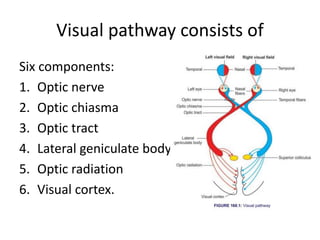
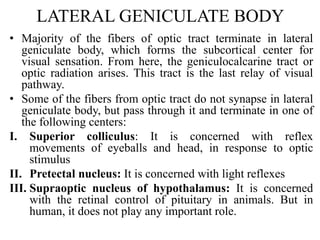
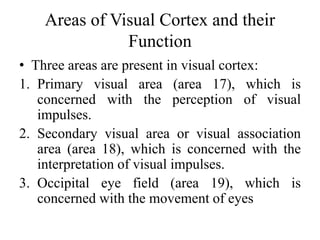
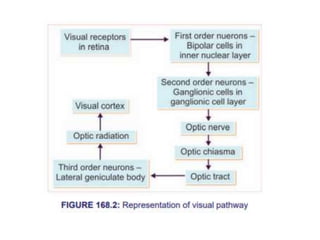
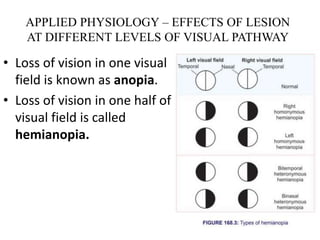
The visual pathway consists of 6 components - optic nerve, optic chiasma, optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiation, and visual cortex. The optic nerve carries signals from the retina to the optic chiasma where nerve fibers cross. The optic tract then carries crossed and uncrossed fibers to the lateral geniculate body. From there, the optic radiation carries signals to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe. Lesions in different parts of the pathway cause different types of visual field defects, such as homonymous or heteronymous hemianopia.