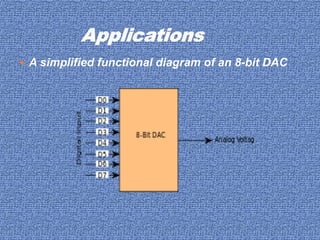
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) converts an analog signal into a digital signal. It allows analog signals from the physical world to be processed digitally. Common types of ADCs include dual slope, successive approximation, flash, and delta-sigma converters. Digital-to-analog converters (DACs) perform the opposite conversion, taking a digital signal and outputting an analog voltage or current. Examples of DAC usage include audio signal generation and electric motor speed control. The document discusses improving the performance of high-speed, high-resolution ADCs and DACs through open-loop circuitry and time-interleaving techniques.