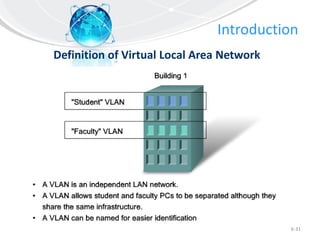
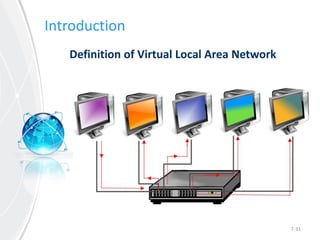
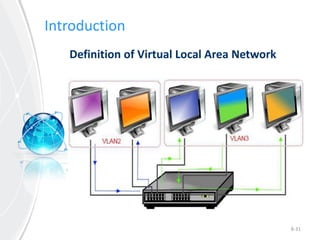
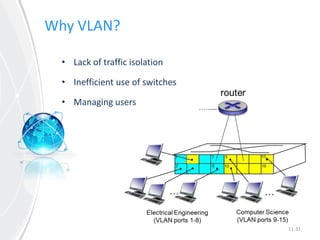
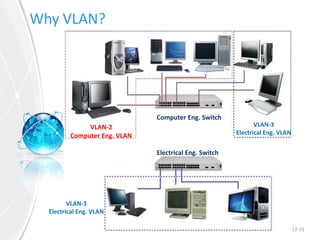
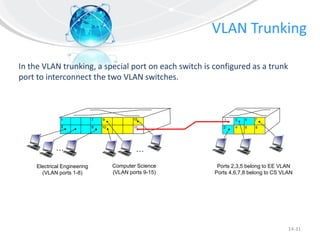
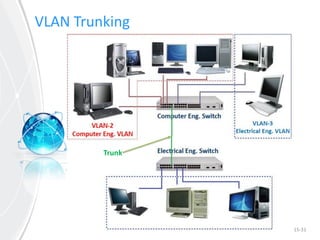
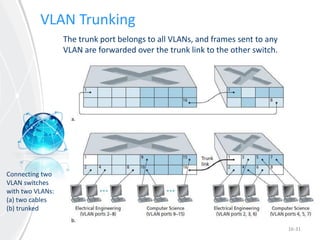
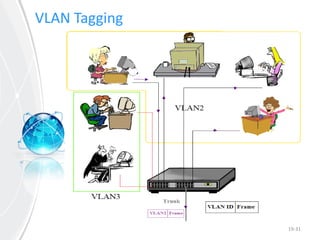
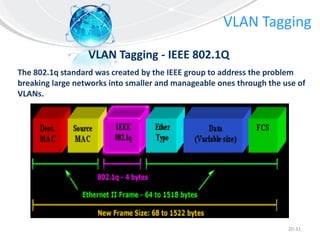
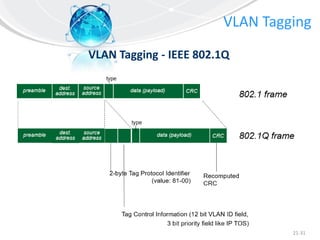
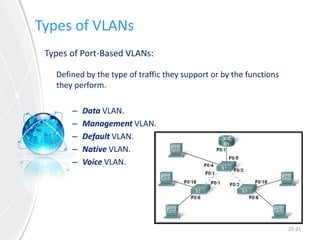
This document provides an overview of virtual local area networks (VLANs). It defines VLANs and discusses why they are used to logically segment physical networks. VLAN trunking is described as using a trunk port to interconnect VLAN switches. VLAN tagging is explained as a method to identify packets traversing trunk links by adding a tag to frames. Different types of VLANs are outlined such as static, dynamic, data, management, default and native. Finally, advantages like increased performance and disadvantages like management complexity are highlighted.

















![References
30-31
[1] James F. Kurose & Keith W. Ross, Computer Networking a t
T Top-Down Approach, Sixth edition
[2] Andrew S. Tanenbaum, Computer Networks, Fourth edition
[3] www.cyberlone.com
[4] www.firewall.cx
[5] www.wikipedia.org
[6] www.blog.router-switch.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vlan-180520092435/85/Virtual-Local-Area-Network-VLAN-30-320.jpg)
