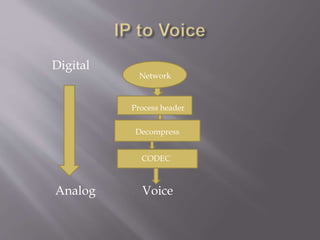
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) allows users to make voice calls using an Internet connection instead of a regular phone line. VoIP converts analog voice signals into digital data that can be sent over the Internet or IP networks. This involves sampling the analog voice, encoding it using codecs into data packets with headers, transmitting the packets over the network, then decoding and reconstructing the analog voice at the destination. Common standards like H.323 are used to facilitate VoIP calls and ensure quality of service over IP networks.