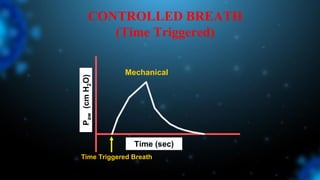
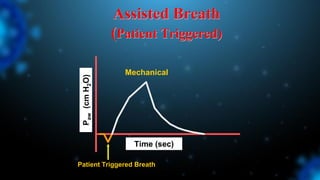
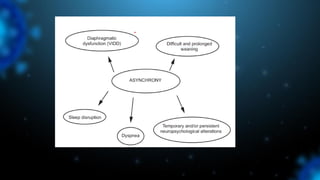
1) Ventilator asynchrony occurs when a ventilator fails to synchronize with a patient's breathing pattern, resulting in ineffective or uncomfortable ventilation.
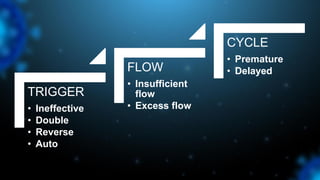
2) There are several types of asynchrony including trigger, flow, and cycle asynchrony which can be caused by inappropriate ventilator settings or patient factors.
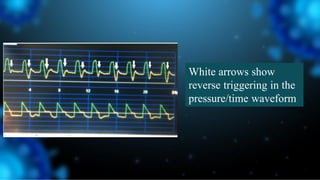
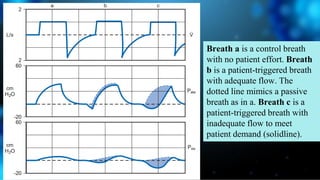
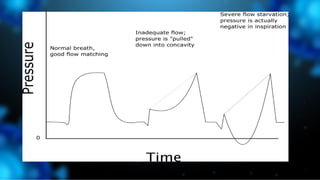
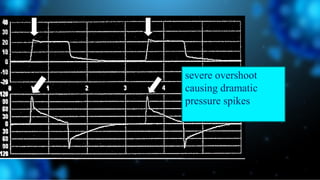
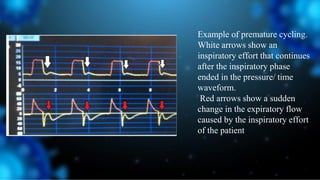
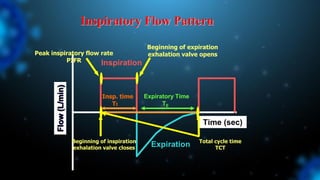
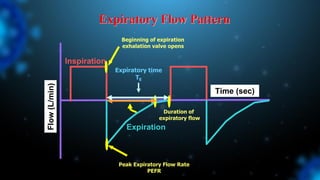
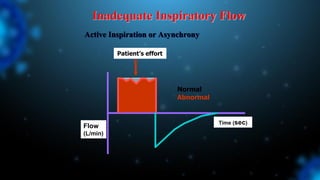
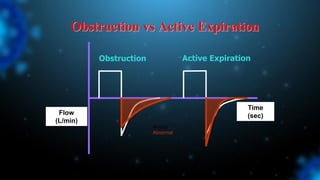
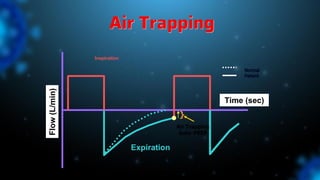
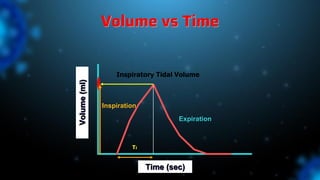
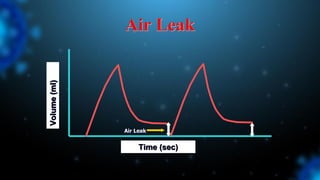
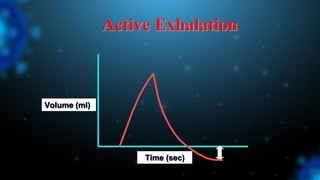
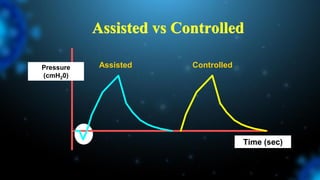
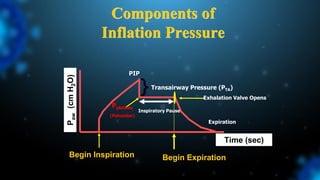
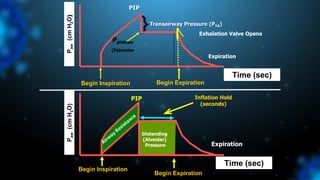
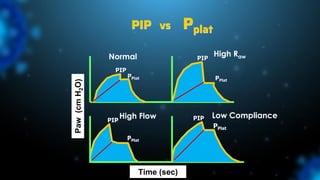
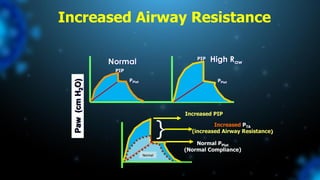
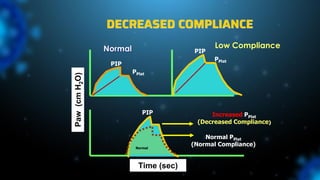
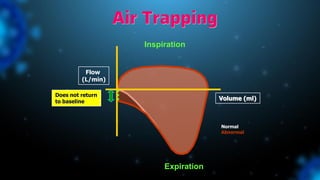
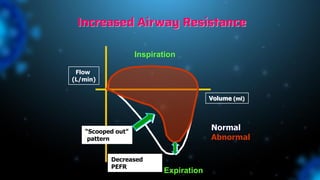
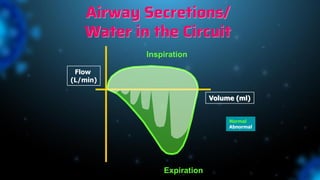
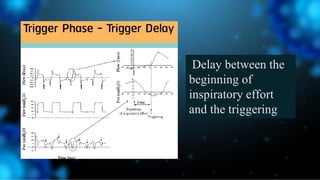
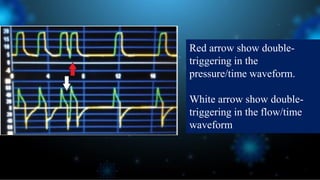
3) Identifying the type of asynchrony through ventilator waveforms helps determine the appropriate therapeutic strategy such as adjusting ventilator settings, managing secretions, or reducing sedation/paralysis.







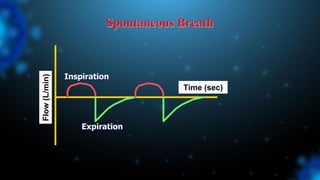
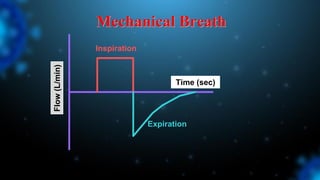



















![Cause of Asynchrony
Respiratory drive is high
Delivered ventilatory support is insufficient (eg, tidal volume [VT] or V
̇ E too
low)
Neural TI is longer than the TI set on the ventilator
Solution of Asynchrony
Increase inspiratory time
Modes that allow variation in tidal volume, such as PCV
Decrease the cycling threshold percentage (PSV)
Patient factor-Correct underlying fever, anxiety](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ventilatorasynchrony-240414163553-d879241a/85/VENTILATOR-ASYNCHRONY-pathophysiology-and-clinical-relevance-57-320.jpg)