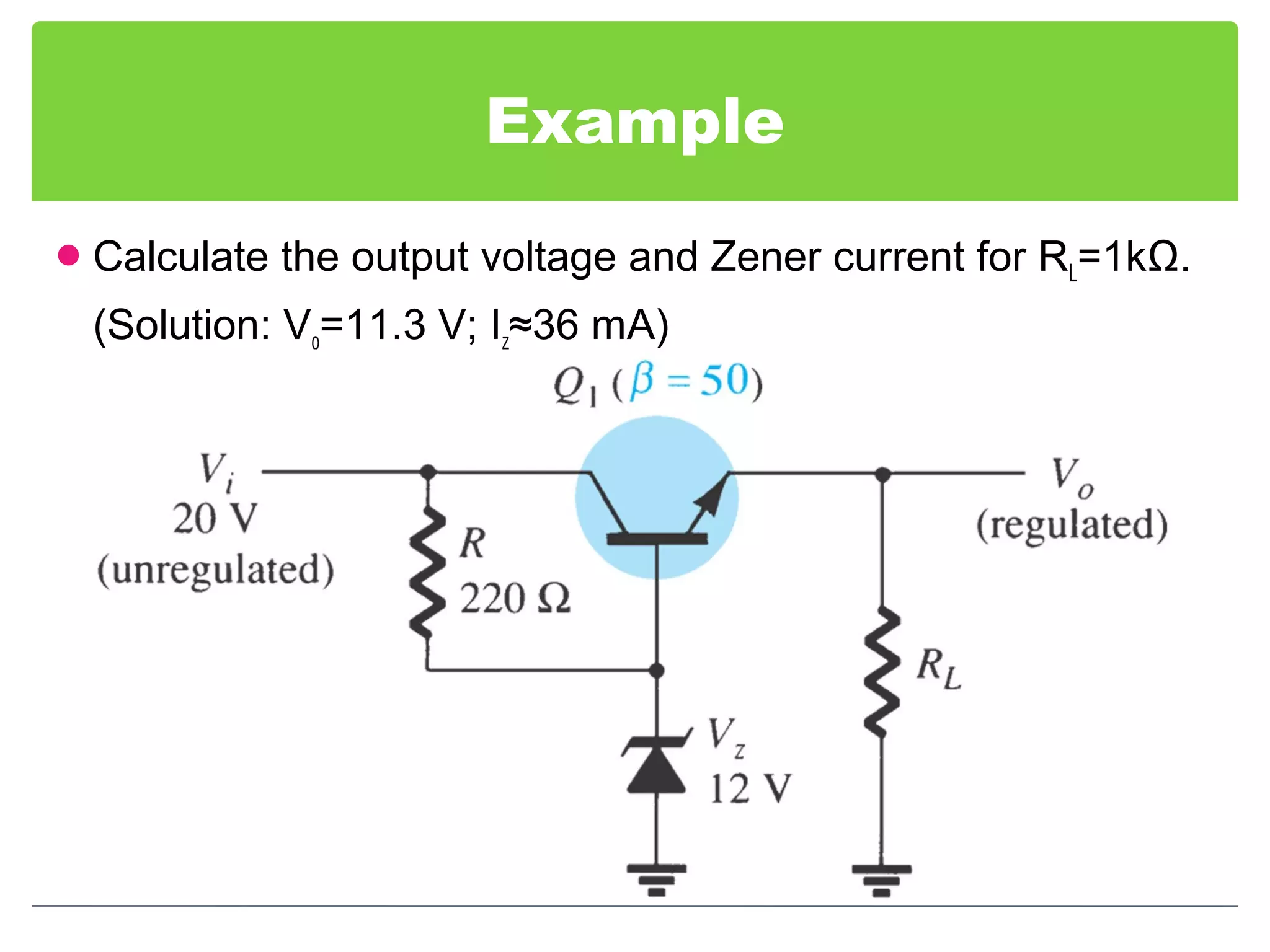
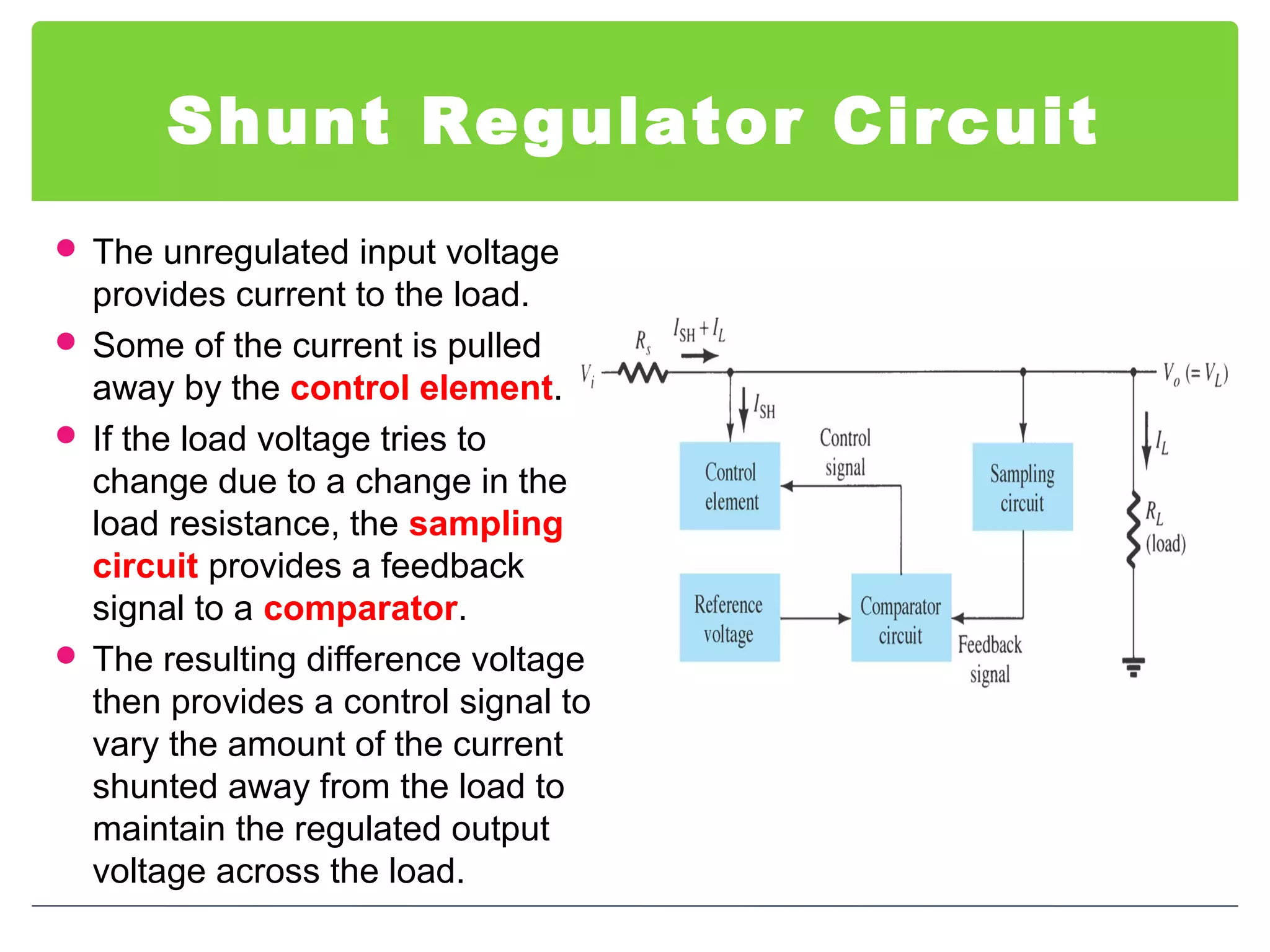
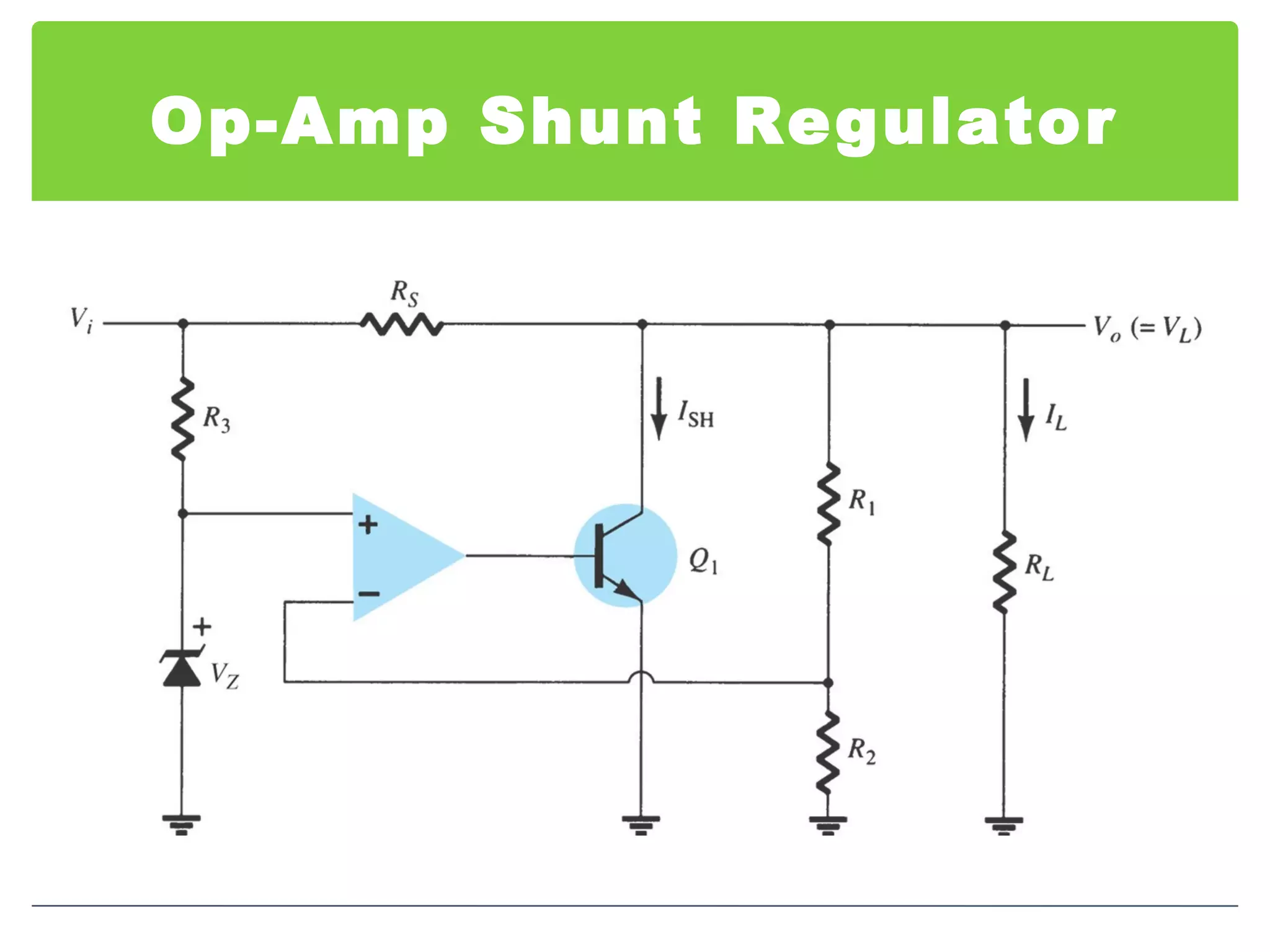
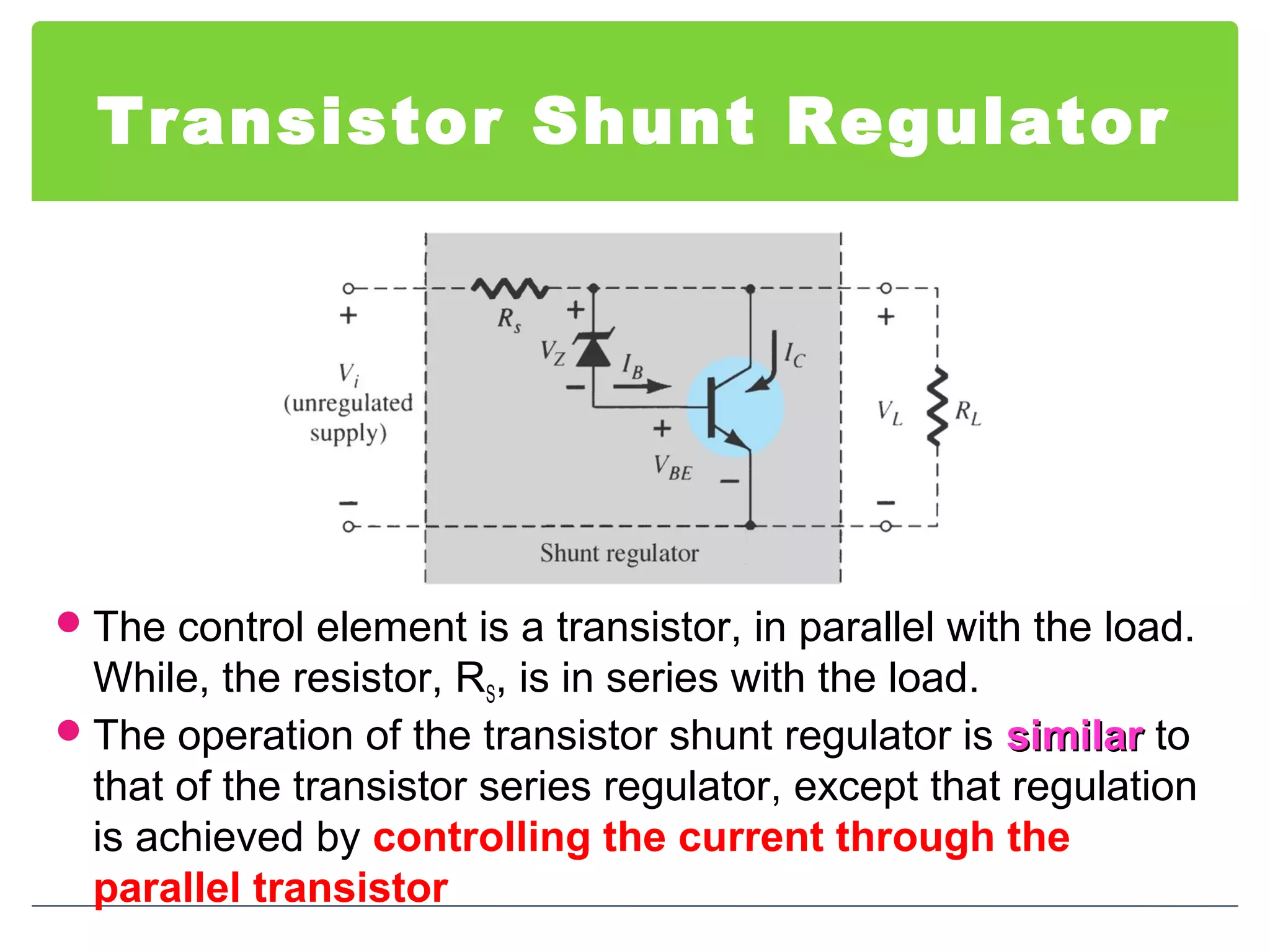
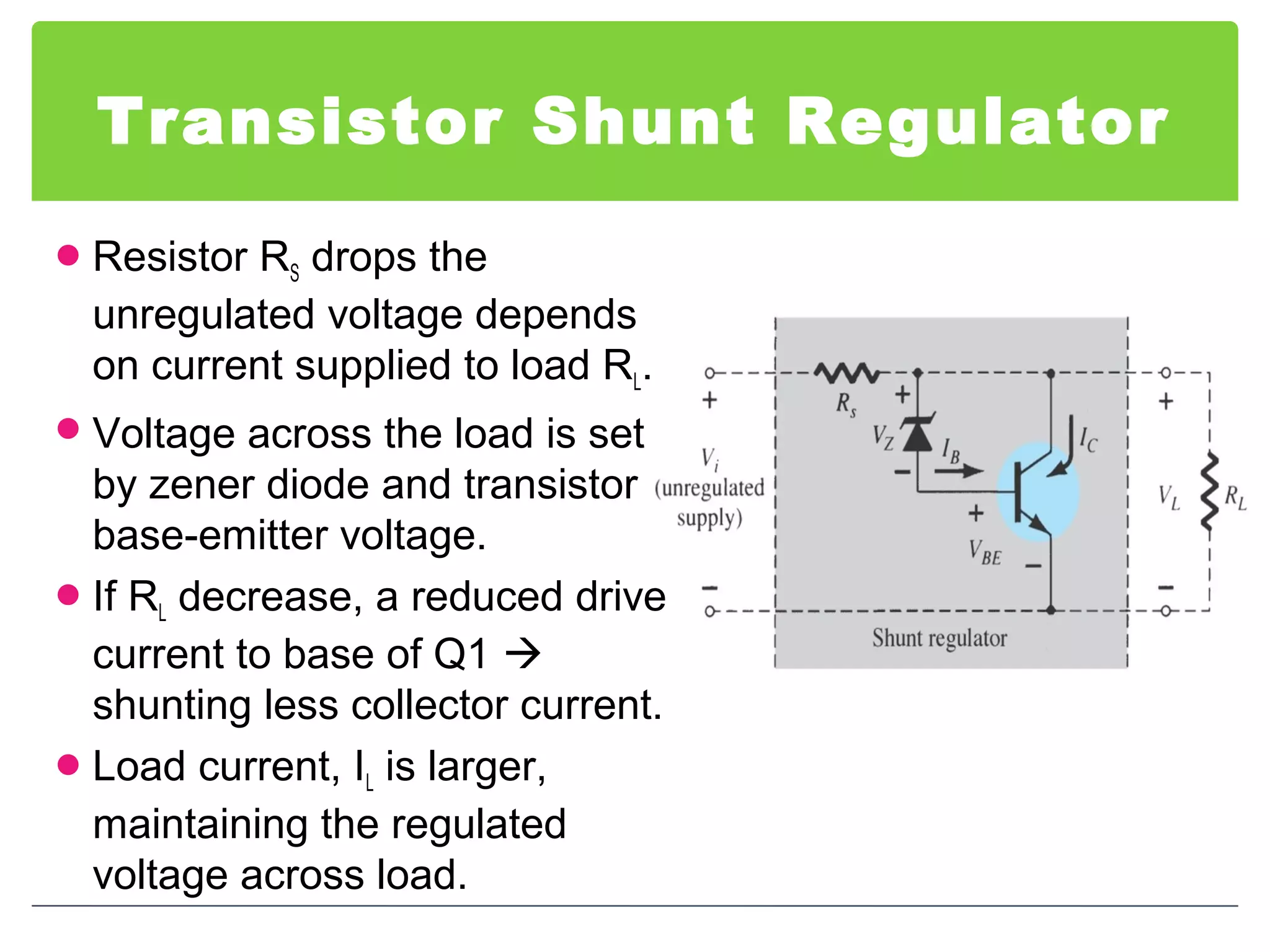
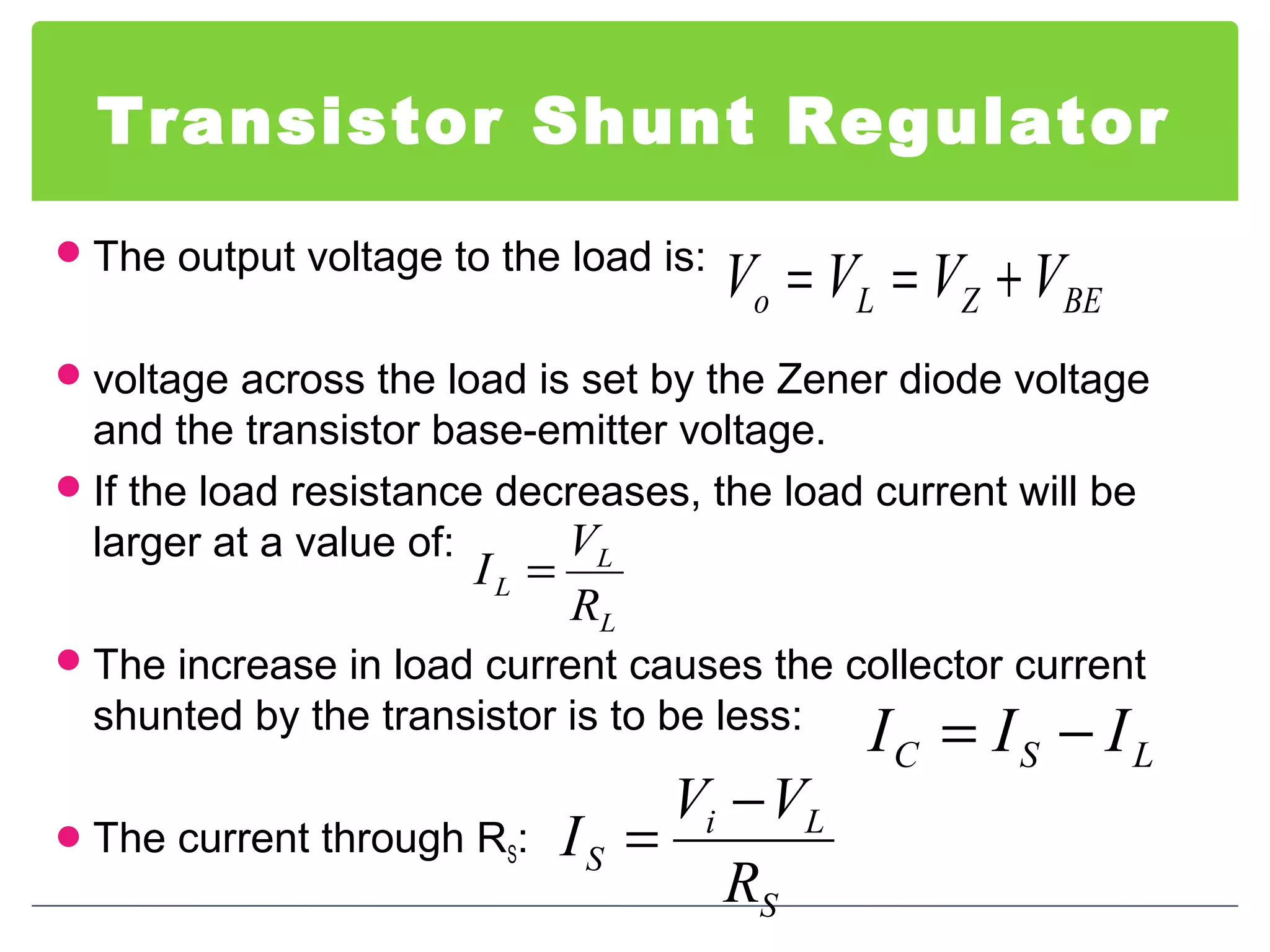
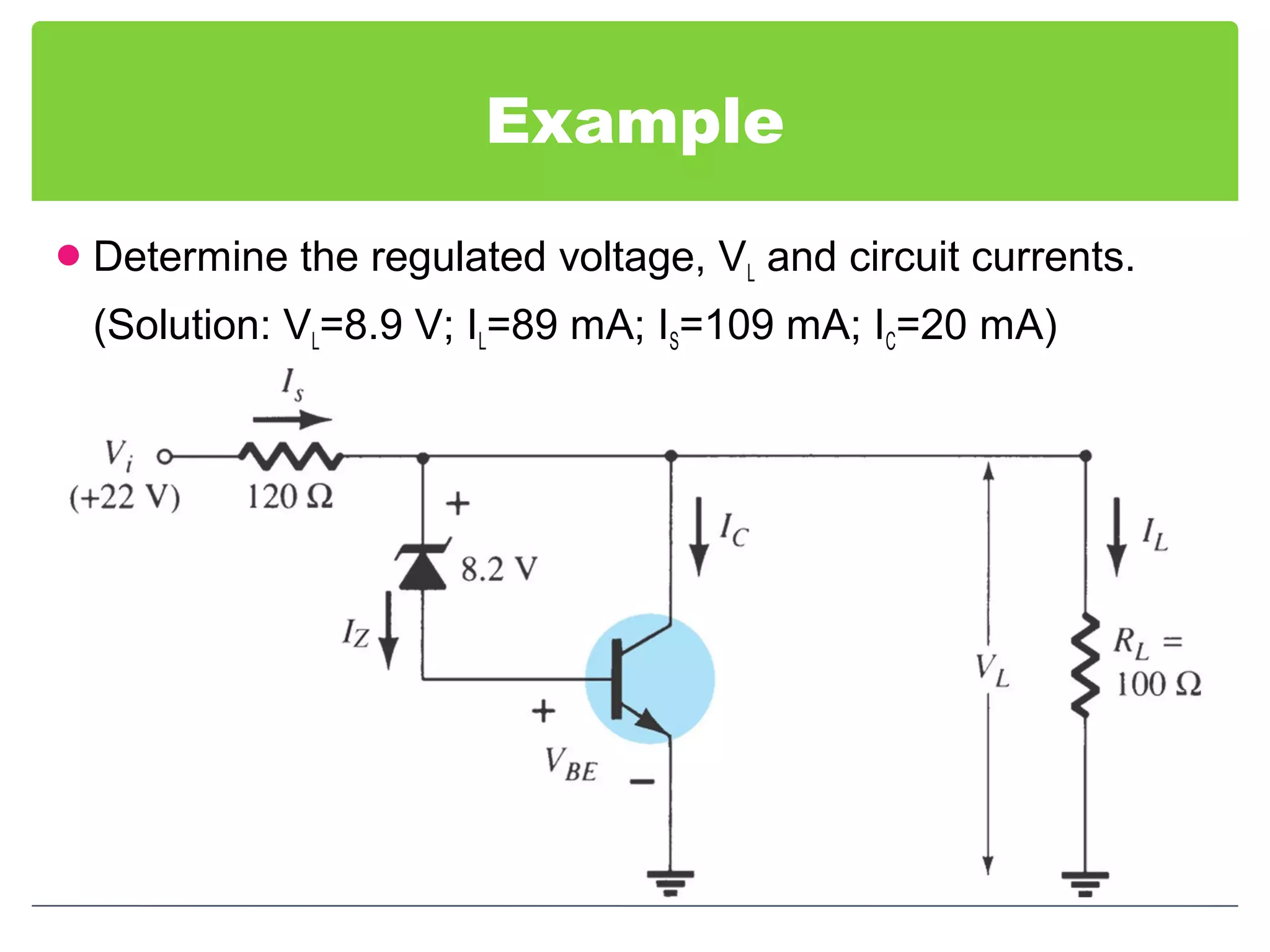
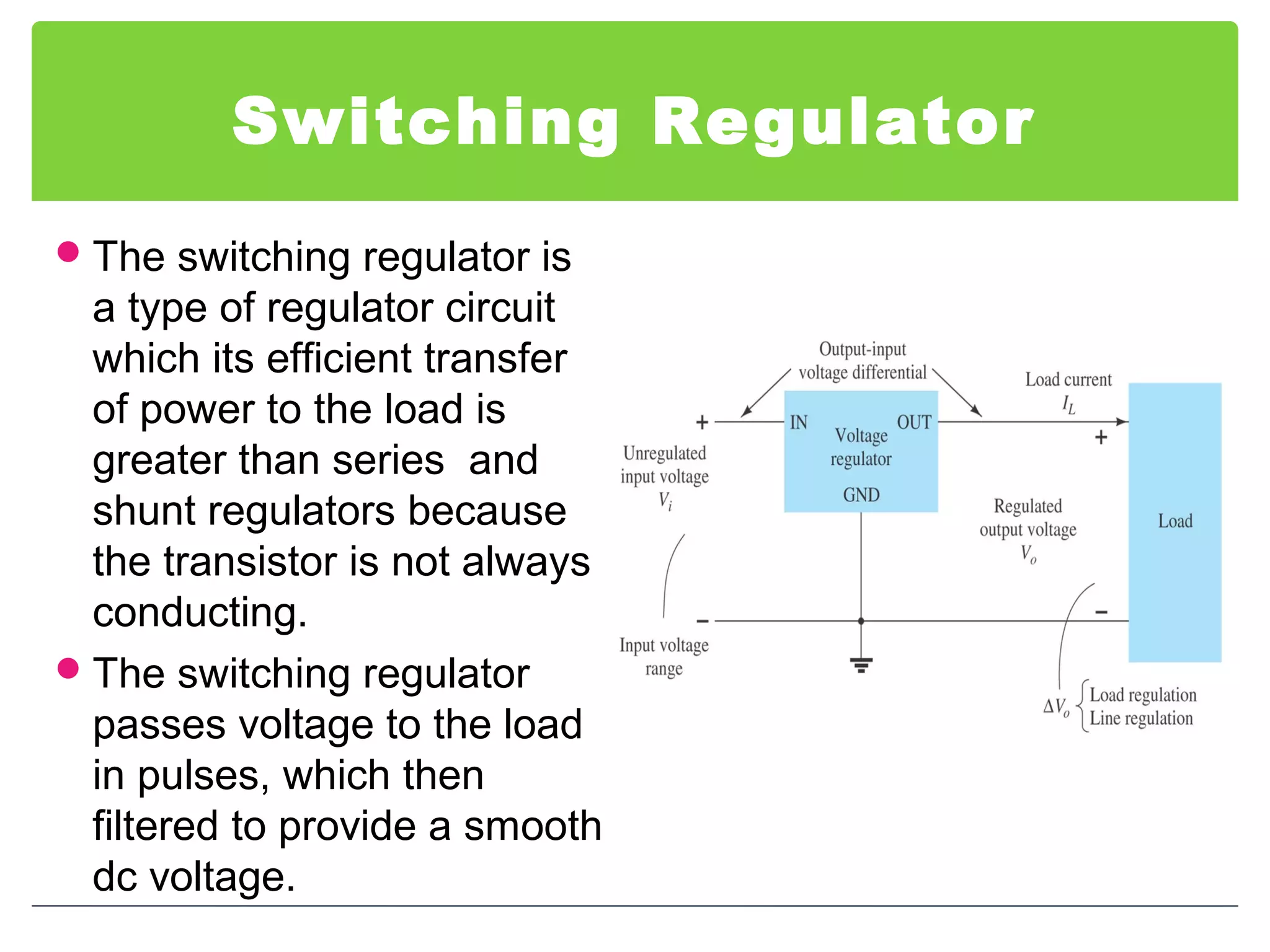
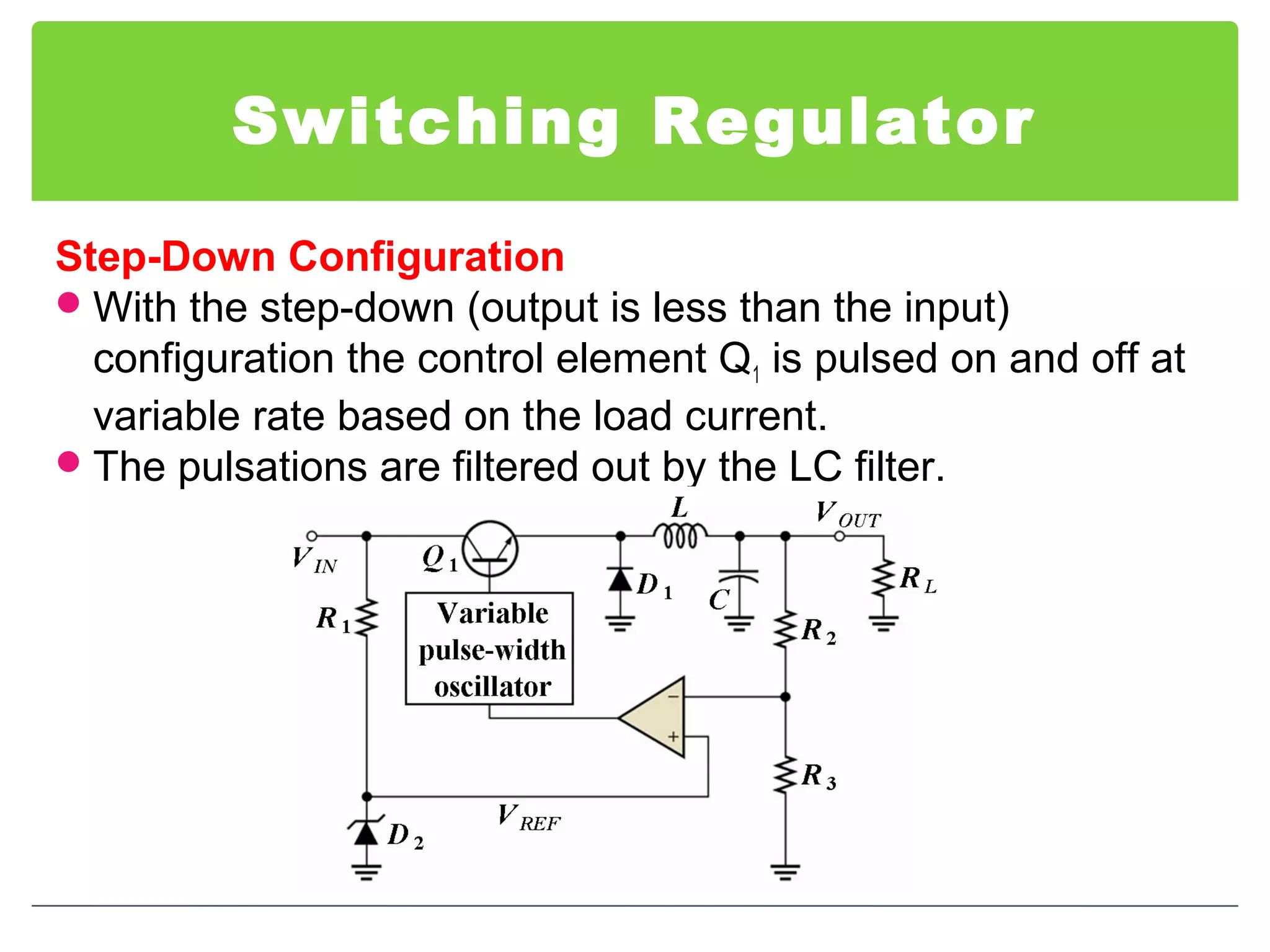
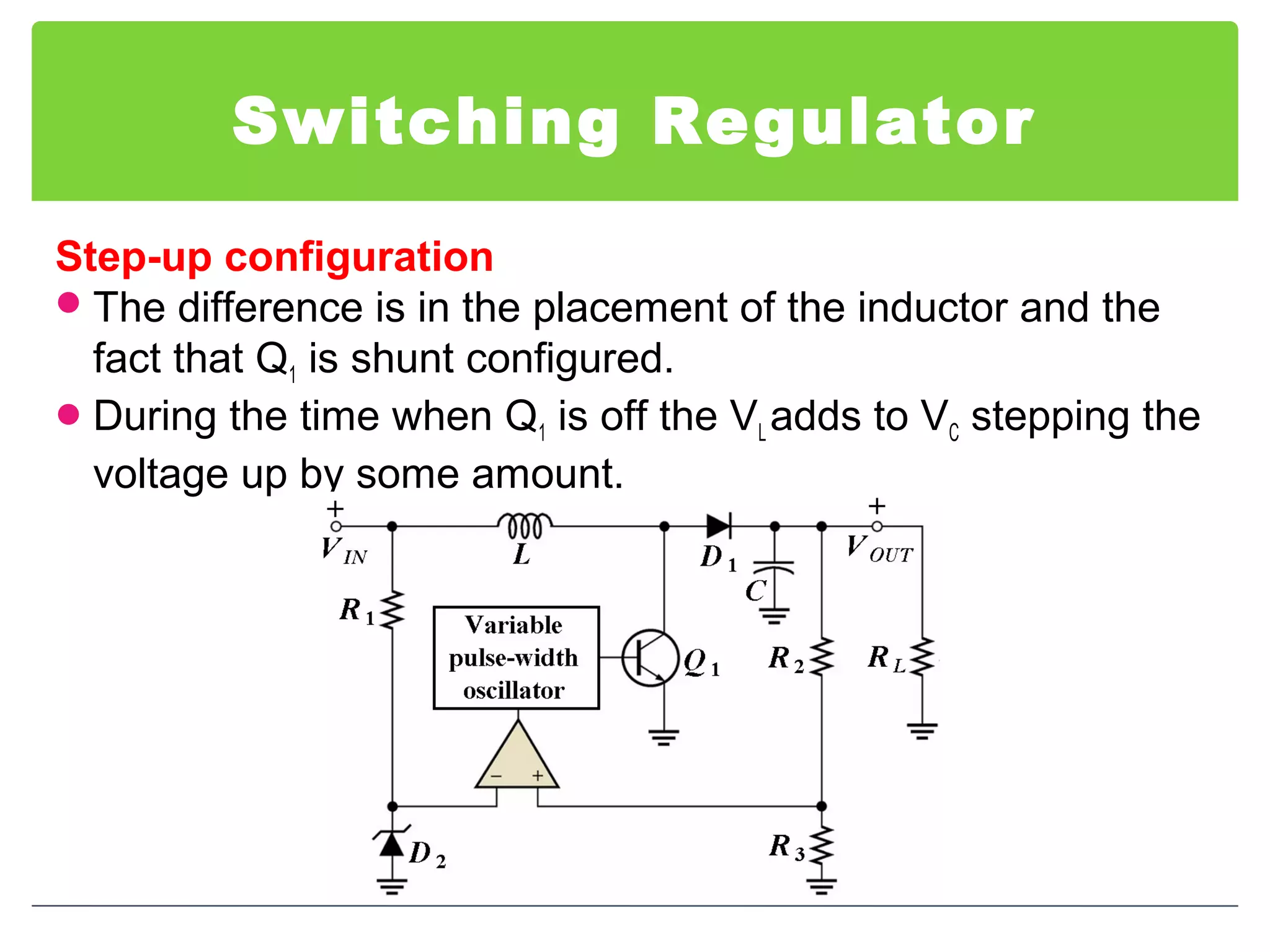
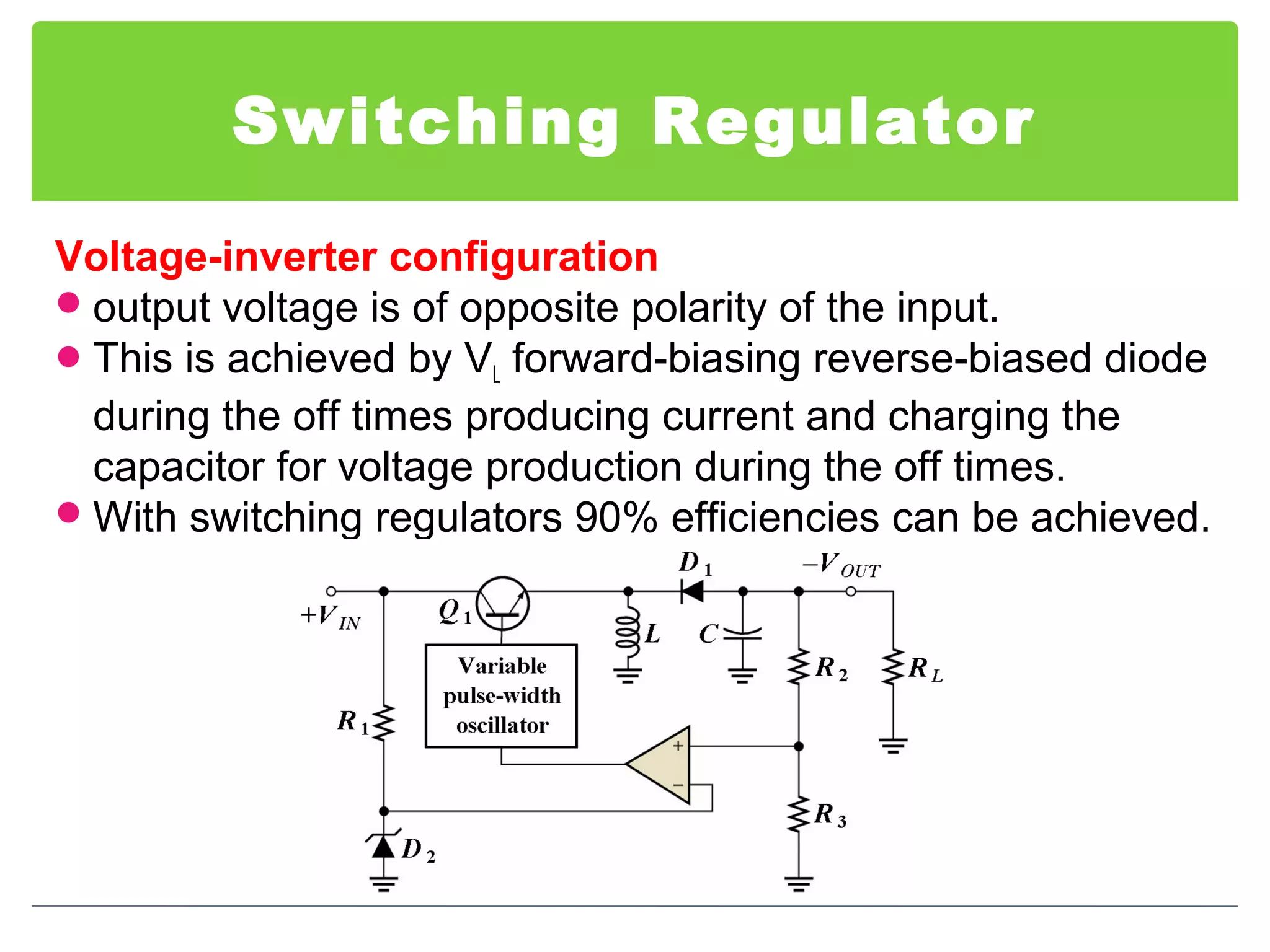
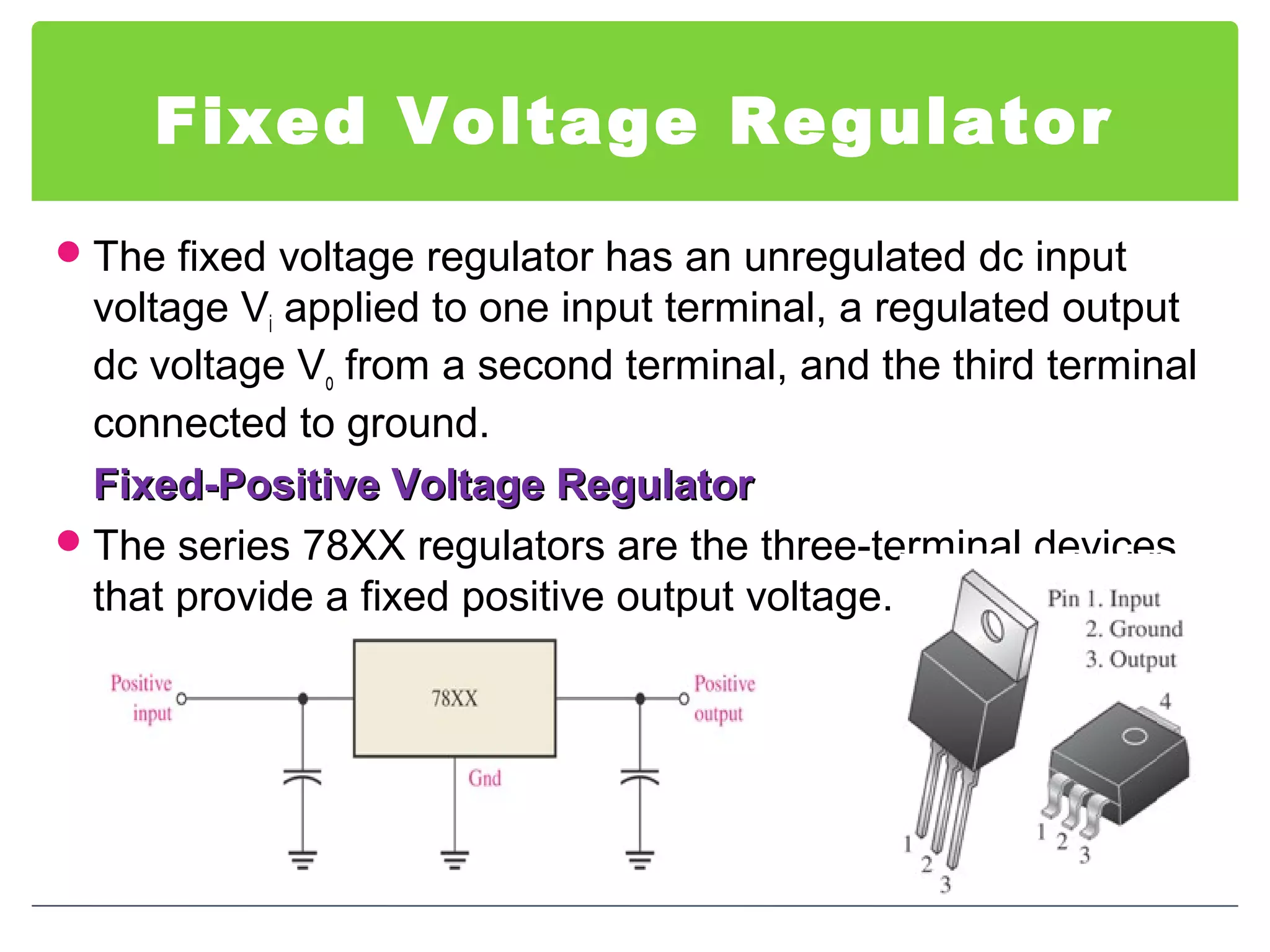
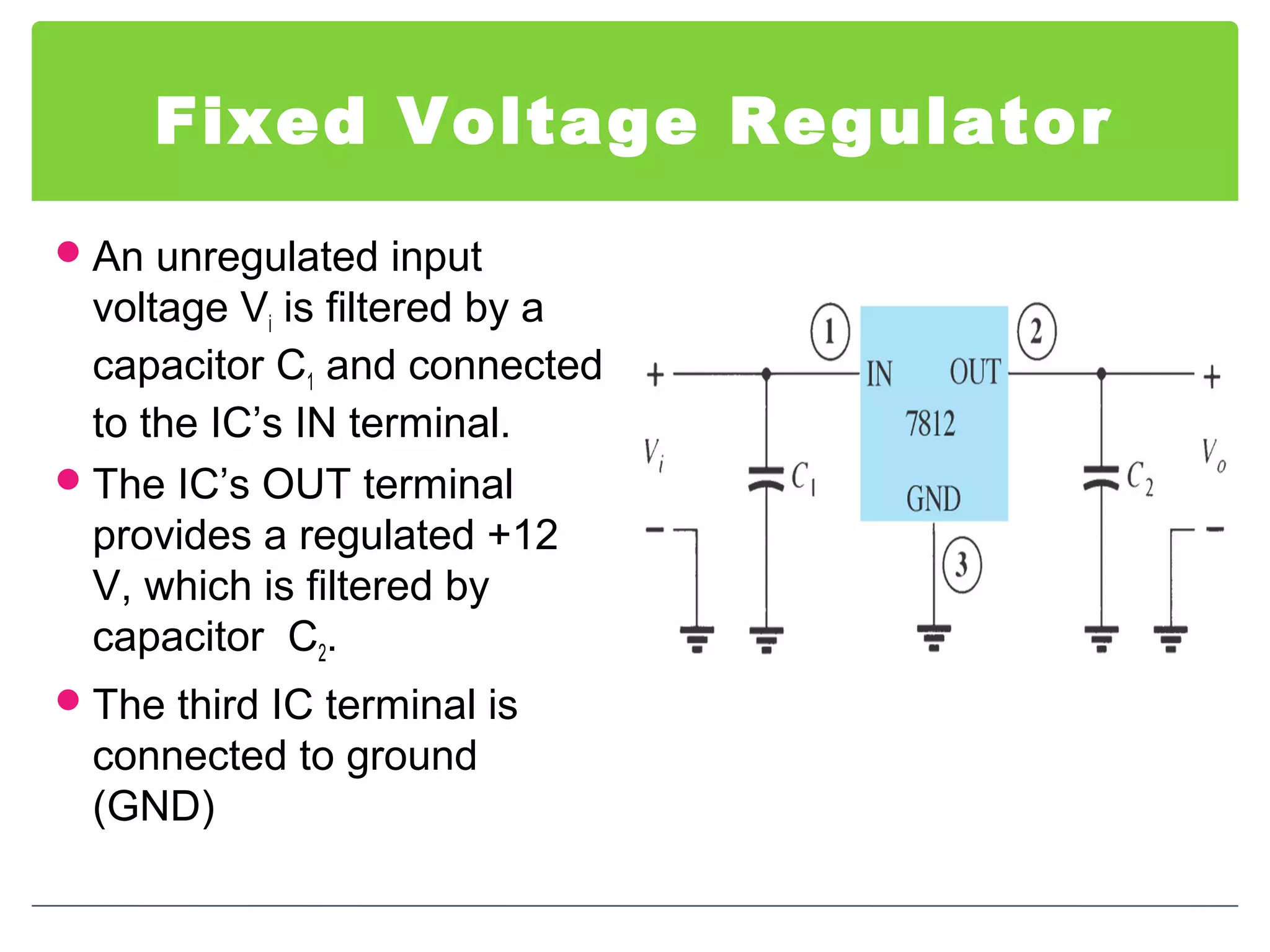
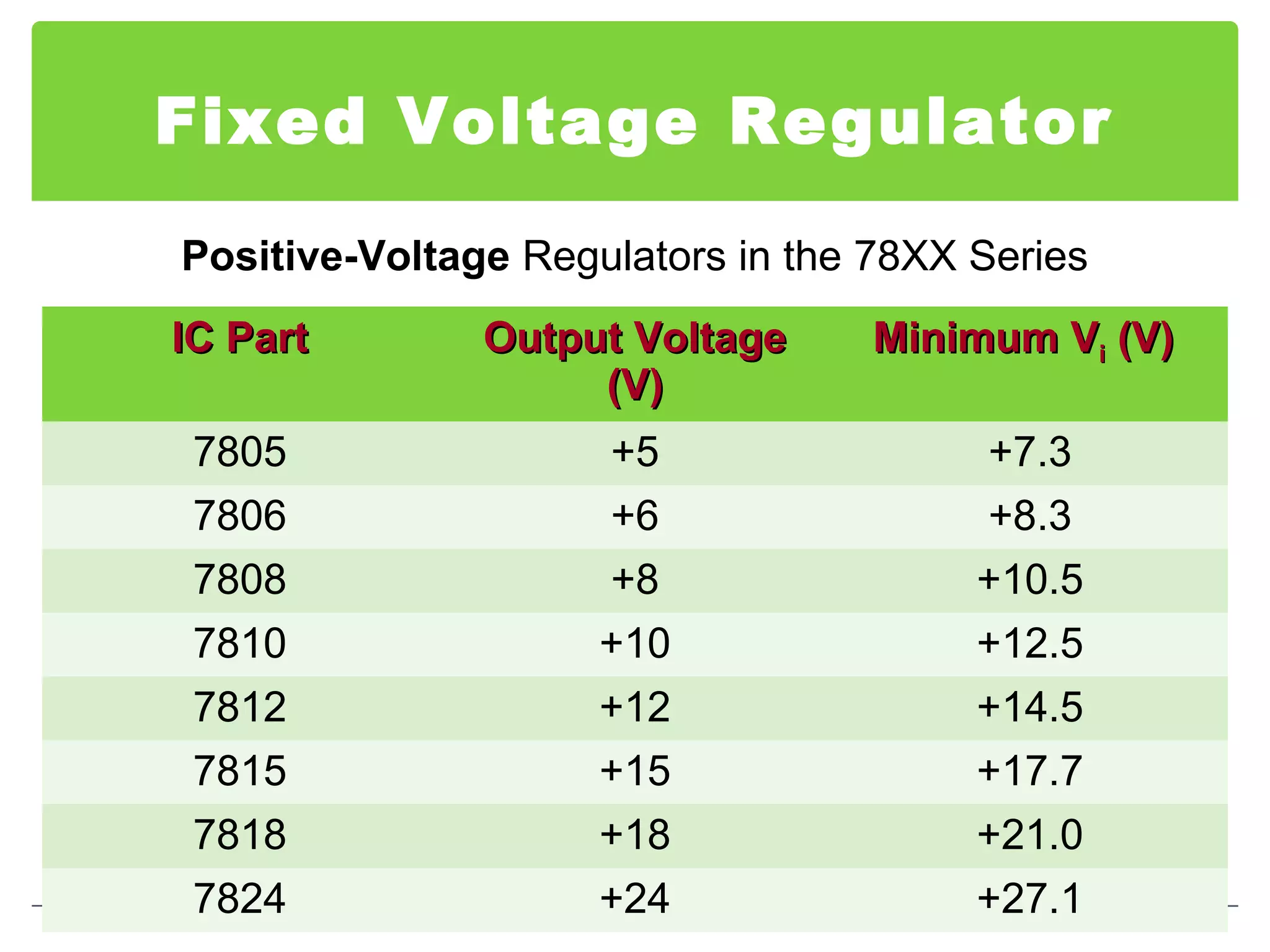
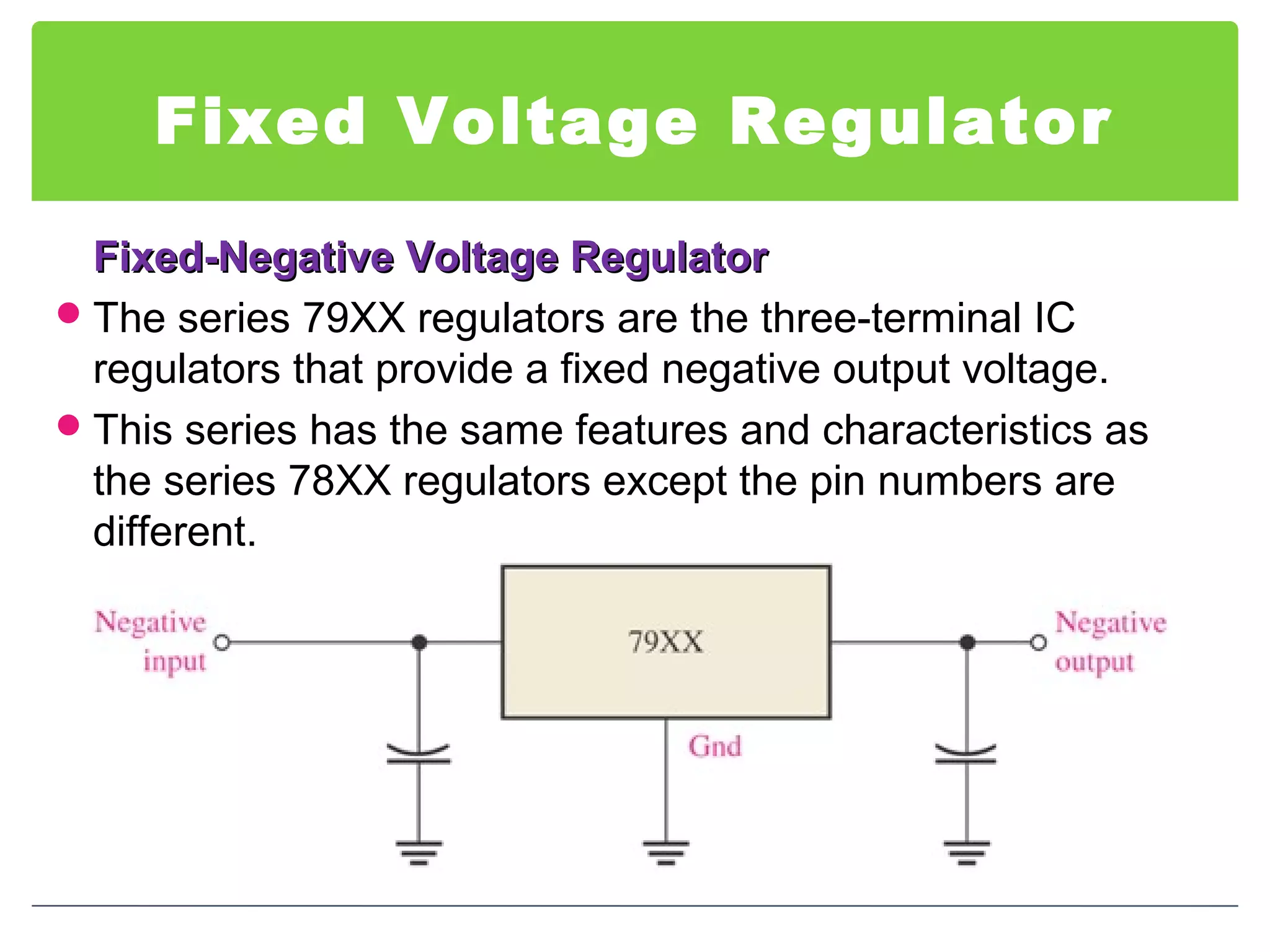
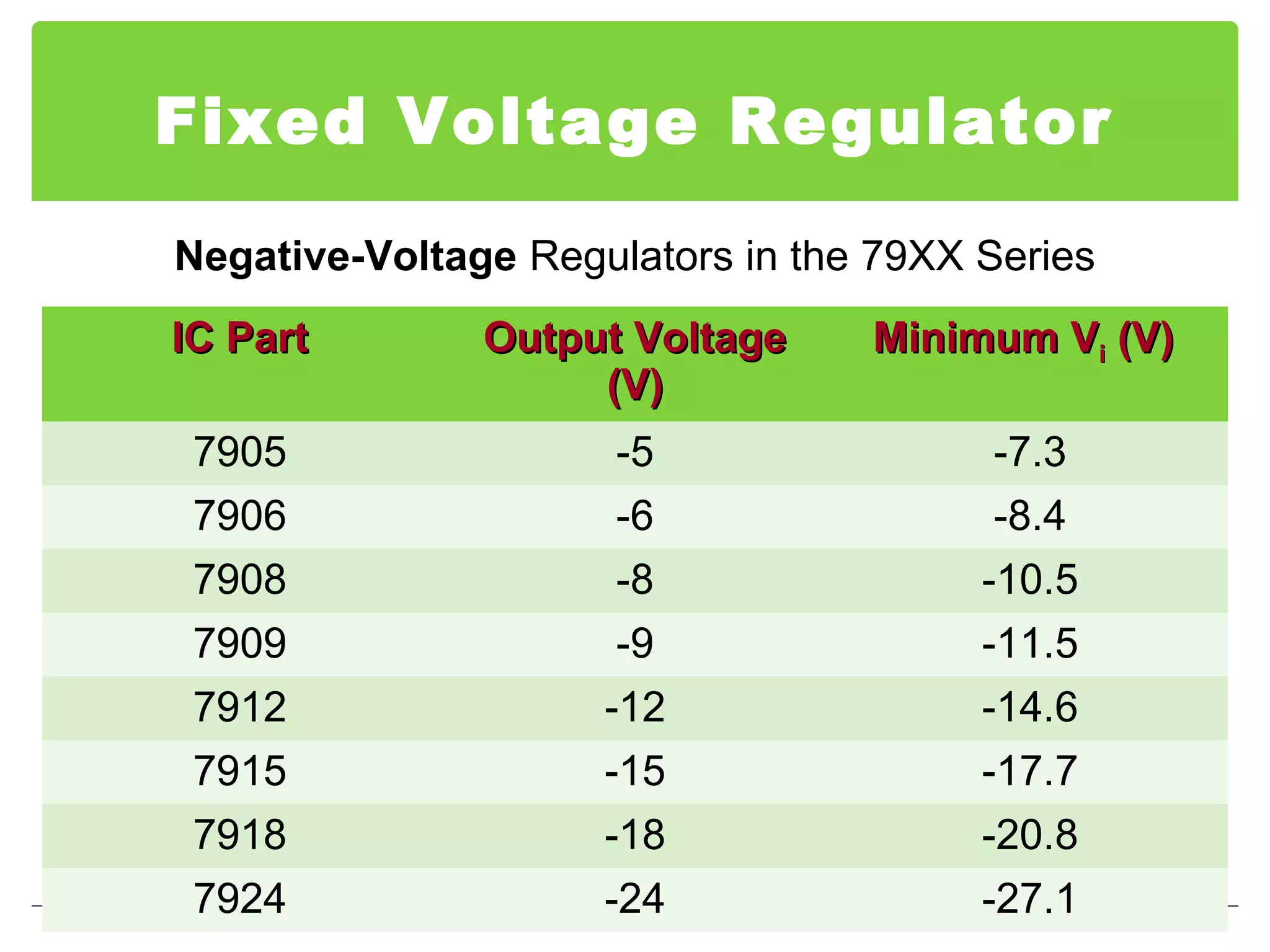
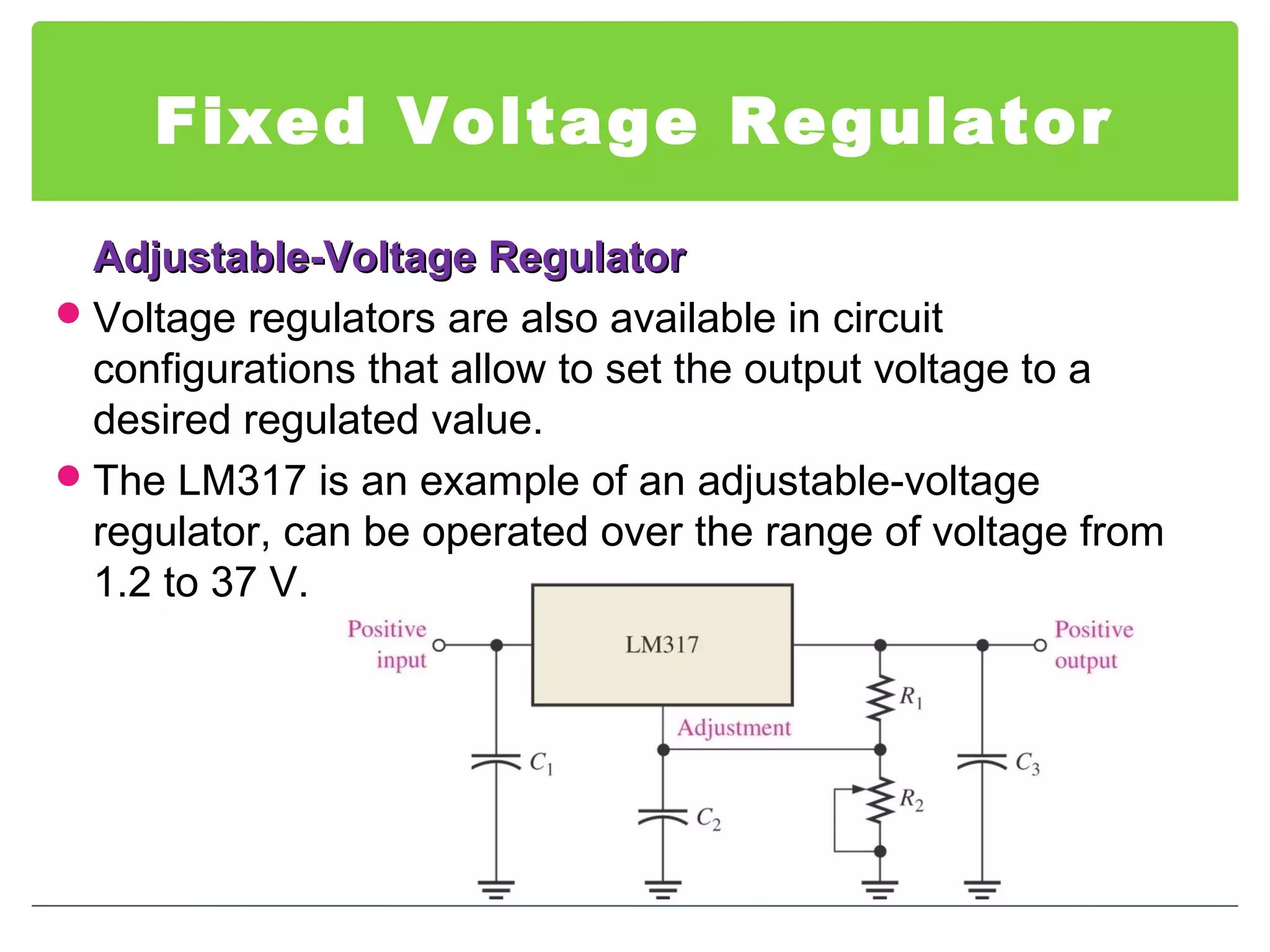
This document discusses different types of voltage regulators. It describes linear regulators as either series or shunt types. Series regulators have the control element in series with the load, while shunt regulators have the control element in parallel. Switching regulators are more efficient than linear due to pulsed operation. Integrated circuit voltage regulators are also discussed, including fixed positive, fixed negative, and adjustable output types.