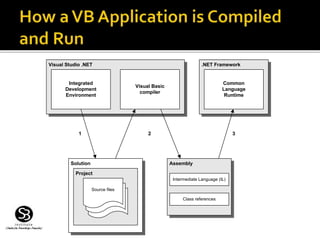
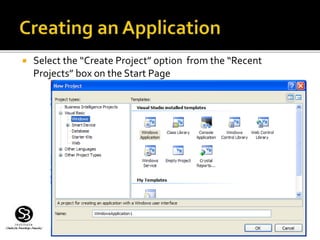
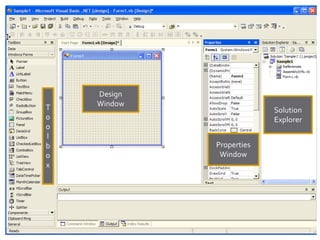
The document describes Visual Studio .NET and Visual Basic .NET. It explains that Visual Studio .NET is an integrated development environment that allows programming applications using multiple .NET languages like Visual Basic, C#, and C++. It provides tools for writing code, debugging, and running applications. Visual Basic .NET is an object-oriented programming language used to create Windows applications with graphical user interfaces. The document provides step-by-step instructions for creating a simple Visual Basic .NET application with buttons and event handling code.