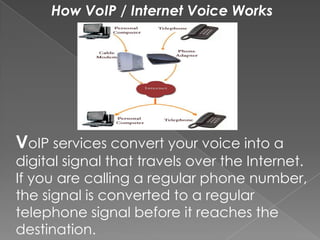
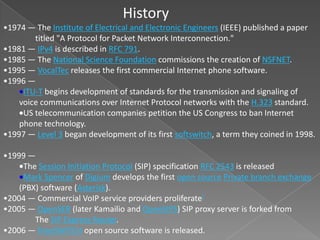
VoIP allows users to make phone calls using a broadband internet connection instead of a traditional phone line. It works by converting voice into digital signals that travel over the internet in packets. Depending on the service, users can call other VoIP users or regular phone numbers. There are several ways to connect to VoIP, including analog telephone adapters, dedicated VoIP phones, or softphones on computers. VoIP offers benefits like lower costs compared to traditional phone service and additional features included free of charge. However, emergency calling can be more difficult with VoIP depending on how location is determined.












![2004 — Commercial VoIP service providers proliferate]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kartikpowerpoit-100117074643-phpapp02/85/Kartik-Powerpoit-16-320.jpg)