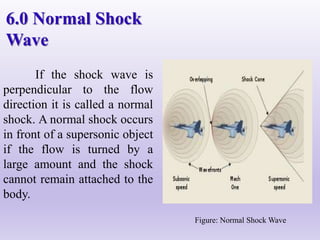
This document discusses shock waves. It defines shock waves as thin regions where supersonic flow is rapidly decelerated to subsonic flow through an adiabatic but non-isentropic process. There are three types of shock waves discussed: normal shock waves, which are perpendicular to flow; oblique shock waves, which are at an angle to flow; and curved shock waves. Examples of normal shock wave formation and oblique shock wave applications in aircraft are provided. Over-expanded and under-expanded flows through converging-diverging ducts are also summarized.