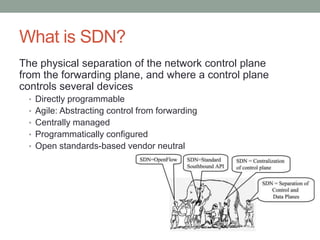
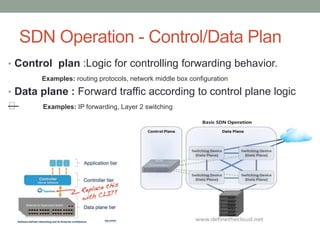
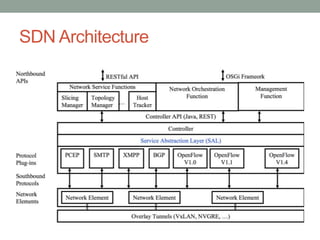
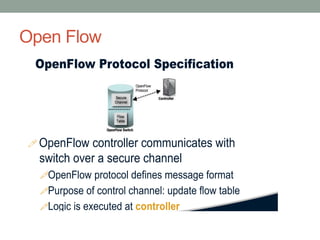
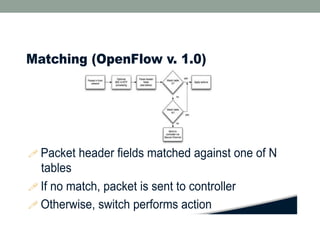
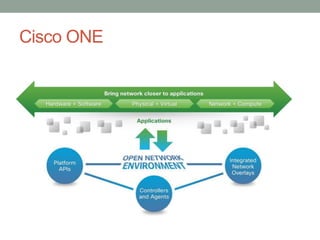
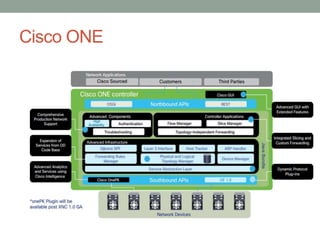
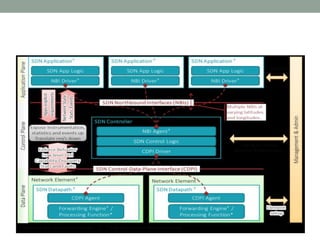
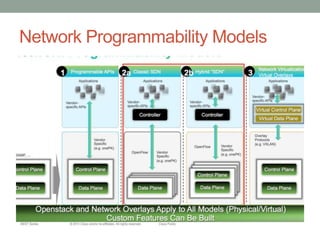
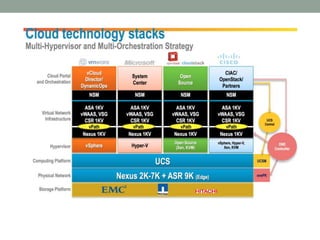
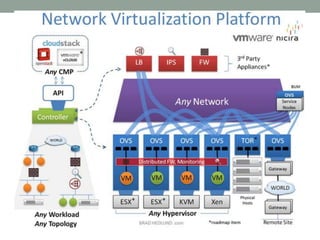
The document discusses Software Defined Networking (SDN), which separates the control plane from the data plane, allowing centralized management and programmability of network resources. It highlights use cases like virtualization, orchestration, automation, and performance optimization, and outlines different SDN architectures and controllers, including OpenFlow and Cisco technologies. The document also touches on network function virtualization and active networks, emphasizing the flexibility and scalability SDN offers.