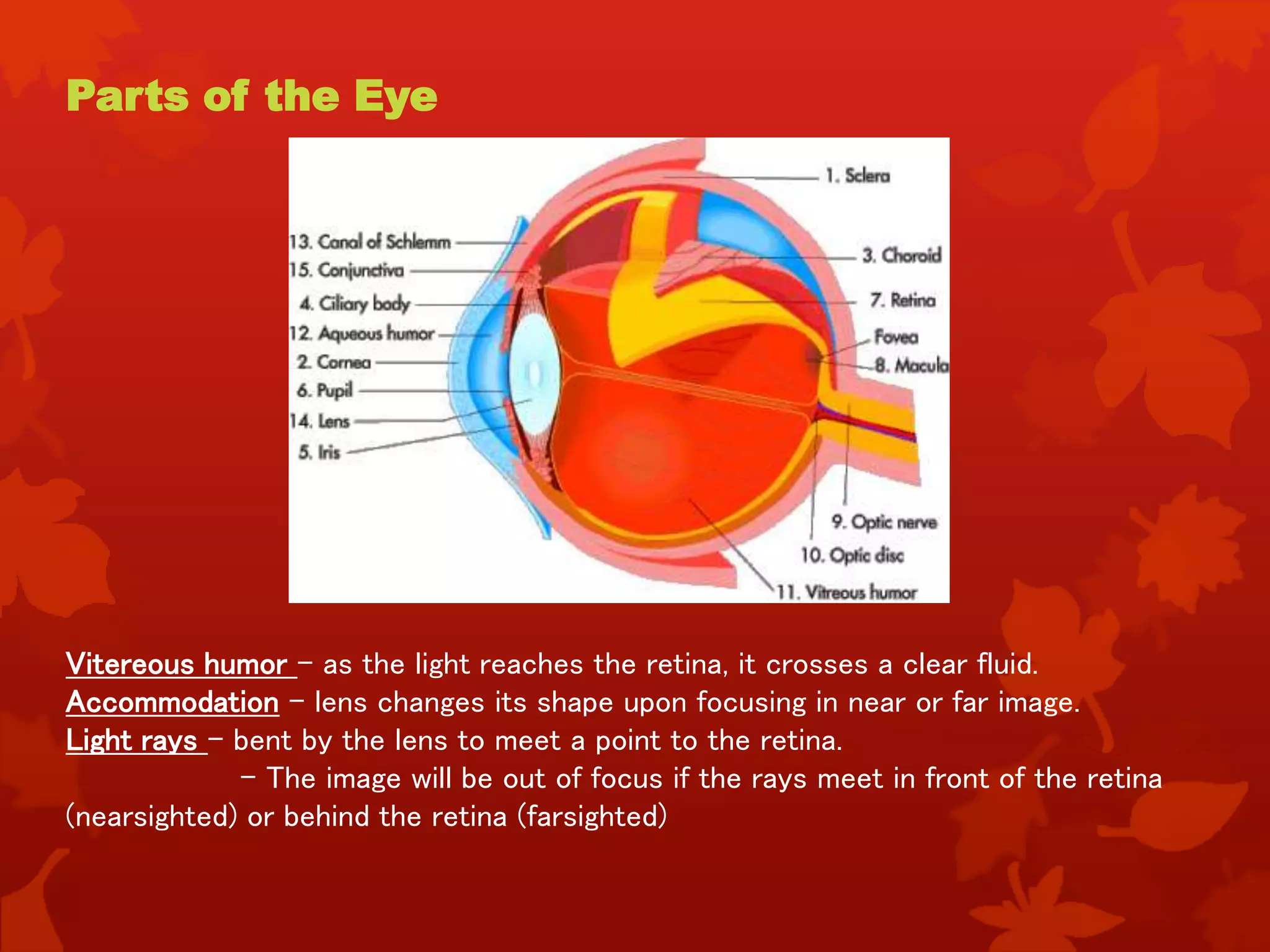
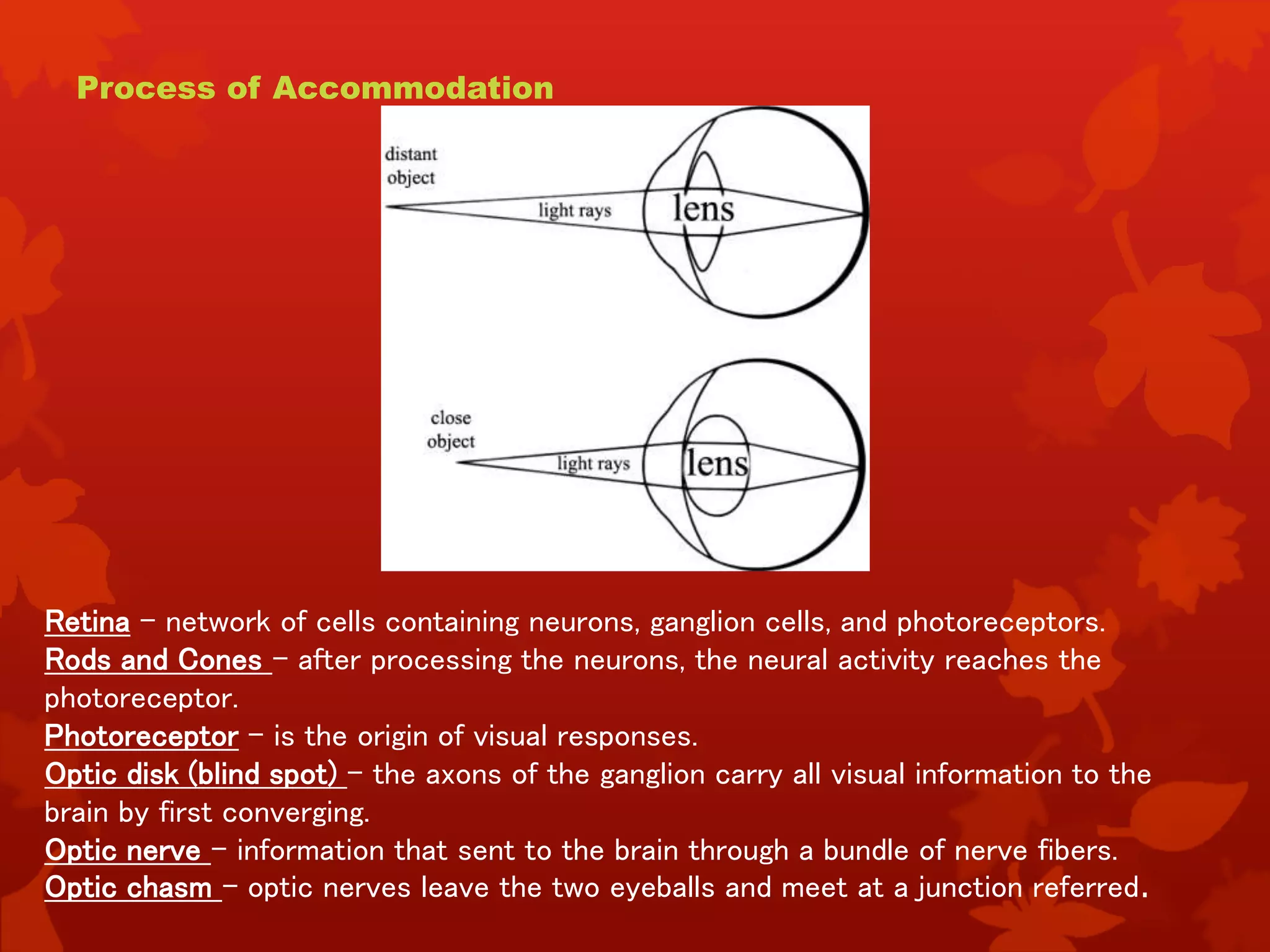
Light enters the eye and passes through the cornea and lens, which focus the image onto the retina. The retina contains photoreceptor cells that convert the image into neural signals sent to the brain via the optic nerve. The pupil regulates the amount of light entering the eye by contracting or dilating. The eye is covered by three coats and contains aqueous humor and vitreous humor to maintain its shape and provide nutrients. Common visual defects result from faults in the eye's structure or optical mechanisms.