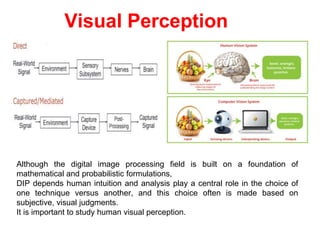
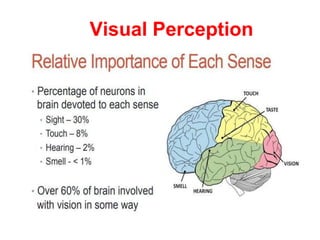
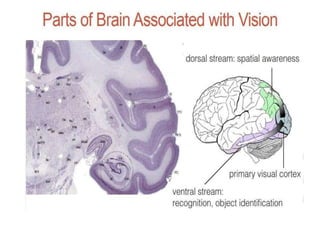
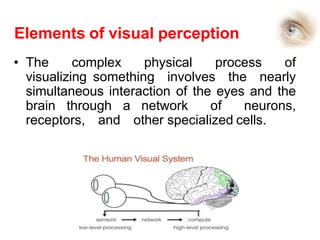
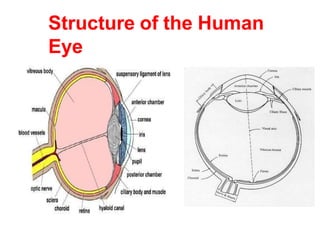
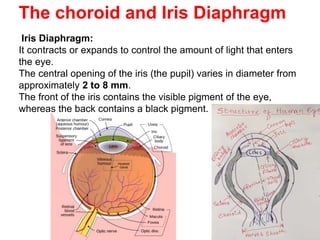
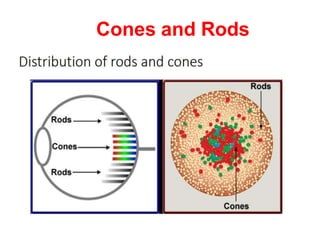
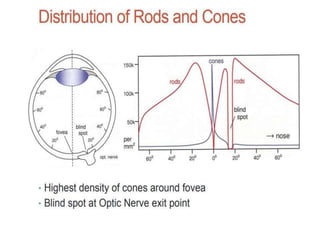
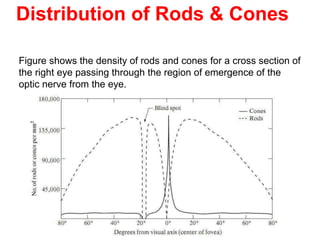
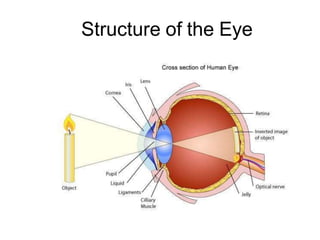
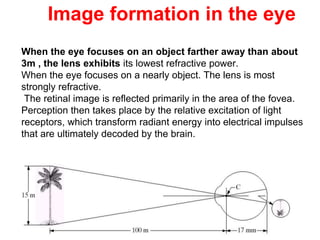
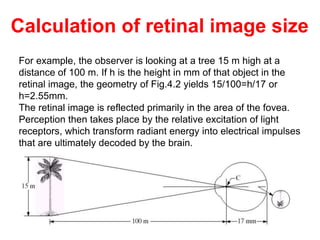
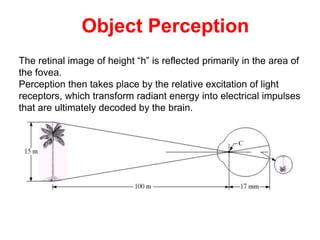
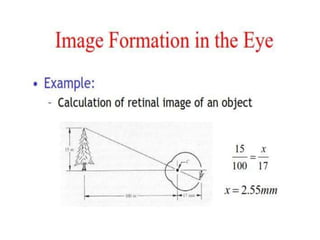
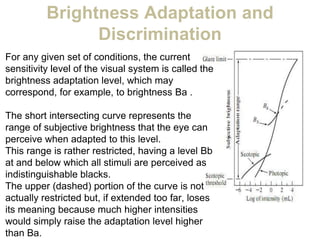
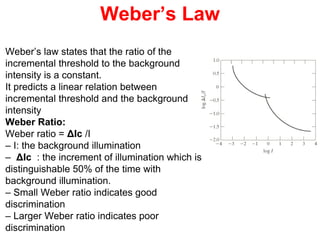
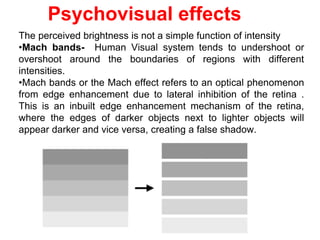
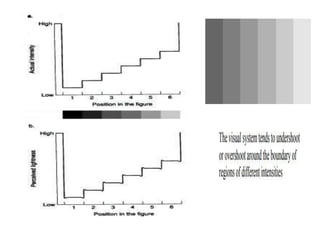
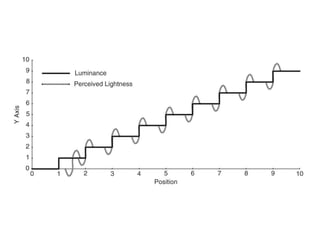
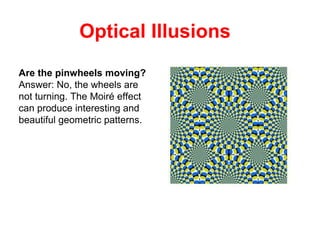
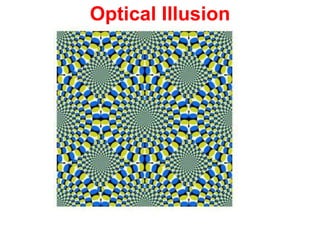
The human visual system allows us to see and understand our environment. It consists of the eye, which contains structures like the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and specialized photoreceptor cells called rods and cones. The eye transforms light into neural signals that travel to the brain for processing. Human visual perception relies on both rods for dim light vision and cones for bright light and color vision. The density and connections of rods and cones in the retina allow for varying levels of visual acuity and light sensitivity. The lens focuses images onto the retina, where photoreceptors convert the images into signals the brain can interpret as vision.