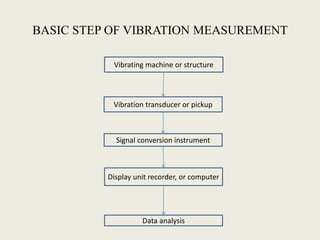
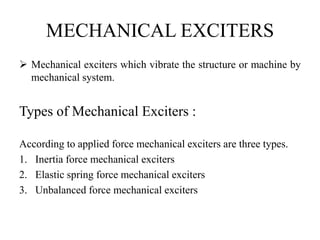
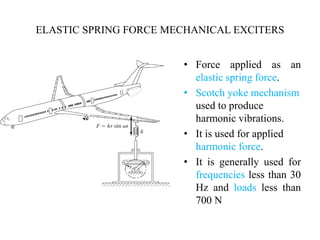
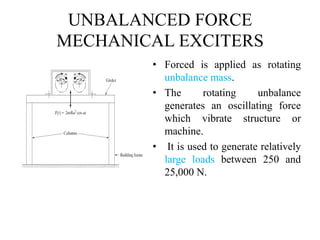
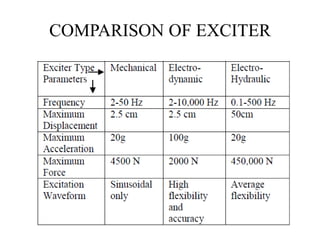
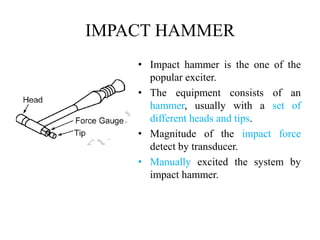
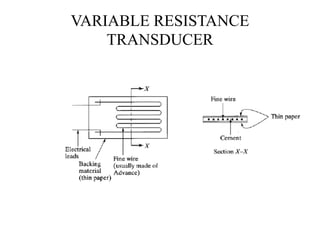
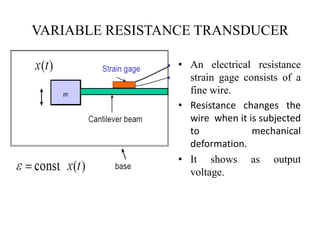
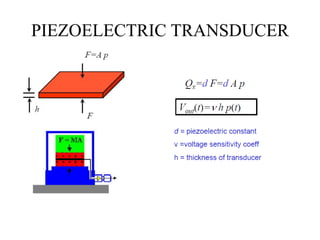
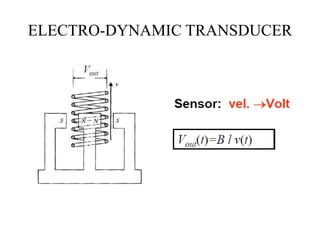
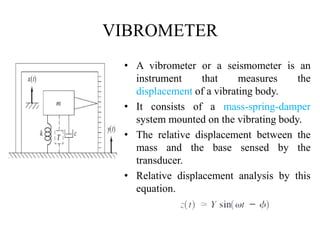
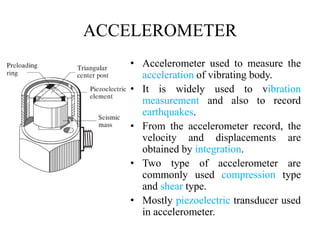
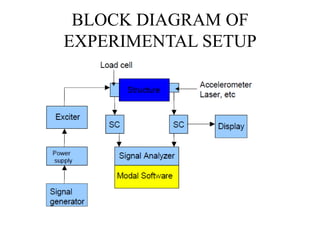
The document discusses vibration measurement. It describes how vibrations are measured to analyze mechanical systems. The key steps are exciting a structure, sensing its response with a transducer, conditioning the signal, and analyzing it. Common exciters include impact hammers and shakers. Transducers like accelerometers convert motion to electrical signals. Conditioning prepares signals for analysis using digital filtering or fast Fourier transforms. Proper equipment selection depends on the application and desired frequency range and force.