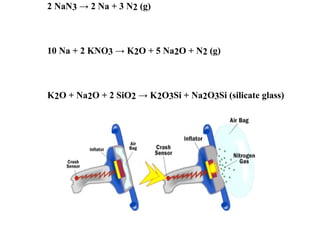
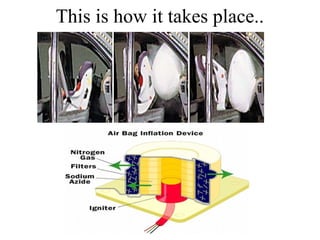
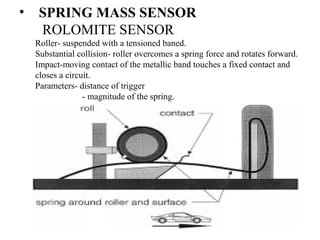
The document discusses airbags as a safety restraint system in automobiles. It begins by providing background on the development of airbags, noting they were created as a soft cushion to land against in a crash. The basics section explains how airbags work based on Newton's second law of motion to slow a passenger's speed to zero during a collision. The main parts of an airbag are described as the bag itself, made of thin nylon fabric, as well as sensors and an inflation system using hot nitrogen gas. The working section then outlines how the system detects a crash and ignites the nitrogen gas to rapidly inflate the airbag. Modern airbag types including side, curtain, and door airbags are also discussed.












![References
[1] A Safety Restraint System of an Automobile.
Tasnim N. Shaikh et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications www.ijera.com
Vol. 3, Issue 5, Sep-Oct 2013, pp.615-621
[2] A Treatise on crash sensing for automotive airbag systems IEEE /ASME transactions on
Mechatronics, Vol. 7, No. 2, JUNE 2002 by Ching-Yao Chan .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airbagsppt-160811143529/85/Airbags-ppt-16-320.jpg)
