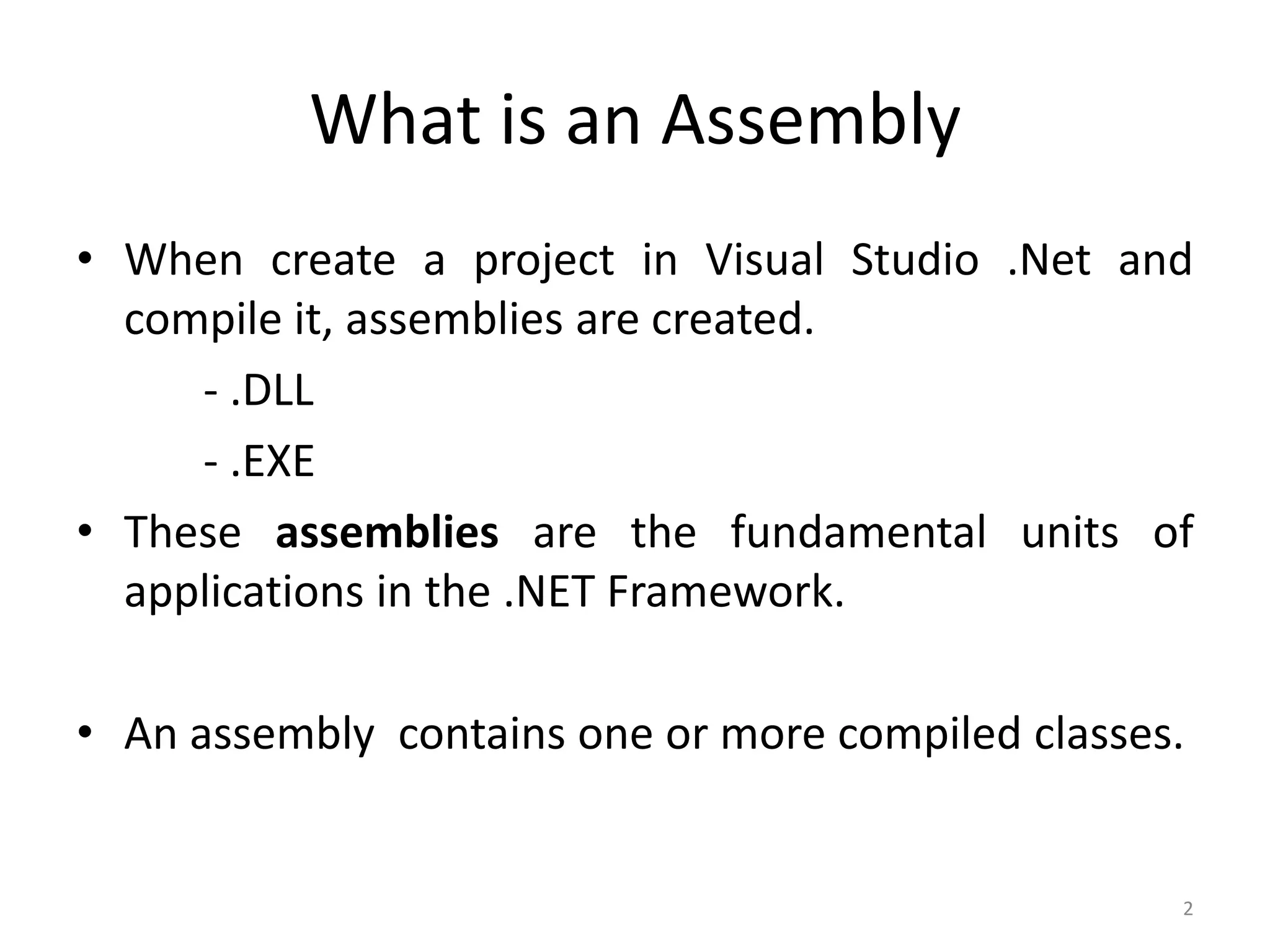
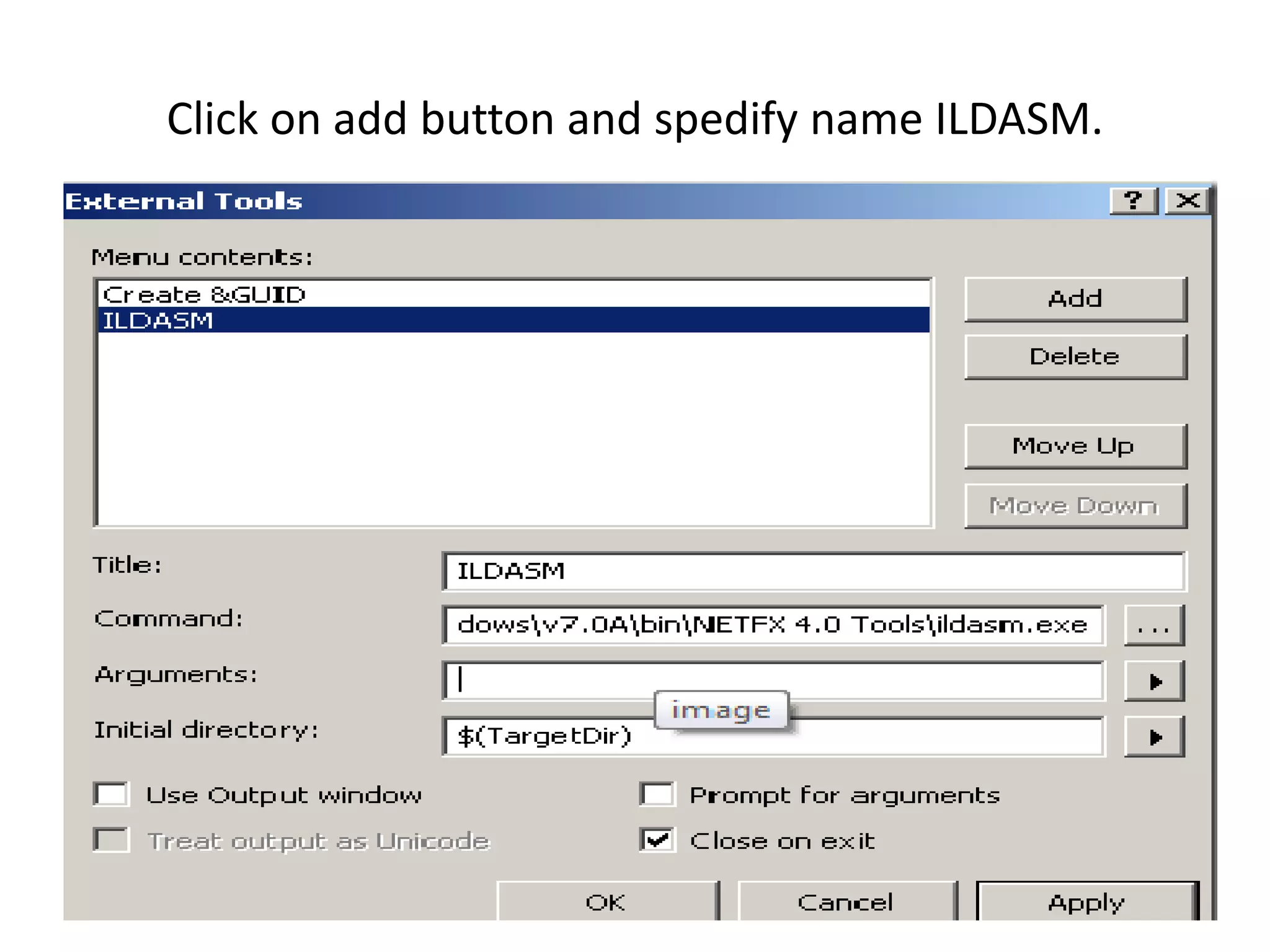
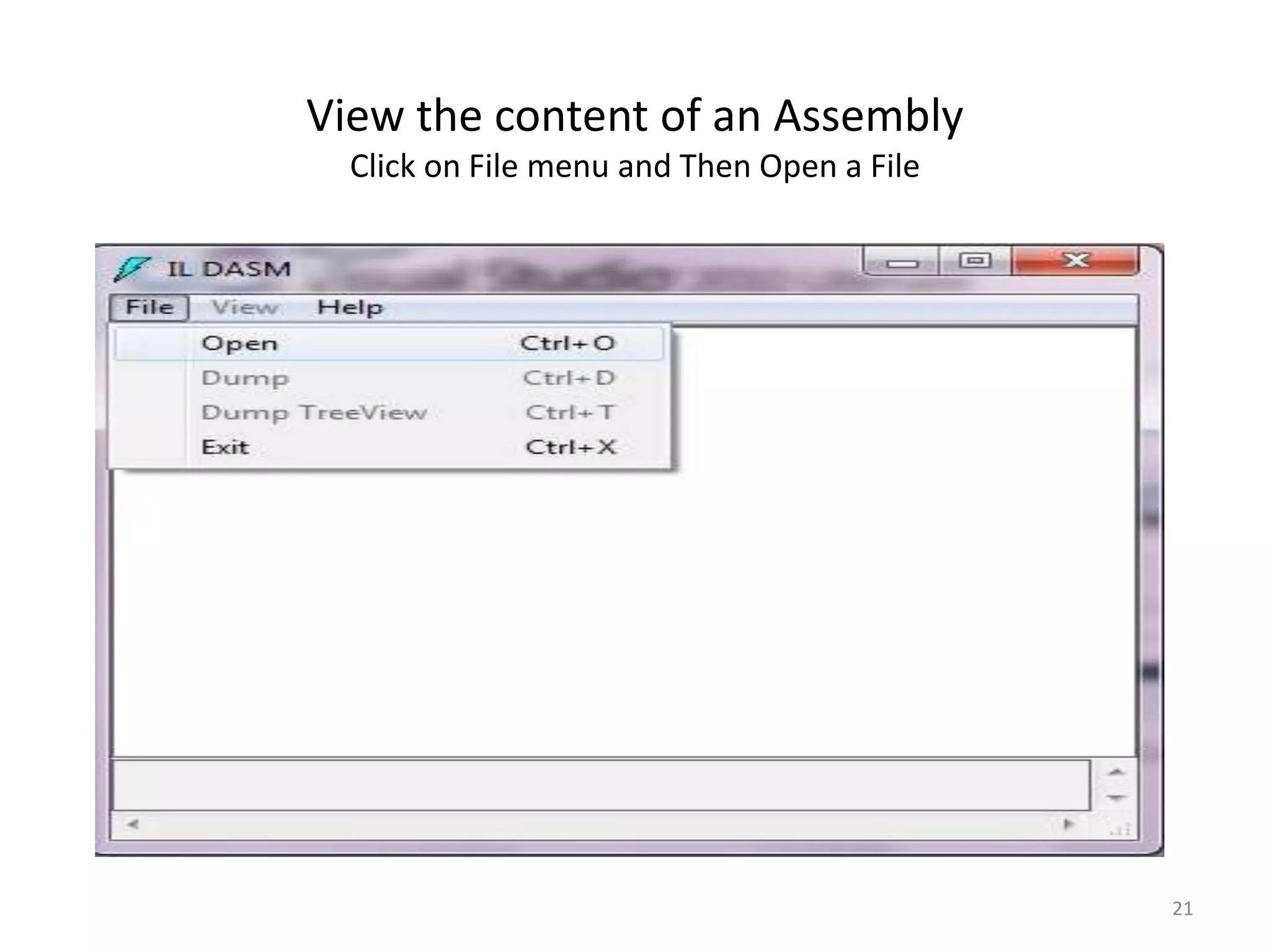
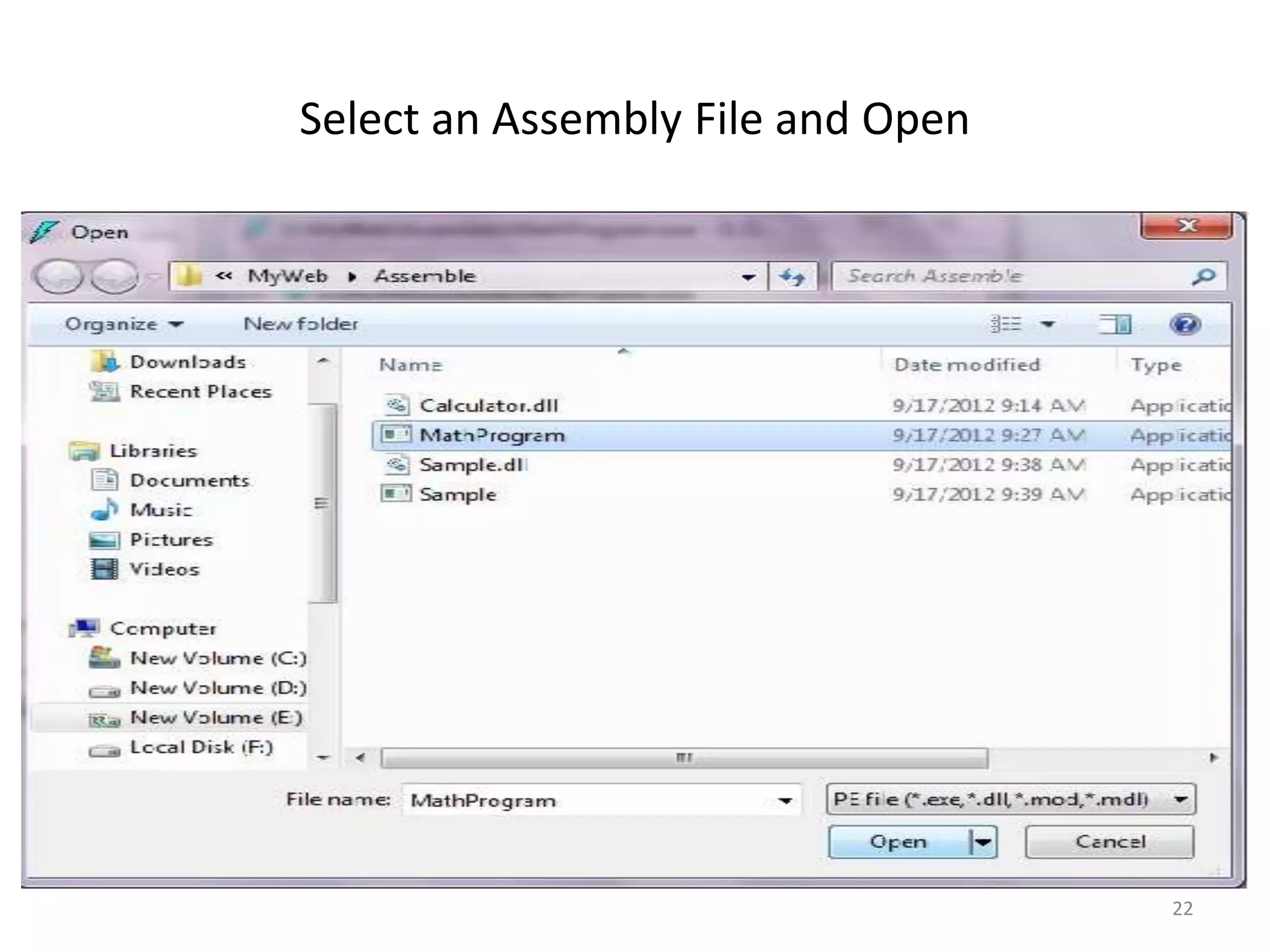
An assembly in .NET contains compiled code and metadata. It can be an EXE or DLL file. When code is compiled, it is translated to IL code and metadata is generated. The IL and metadata are bundled into the assembly file. Assemblies can be private, used by a single app, or shared, used by multiple apps. Shared assemblies are stored in the global assembly cache so they only need to be deployed once. The ILDASM tool allows examining the contents of an assembly.