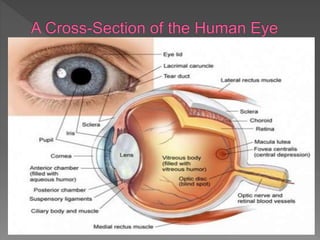
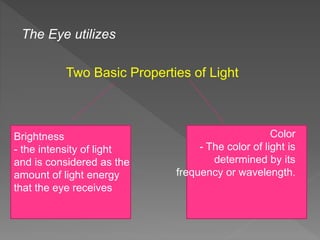
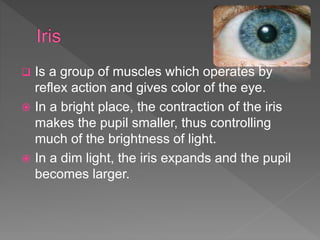
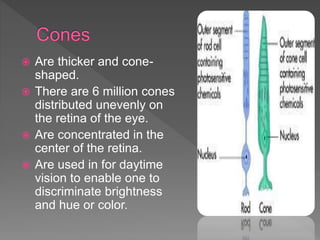
The eye is an amazing organ that allows us to see the outside world. It utilizes light waves, detecting their brightness and color. The eye contains structures like the iris, lens, retina and rods and cones that help it process light and send visual information to the brain. The retina in particular contains photoreceptive cells that are specialized for either low-light or daylight vision and color detection.