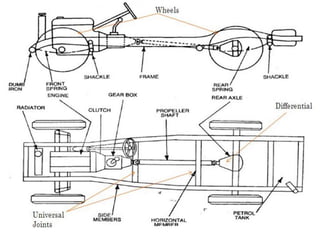
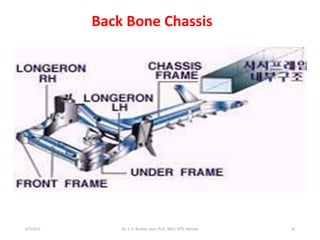
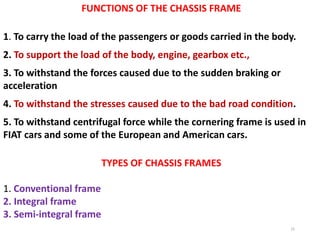
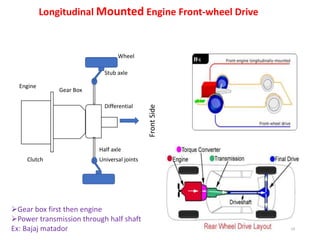
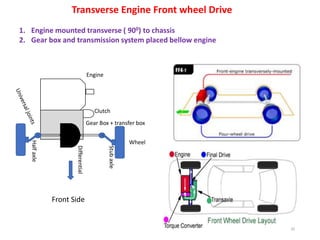
The document provides an introduction to automobiles, including their purpose, classification, components, and chassis types. It defines an automobile as a self-propelled vehicle that produces its own power. Automobiles are classified based on requirements, load capacity, body type, drive type, fuel used, number of wheels/seats, model/make, piston displacement, and control type. The main components are the chassis, body, engine, suspension, lubrication system, transmission system, steering system, electrical system, and fuel supply system. Chassis types include ladder frame, tubular space frame, monocoque, and backbone. The document also describes functions and layouts of the chassis as well as requirements for automobile bodies.