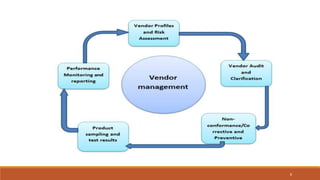
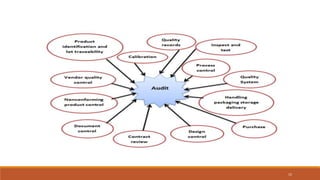
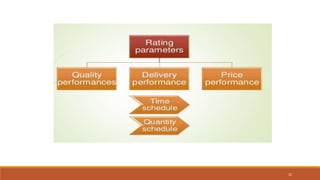
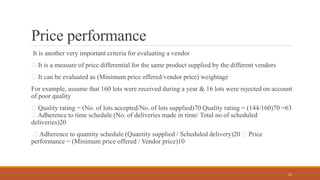
1) Vendor qualification is the process used by finished dosage form manufacturers to approve vendors for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) that will be used in products. It involves selecting vendors based on criteria like quality, delivery, price, and auditing them.
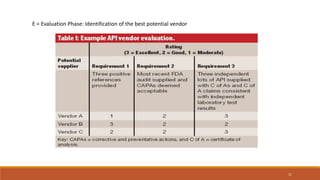
2) Vendors are categorized as A, B, or C depending on which tests they perform on APIs. Category A vendors perform all tests, B vendors are well-known and certified, and C vendors undergo full testing by the manufacturer.
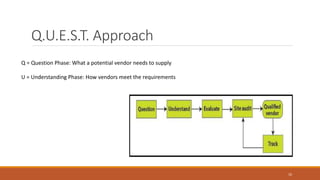
3) The vendor qualification process determines if a vendor is suitable and can consistently supply quality APIs. It aims to develop long-term supplier relationships and ensure regulatory expectations are met.