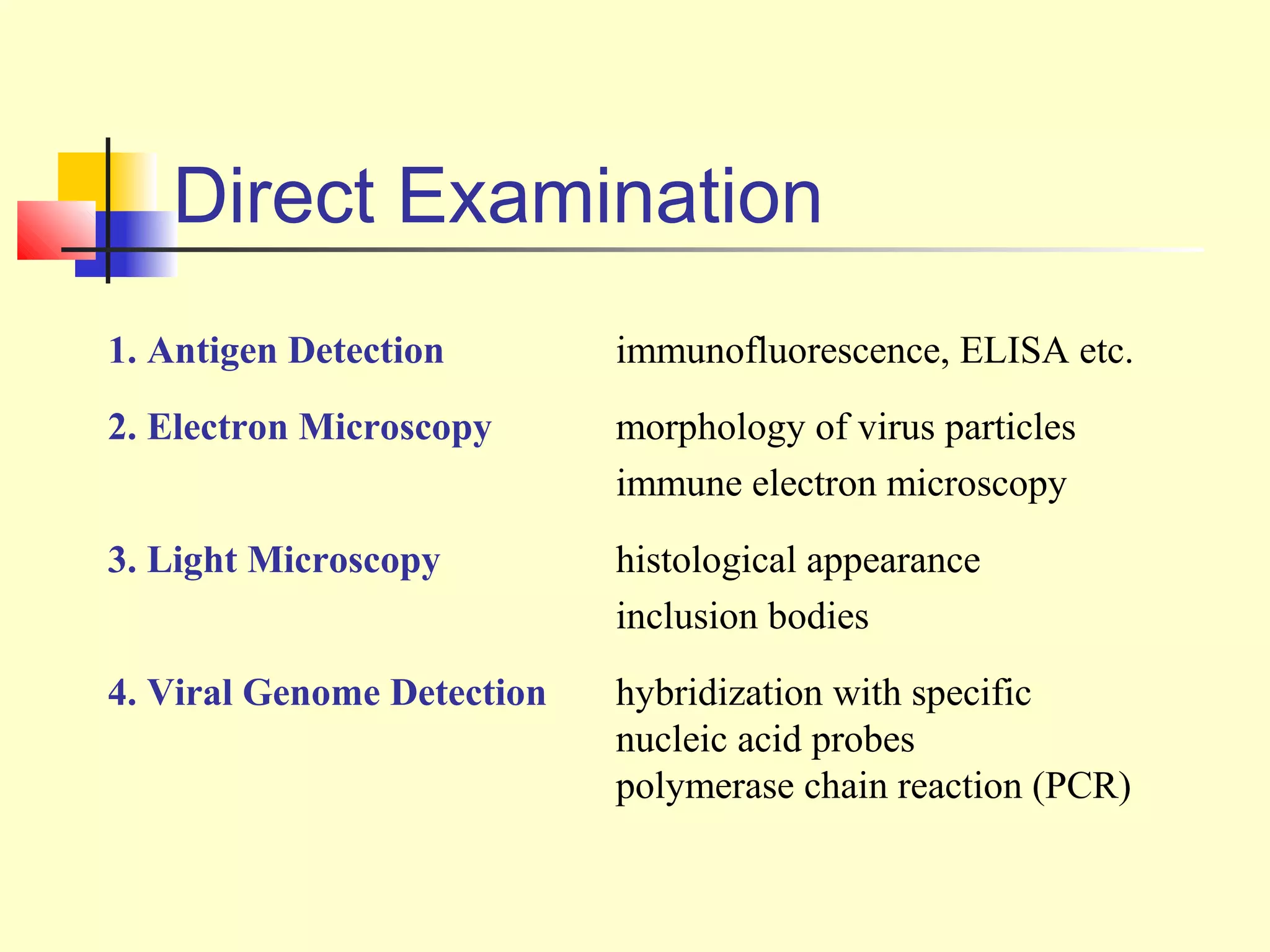
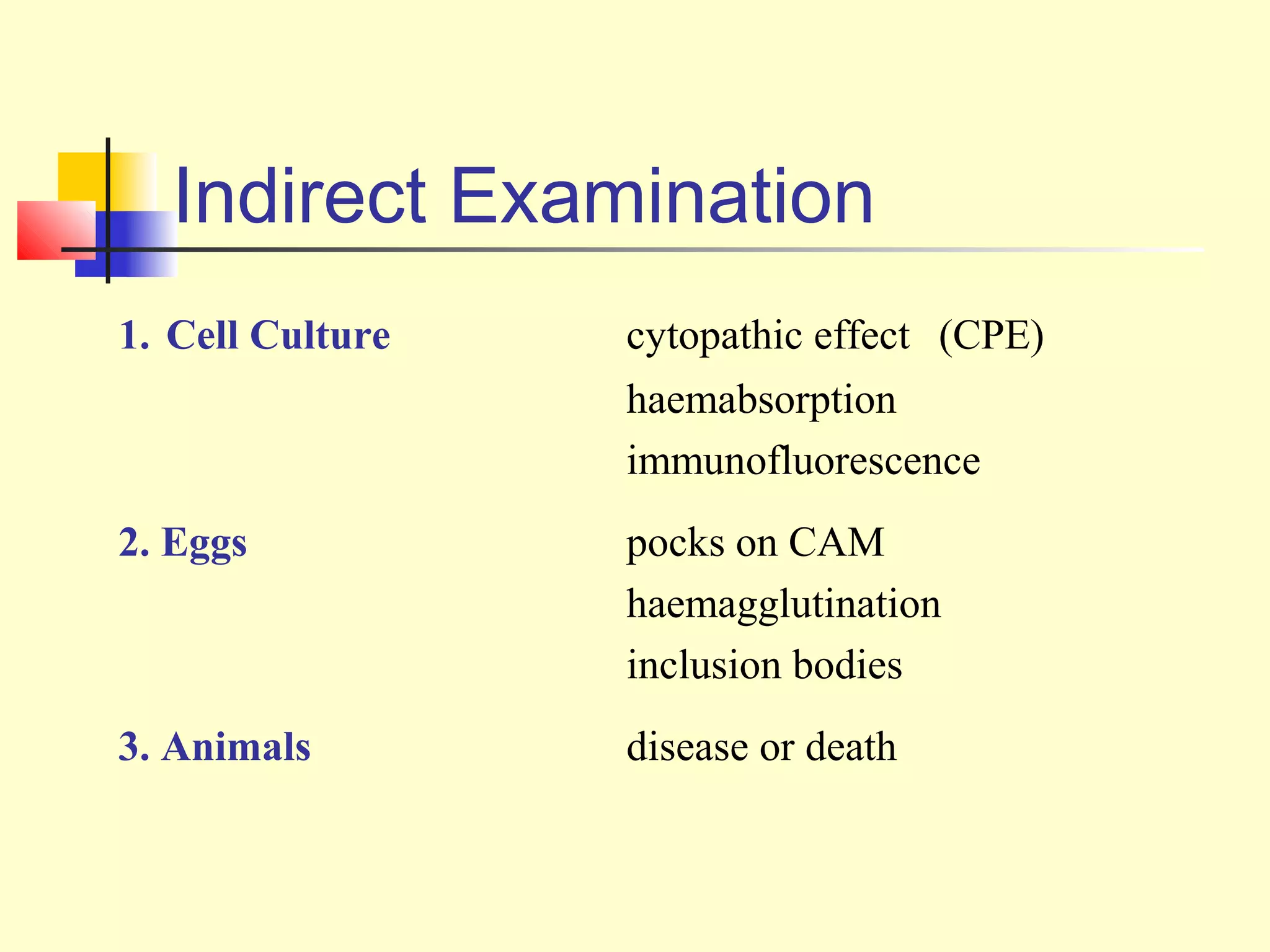
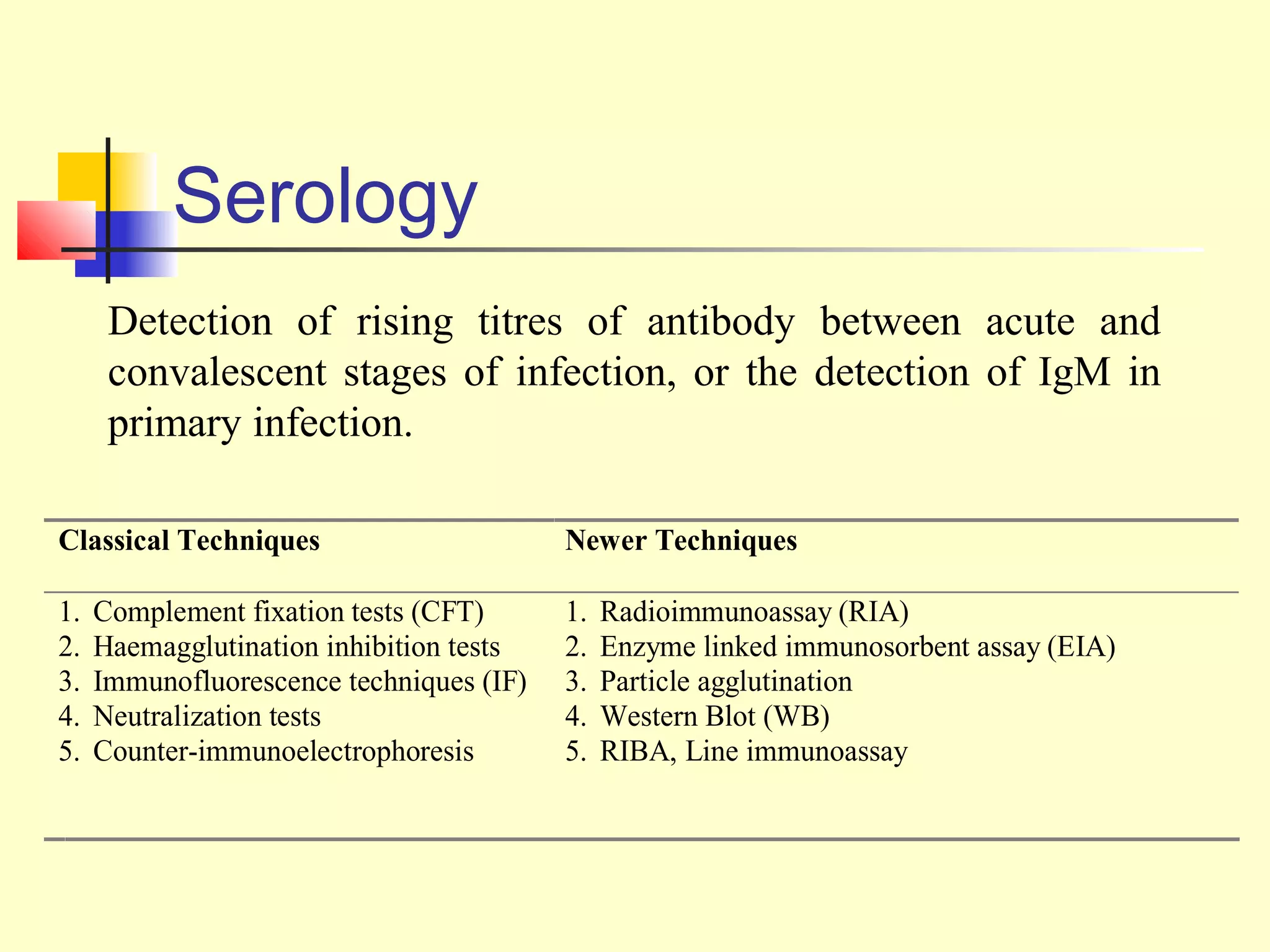
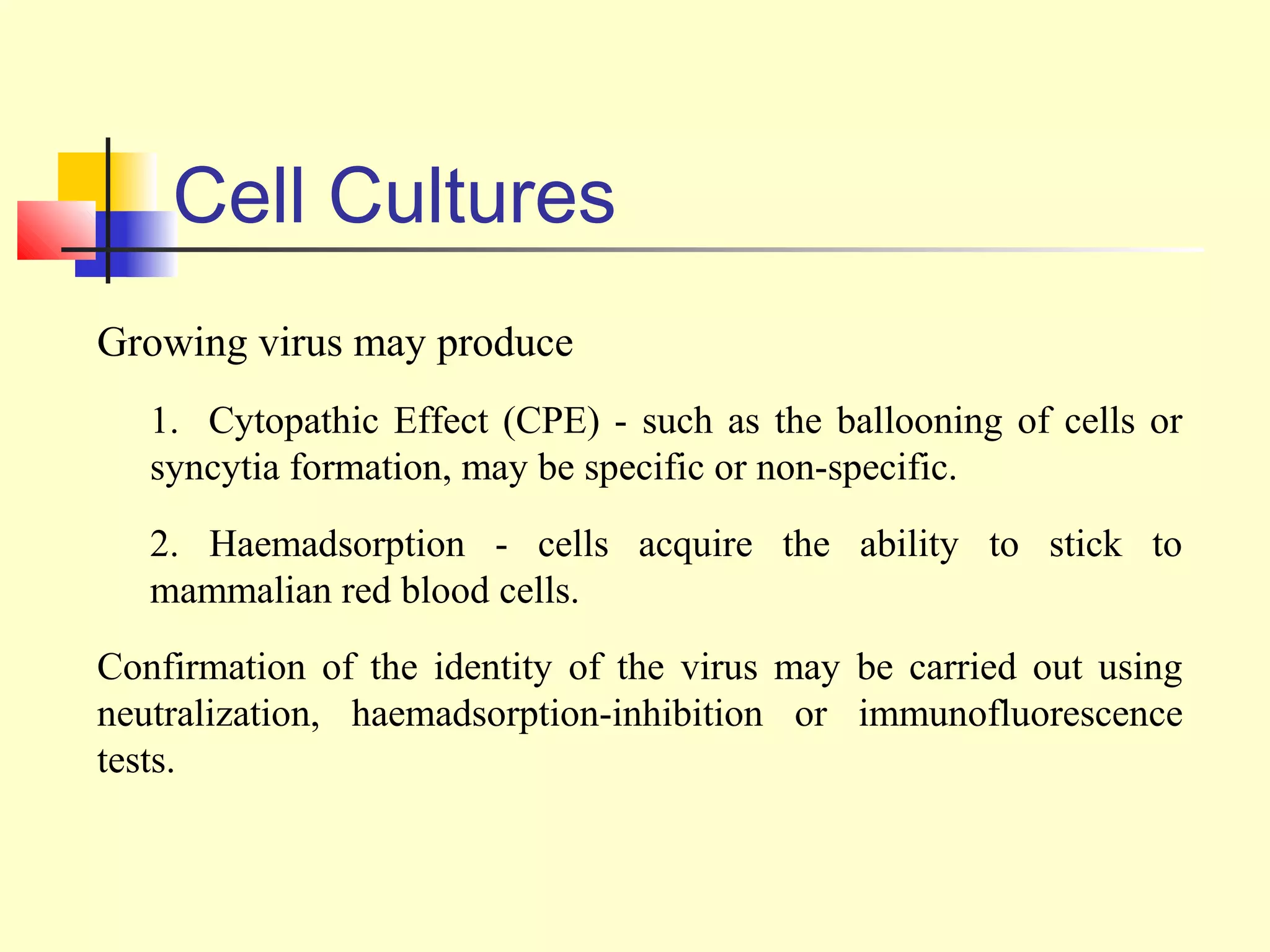
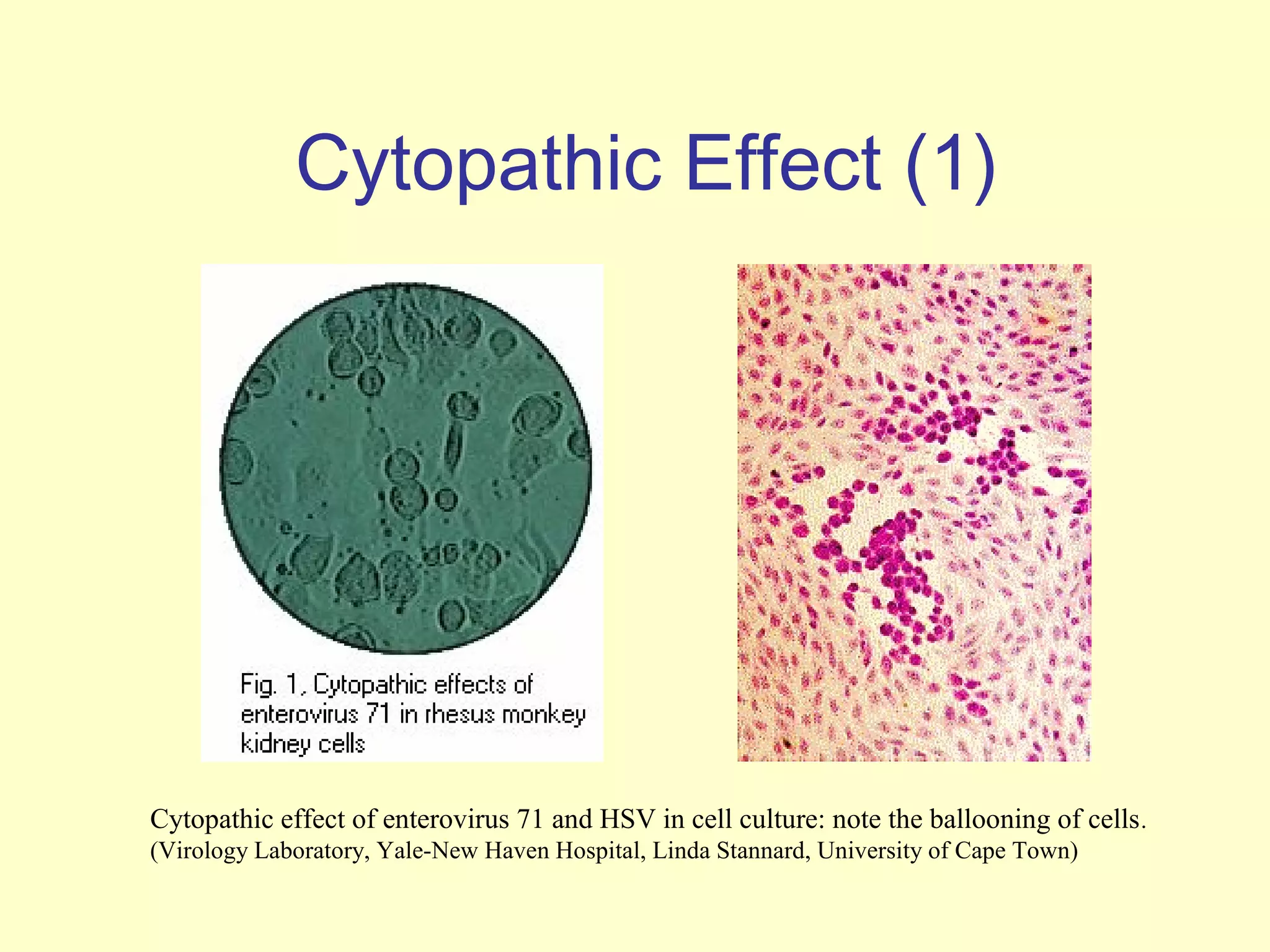
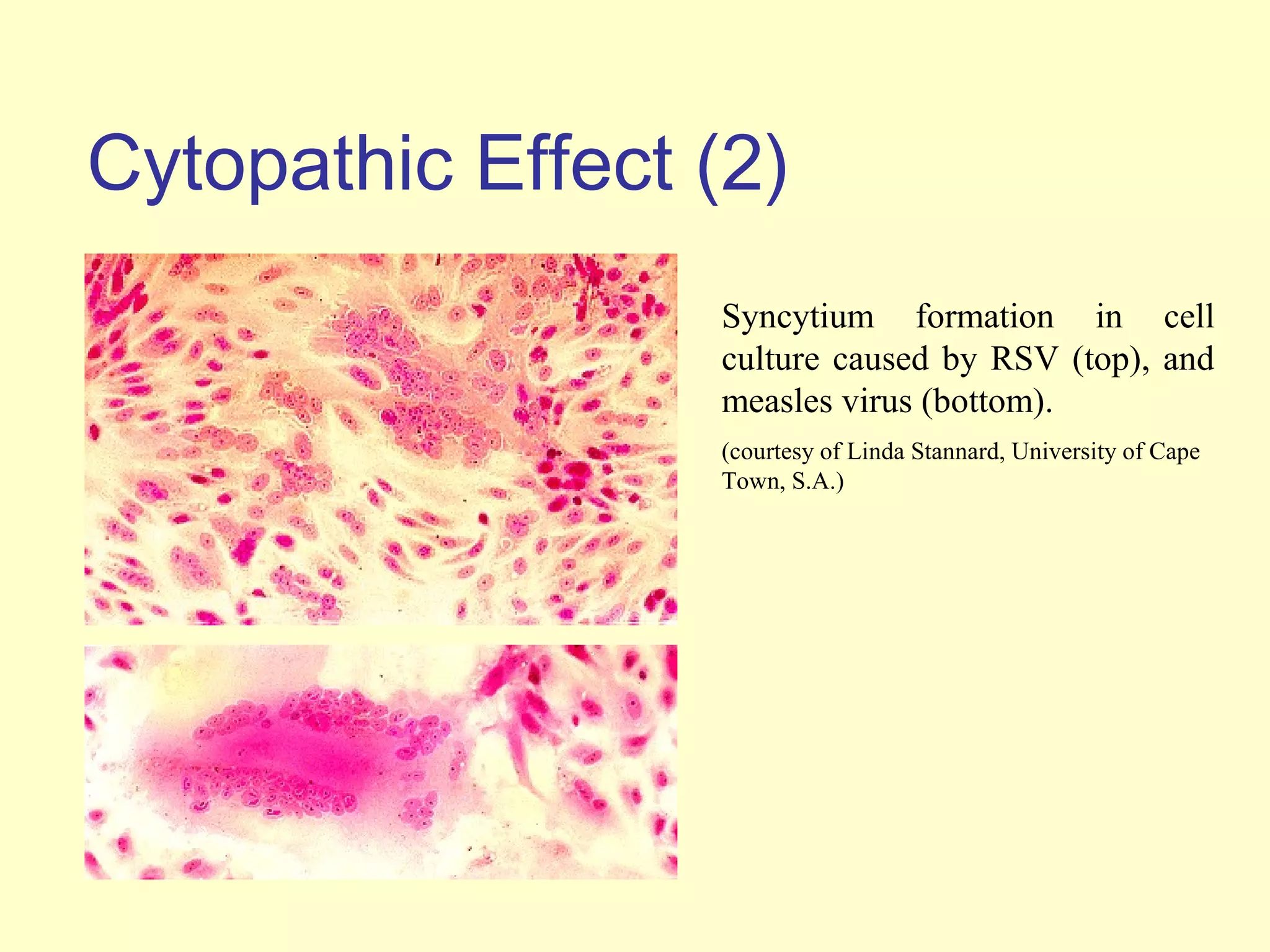
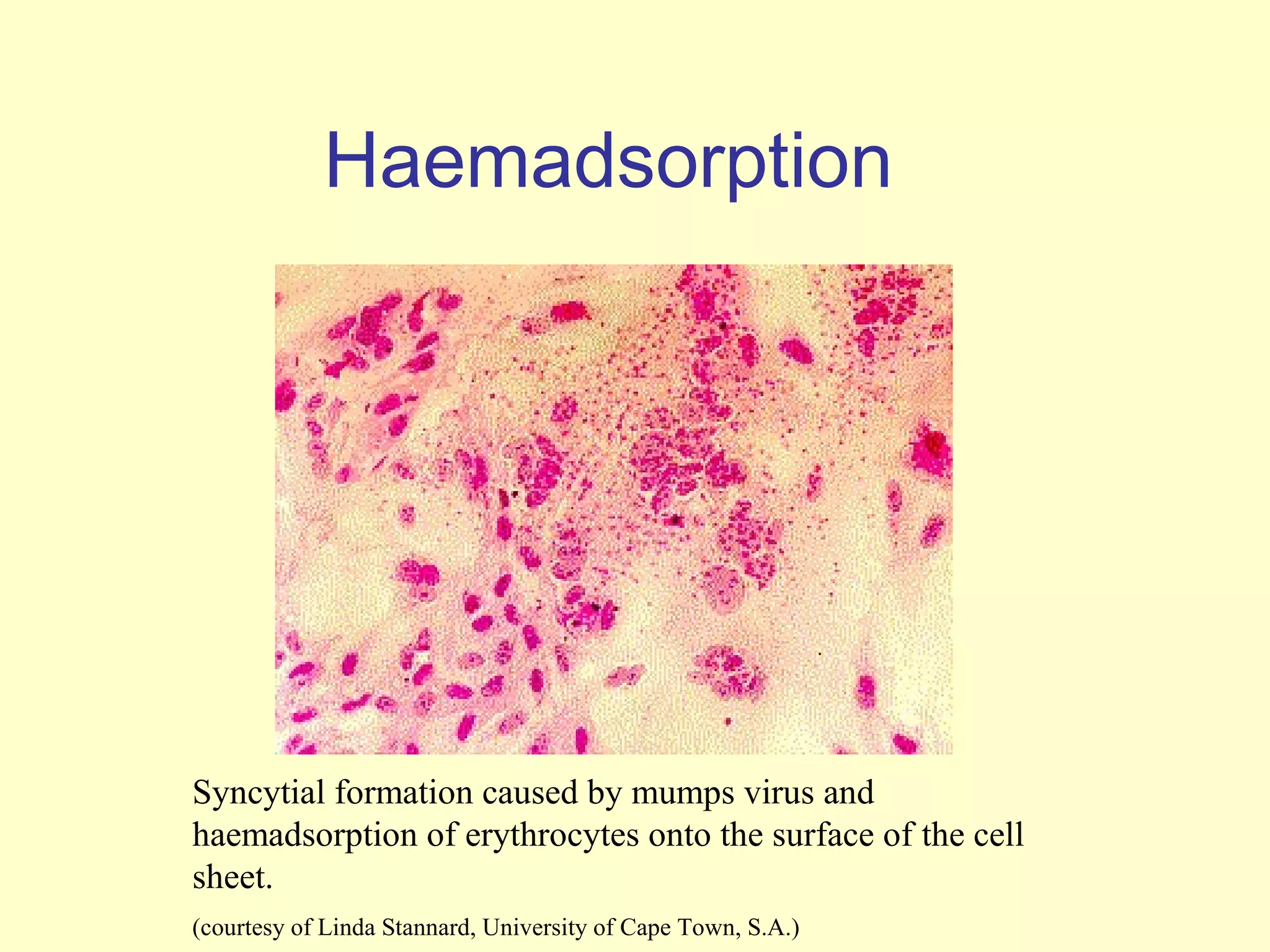
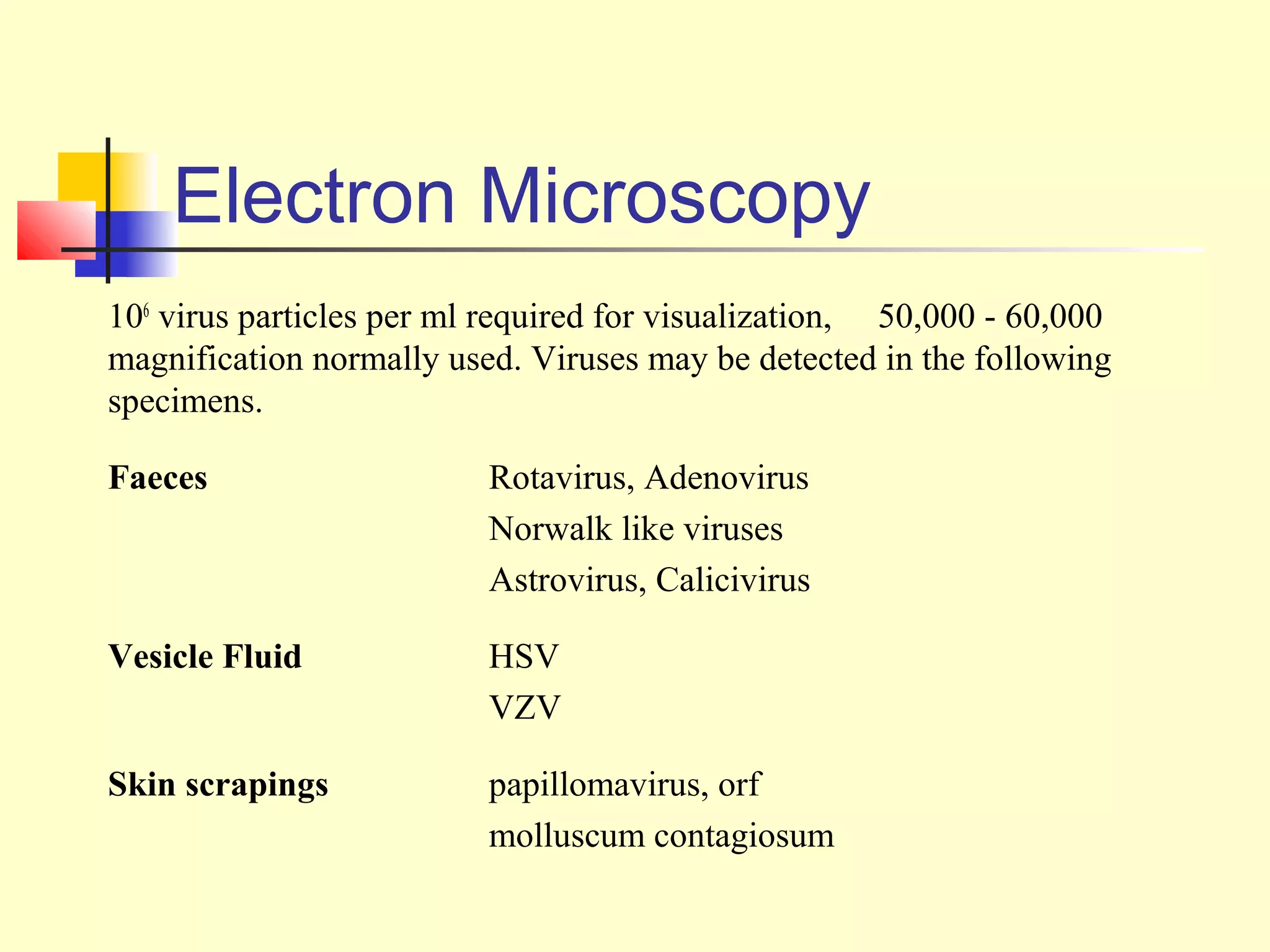
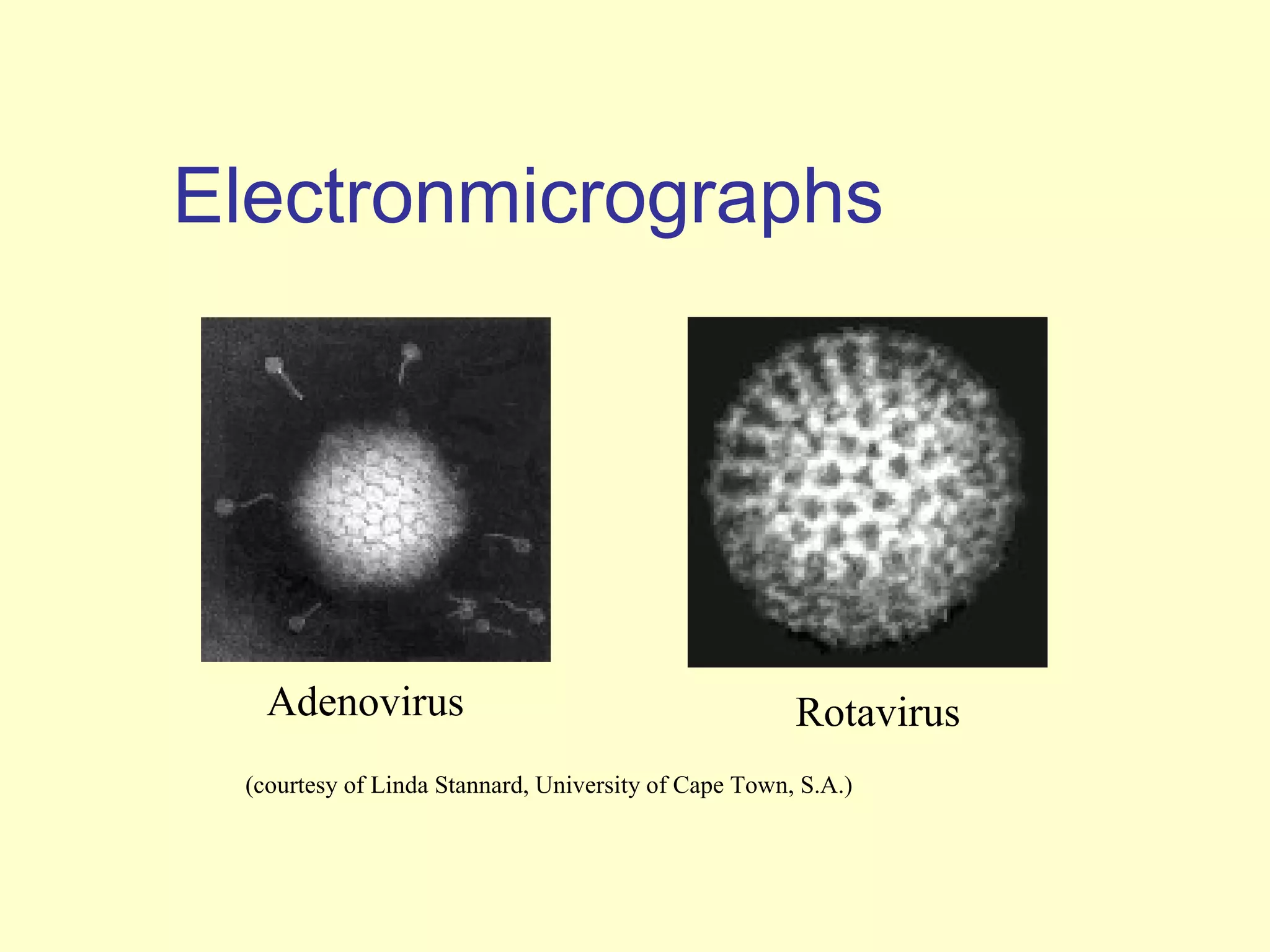
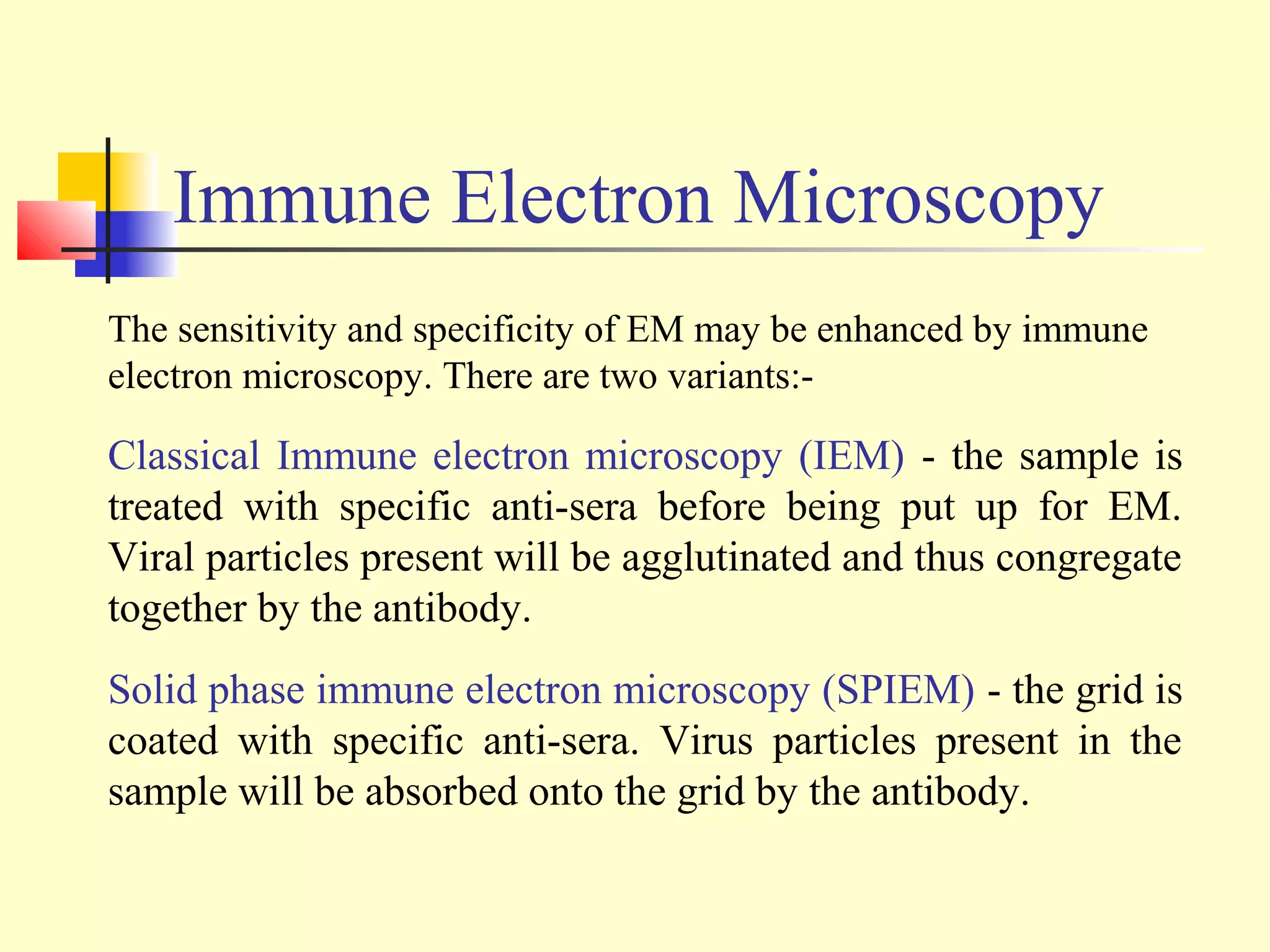
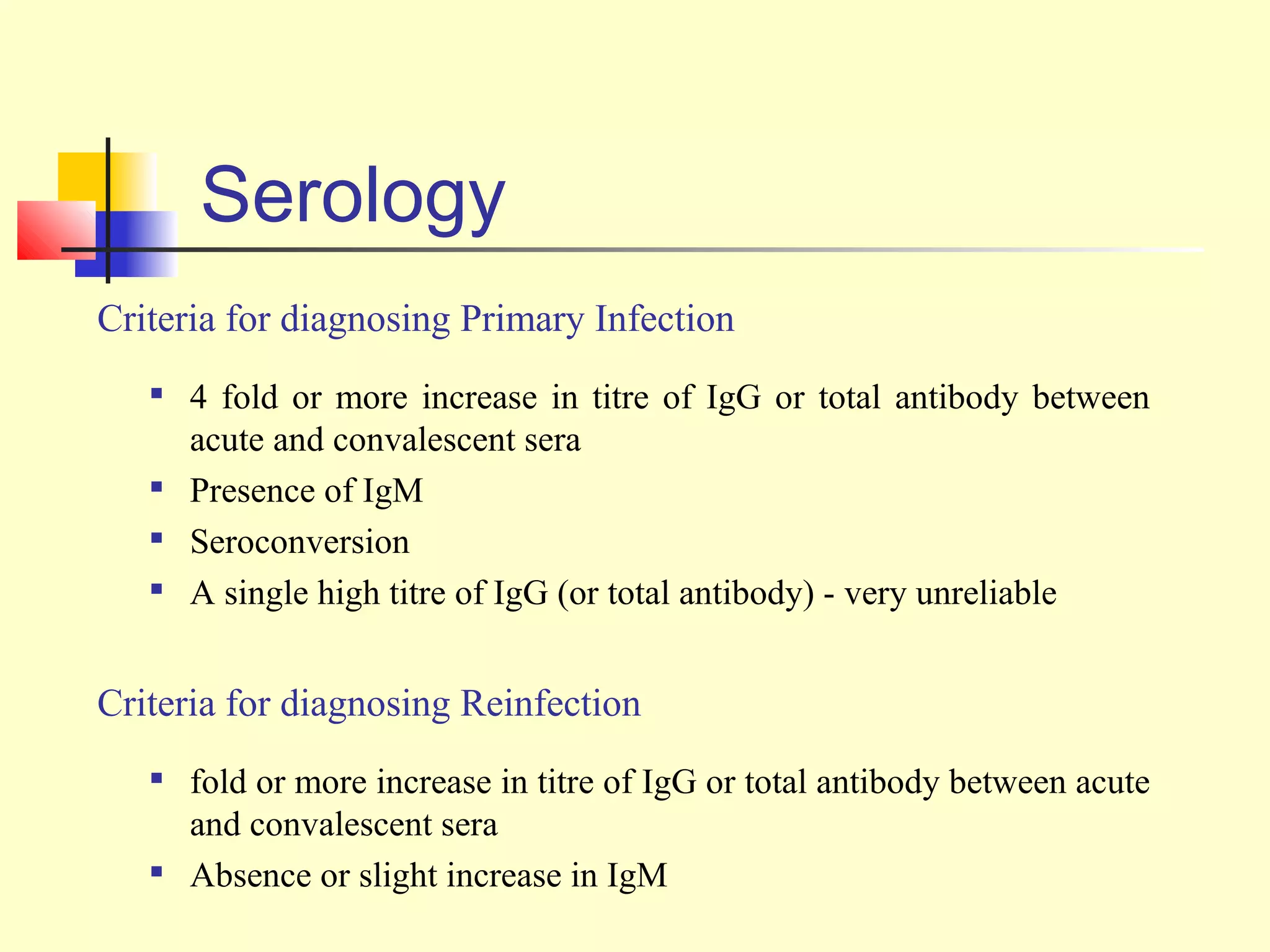
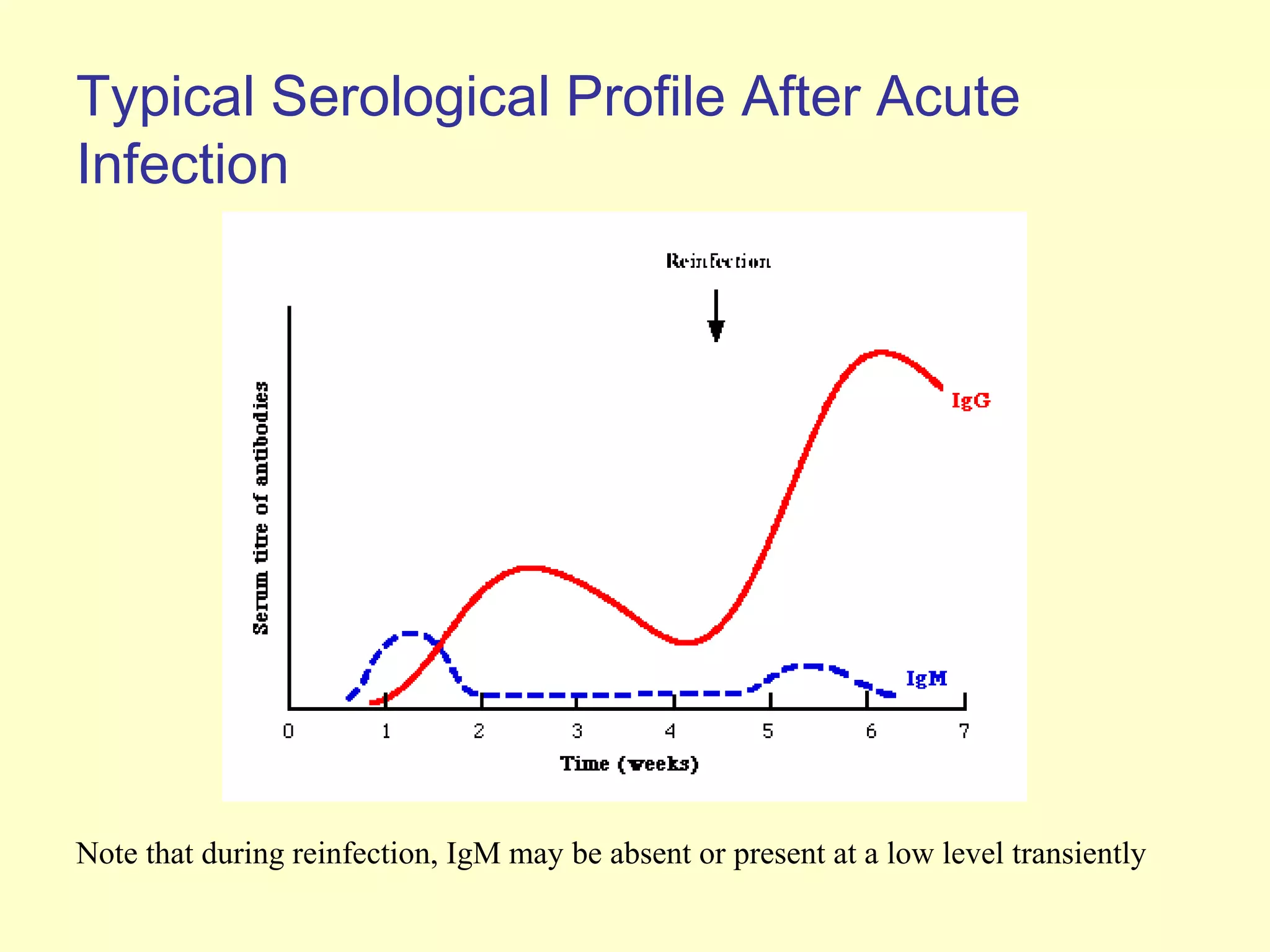
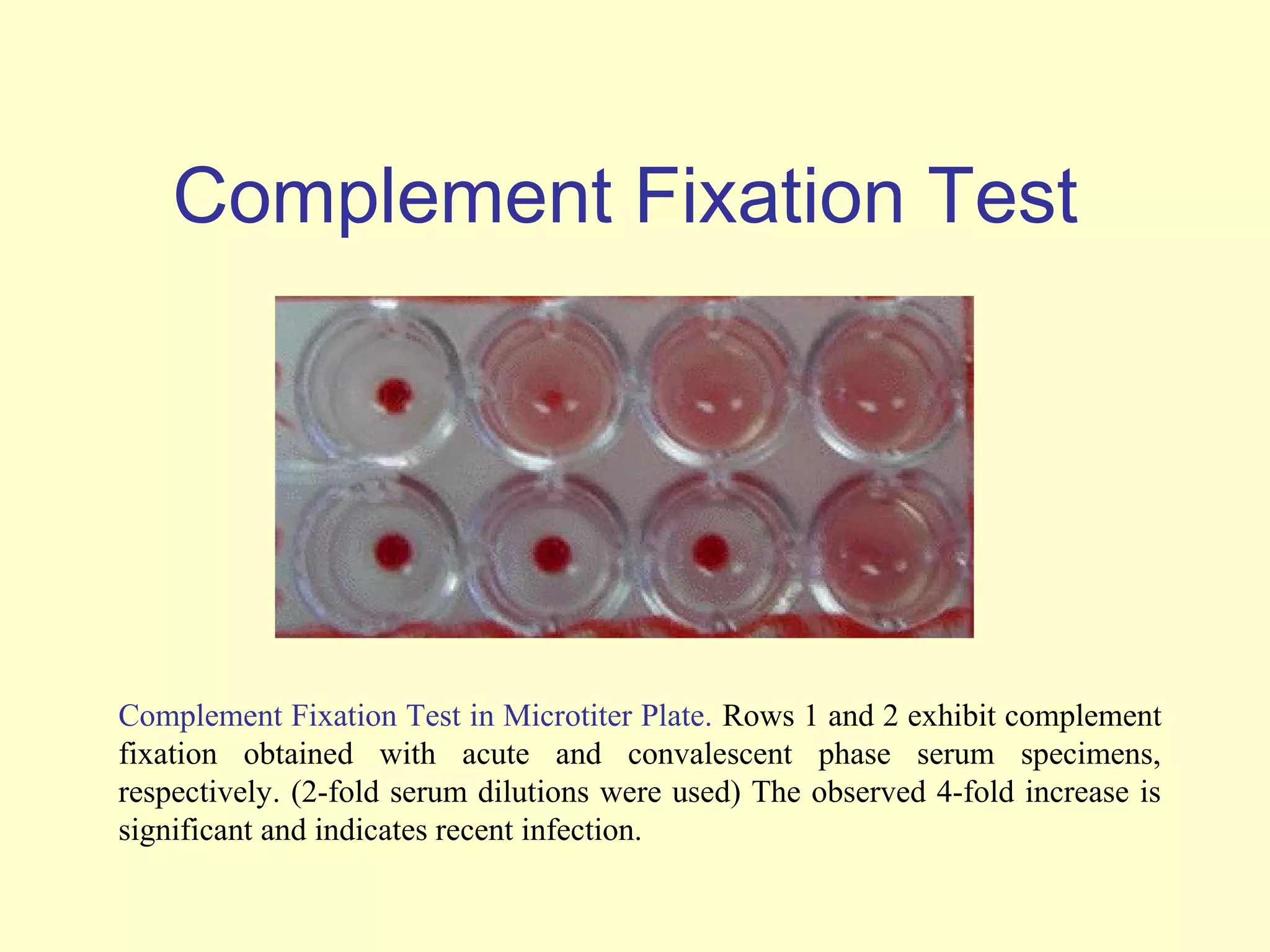
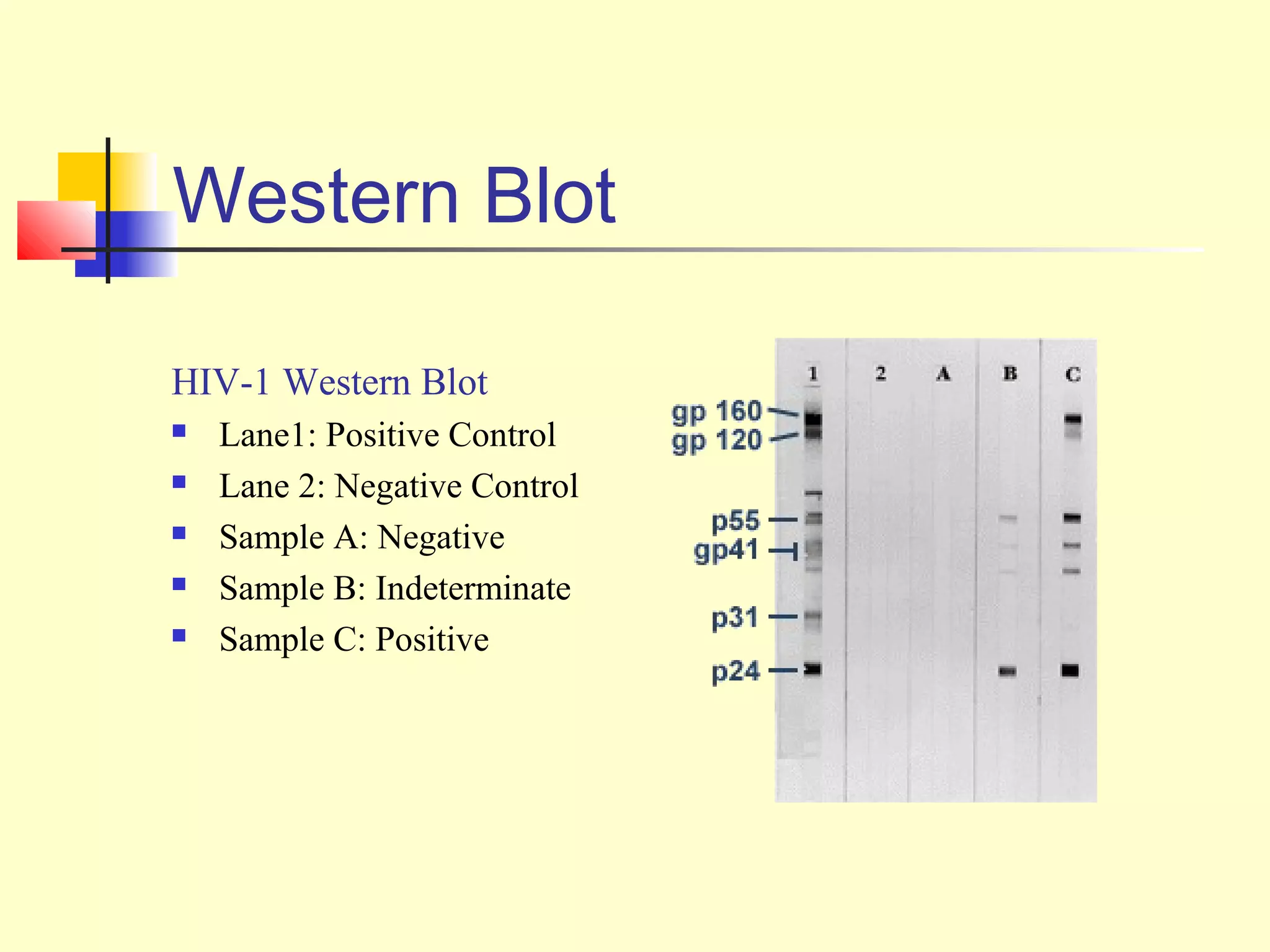
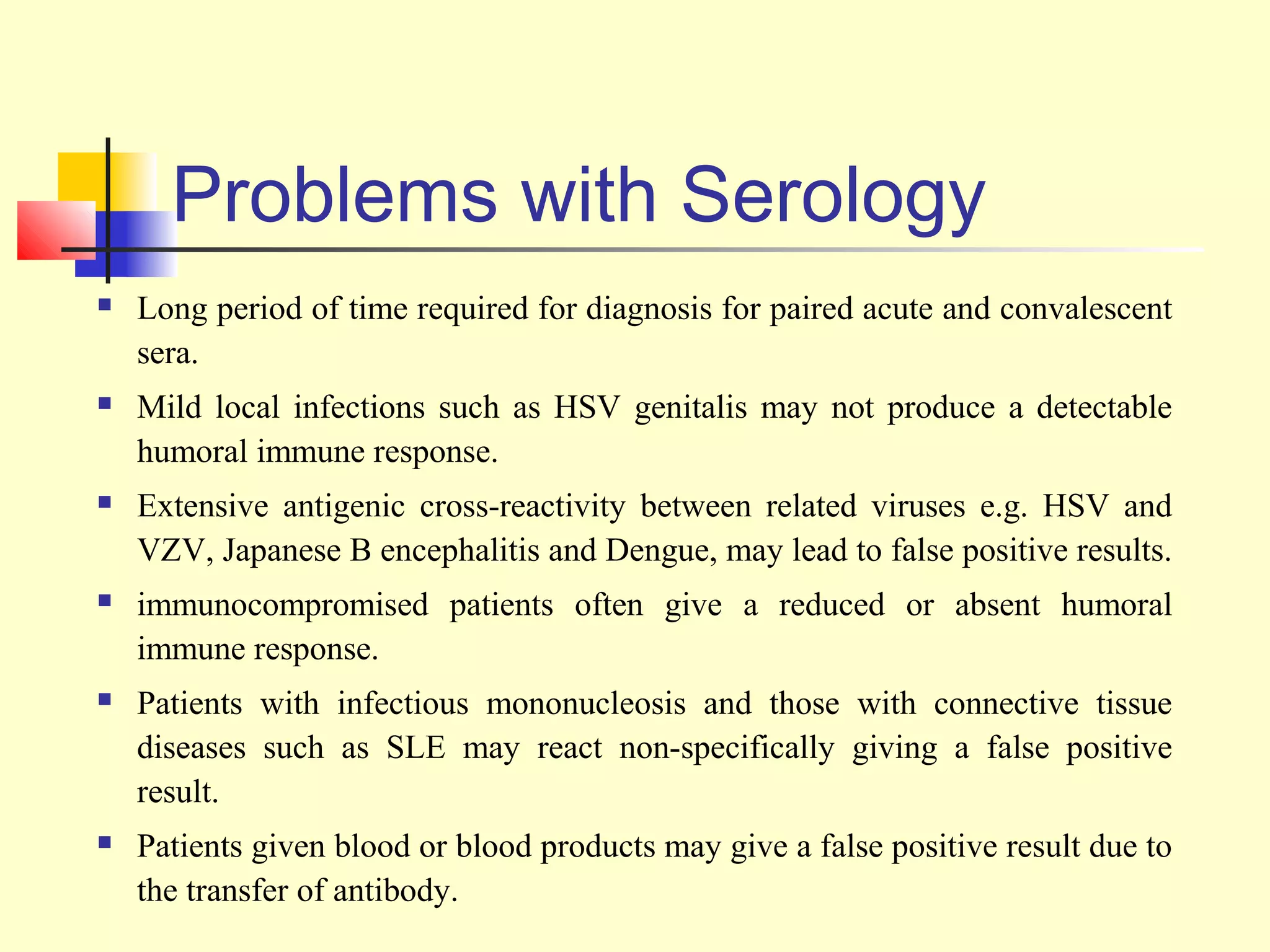
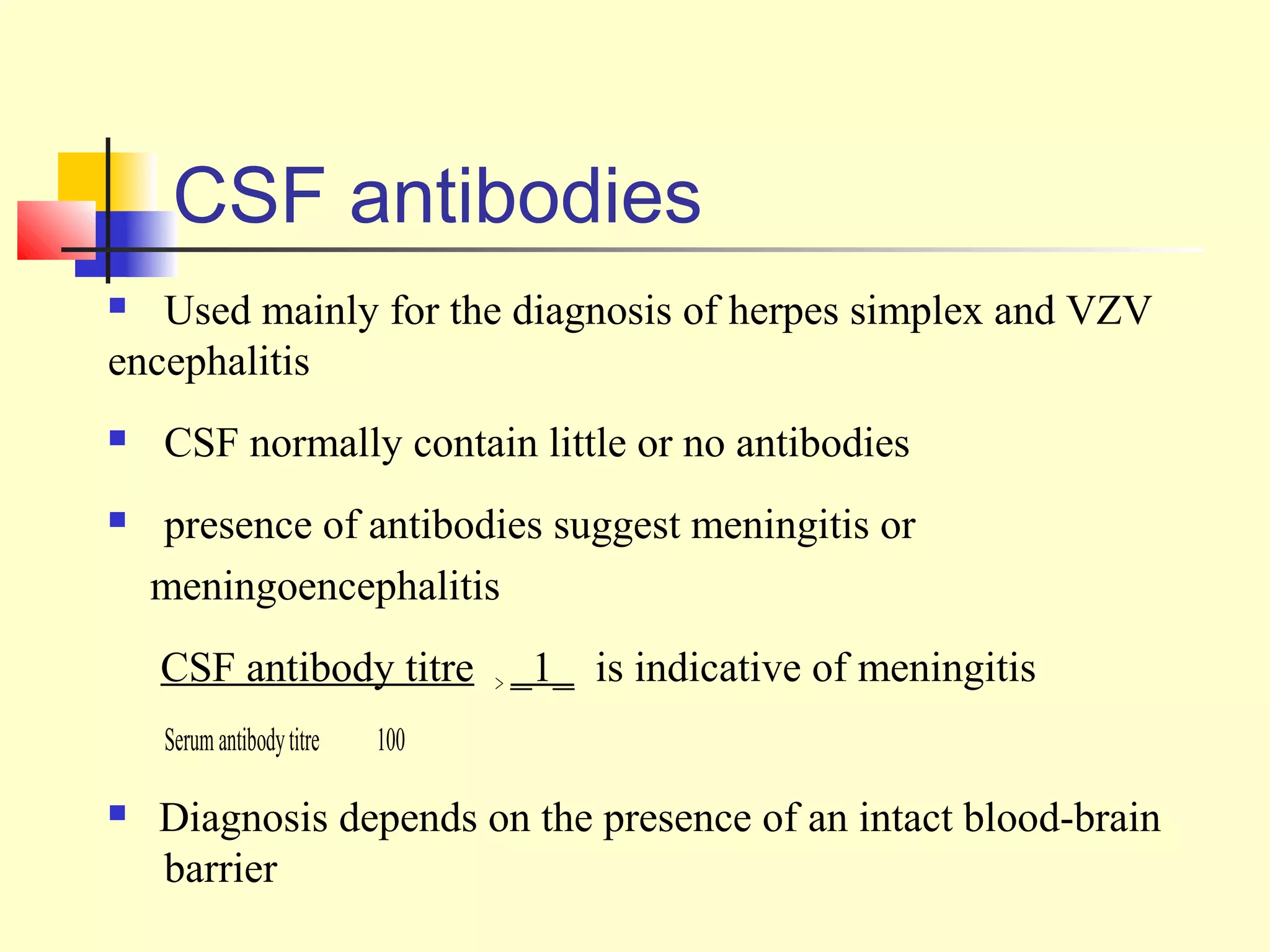
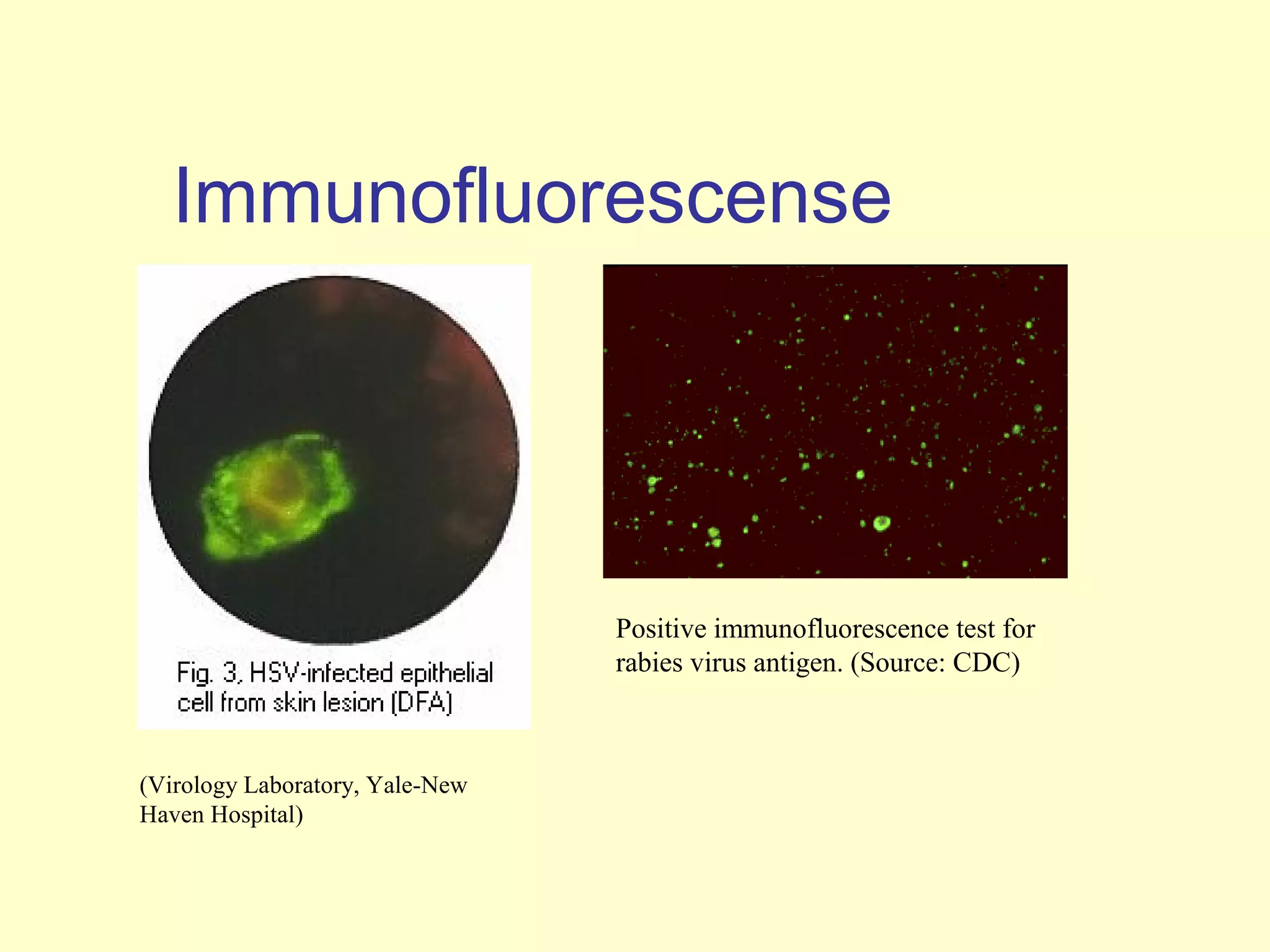
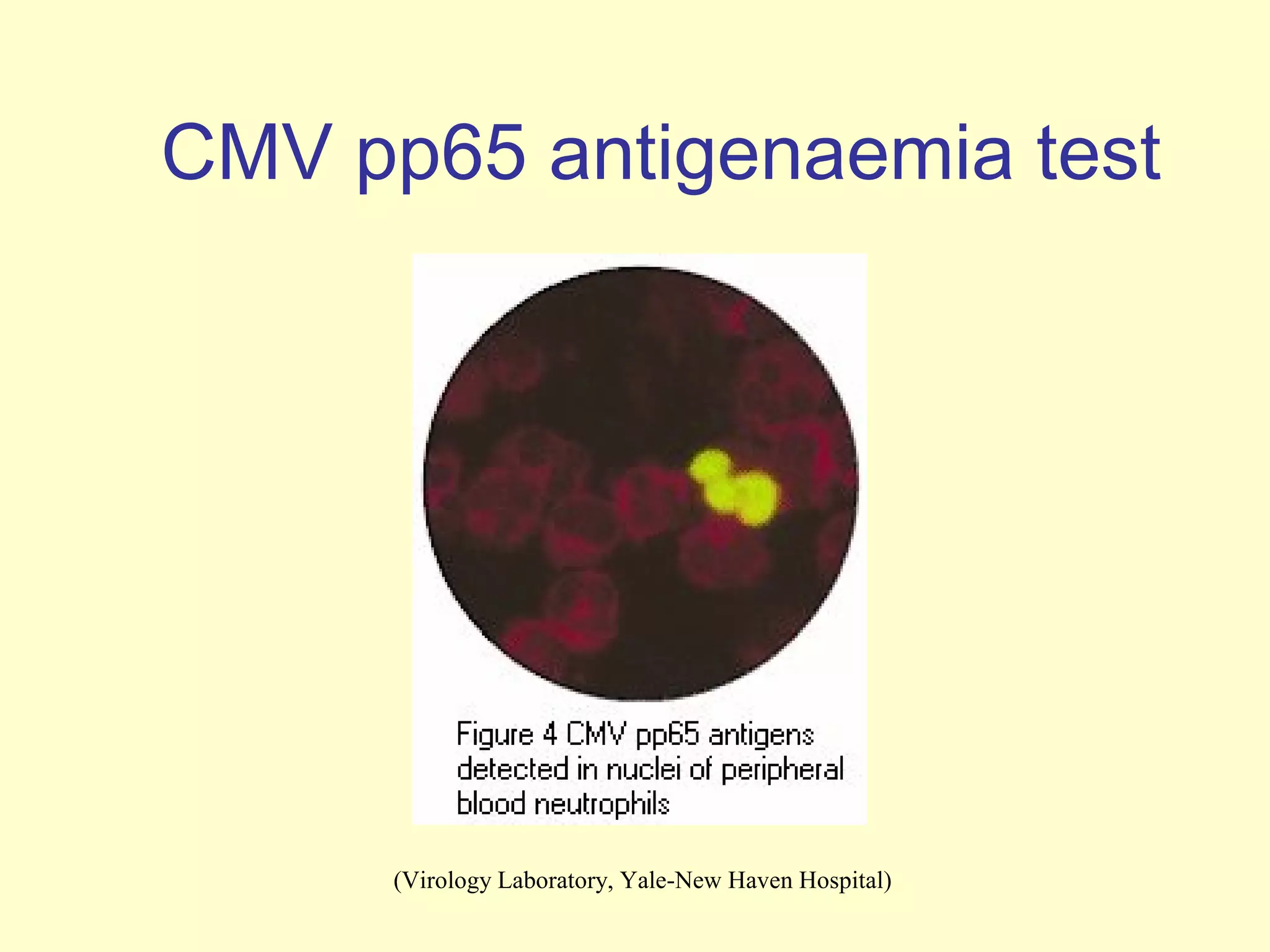
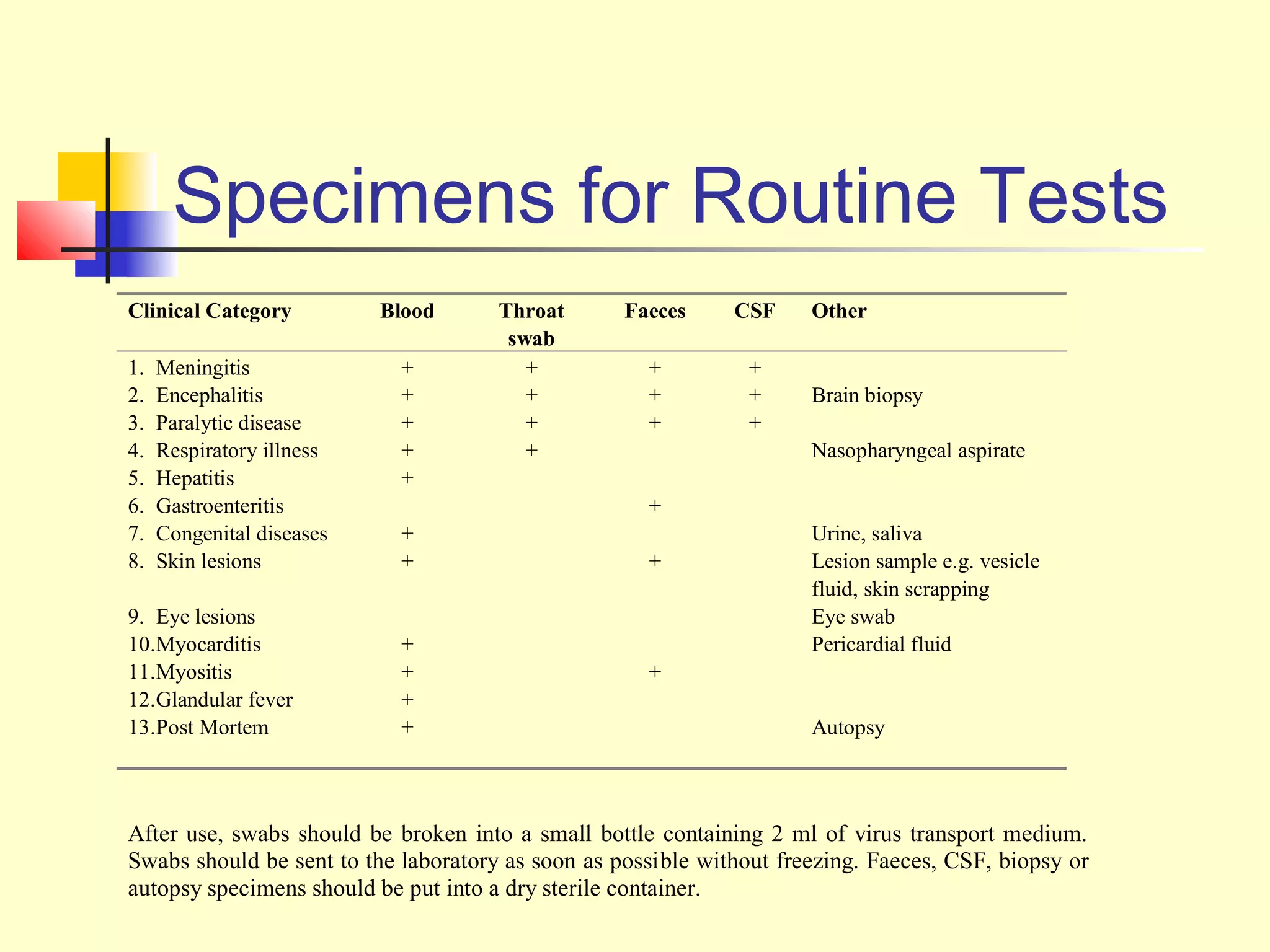
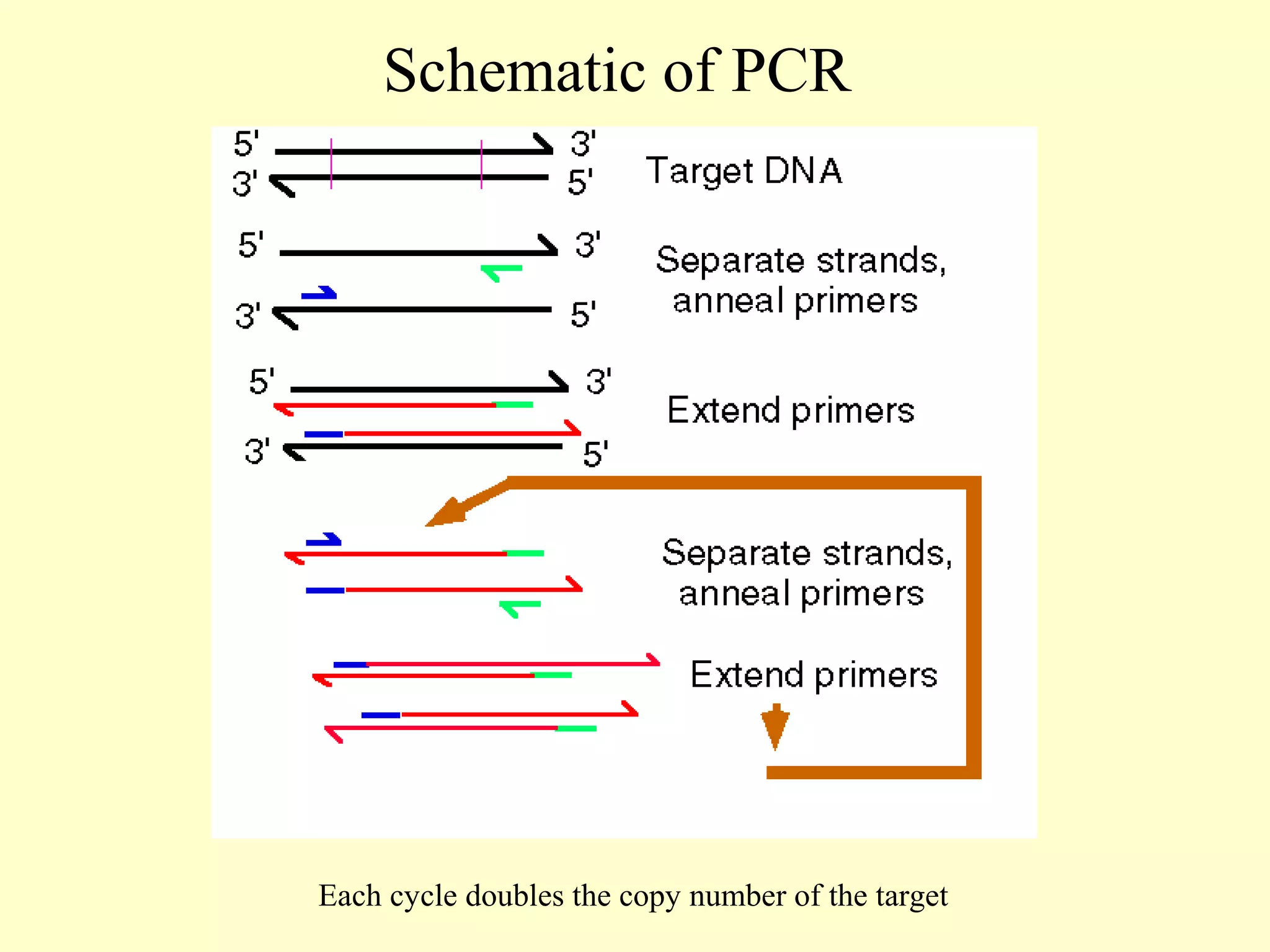
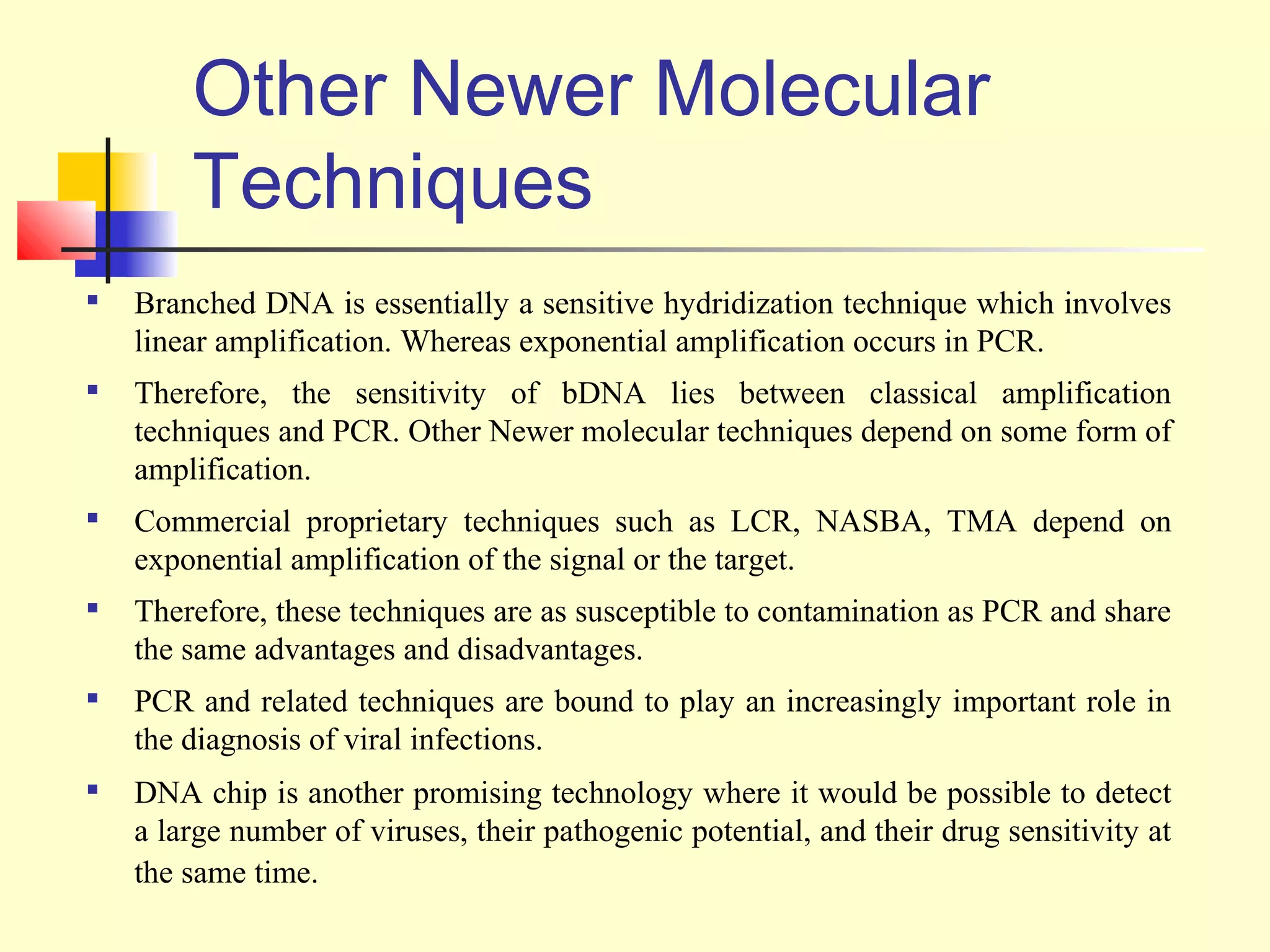
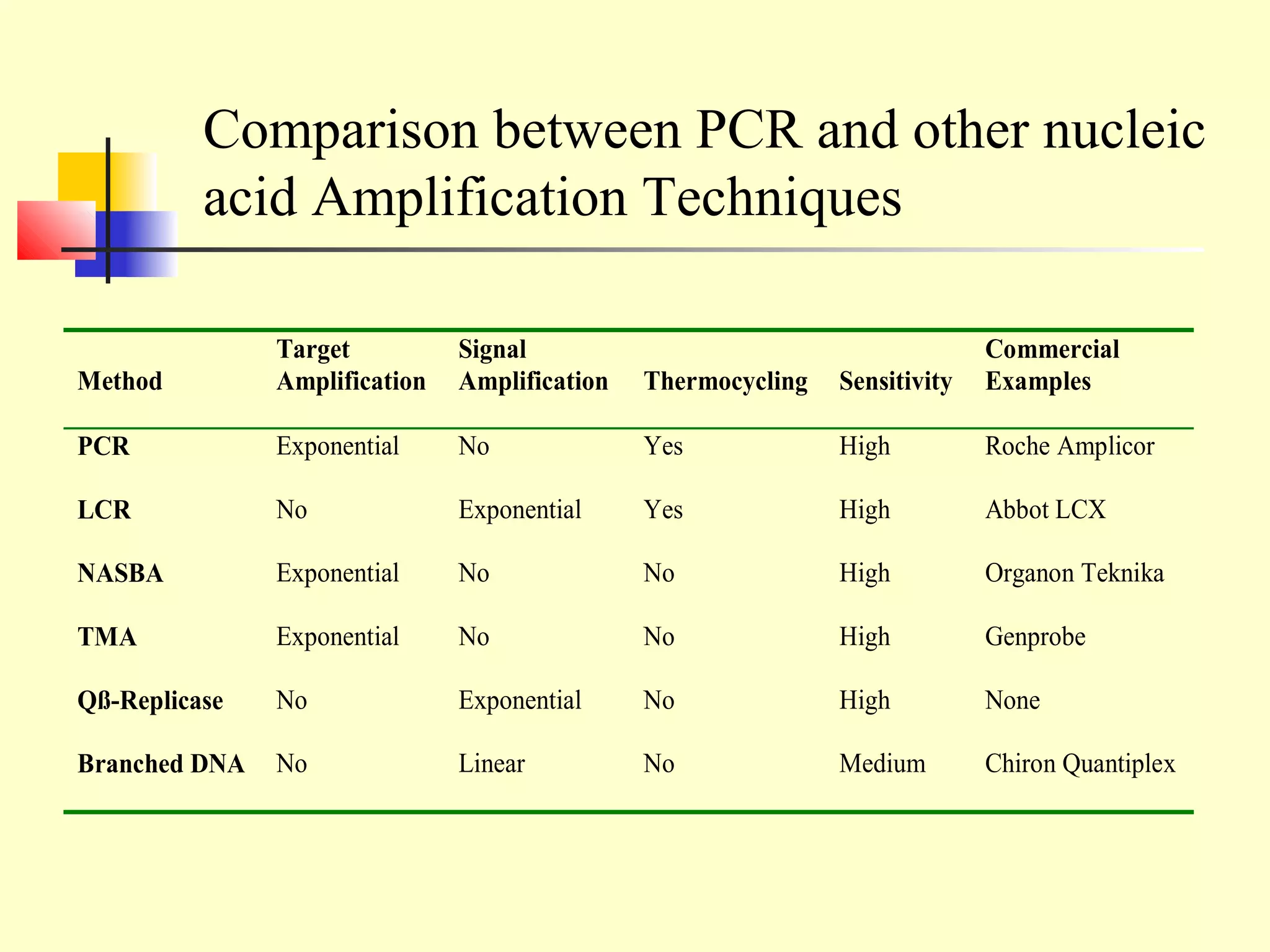
This document provides an overview of virological tests for virus detection and diagnosis. There are three main categories of tests: direct examination to detect viral antigens or genomes, indirect examination using cell culture or animals to isolate viruses, and serology to detect antibodies. Direct methods include antigen detection by immunofluorescence, electron microscopy, PCR and hybridization probes. Indirect methods involve culturing viruses in cell lines or eggs and observing cytopathic effects or hemagglutination. Serology detects rising antibody titers between acute and convalescent patient samples or presence of IgM. Newer molecular techniques like PCR have increased sensitivity but require skill and specialized equipment. Proper specimen collection and a combination of direct, culture and serology tests