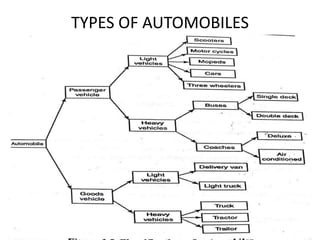
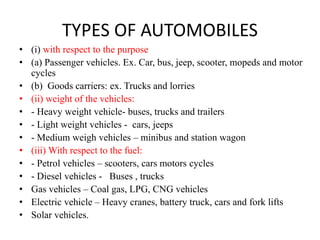
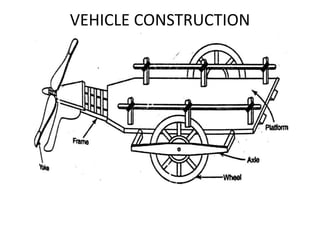
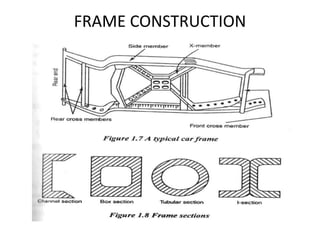
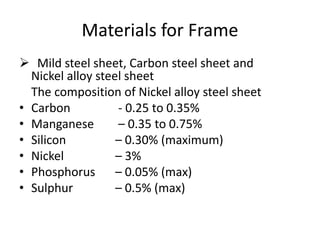
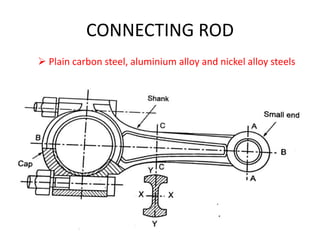
This document discusses vehicle structure and engines. It begins by describing different types of automobiles based on purpose, weight, fuel used, passenger capacity, number of wheels, and driver seat location. It then covers vehicle construction, including chassis classification based on engine location and number of wheels. Frame construction and materials are explained. The components of an automobile engine are defined, including the cylinder block, cylinder liners, piston, connecting rod, piston rings, crankshaft, camshaft, and valves. The document concludes by classifying internal combustion engines and discussing valve timing and variable valve timing.