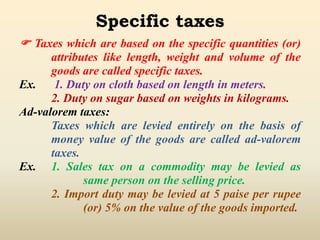
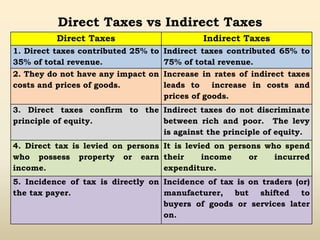
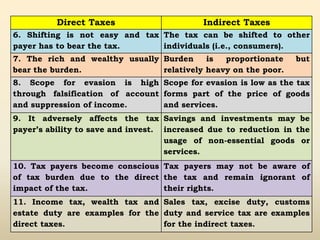
1. Indirect taxes are taxes that are paid indirectly by consumers when purchasing goods or services, with the impact being on one person and the incidence on another.
2. Examples of indirect taxes include excise duty, customs duty, sales tax, service tax, and octroi. These taxes can be shifted from the original payer to other persons.
3. While indirect taxes constitute a major source of government revenue, they are generally considered regressive as the tax burden does not vary based on ability to pay.