The presentation outlines India's Budget for 2025-26, highlighting significant tax relief measures and a focus on development across various sectors, including support for the middle class, farmers, and urban workers. It includes proposals such as increasing tax exemptions for income up to ₹12 lakh, funding for agricultural and rural development, and enhancing access to credit for micro and small enterprises. Additionally, it aims to promote domestic manufacturing, clean technology, and improvements in health and education infrastructure.




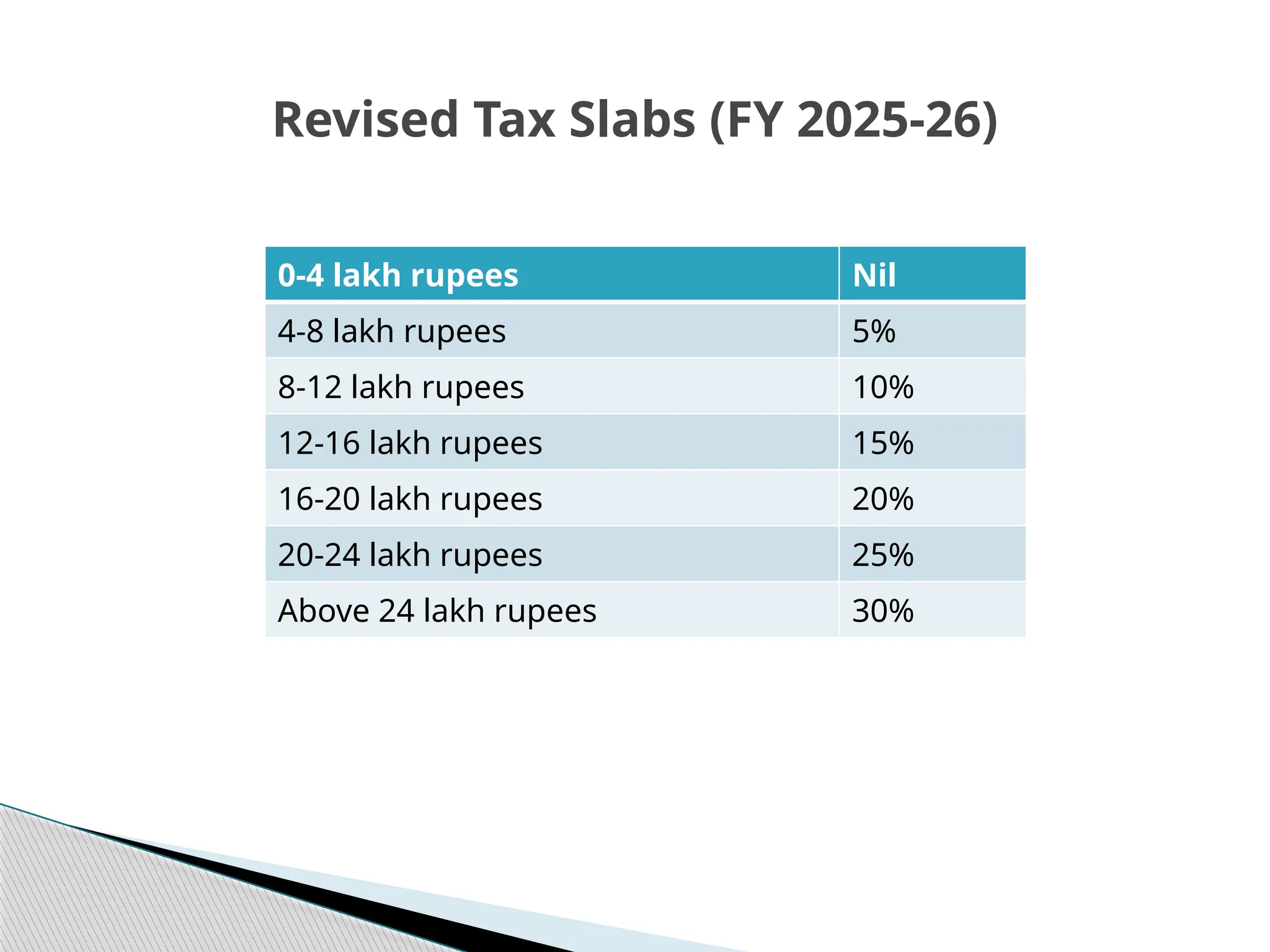
![ In this Budget Govt has announced that there will be No Income Tax
payable upto income of ₹12 lakh (i.e. average income of ₹1 lakh per
month other than special rate income such as capital gains) under
the new regime.
For the Salaried Class, No Income Tax is applicable Rll annual
income of ₹12.75 lakh, due to standard deducRon benefit available
to salaried class of ₹75,000
The total tax benefit of slab rate changes and rebate at different
income levels can be illustrated with examples.
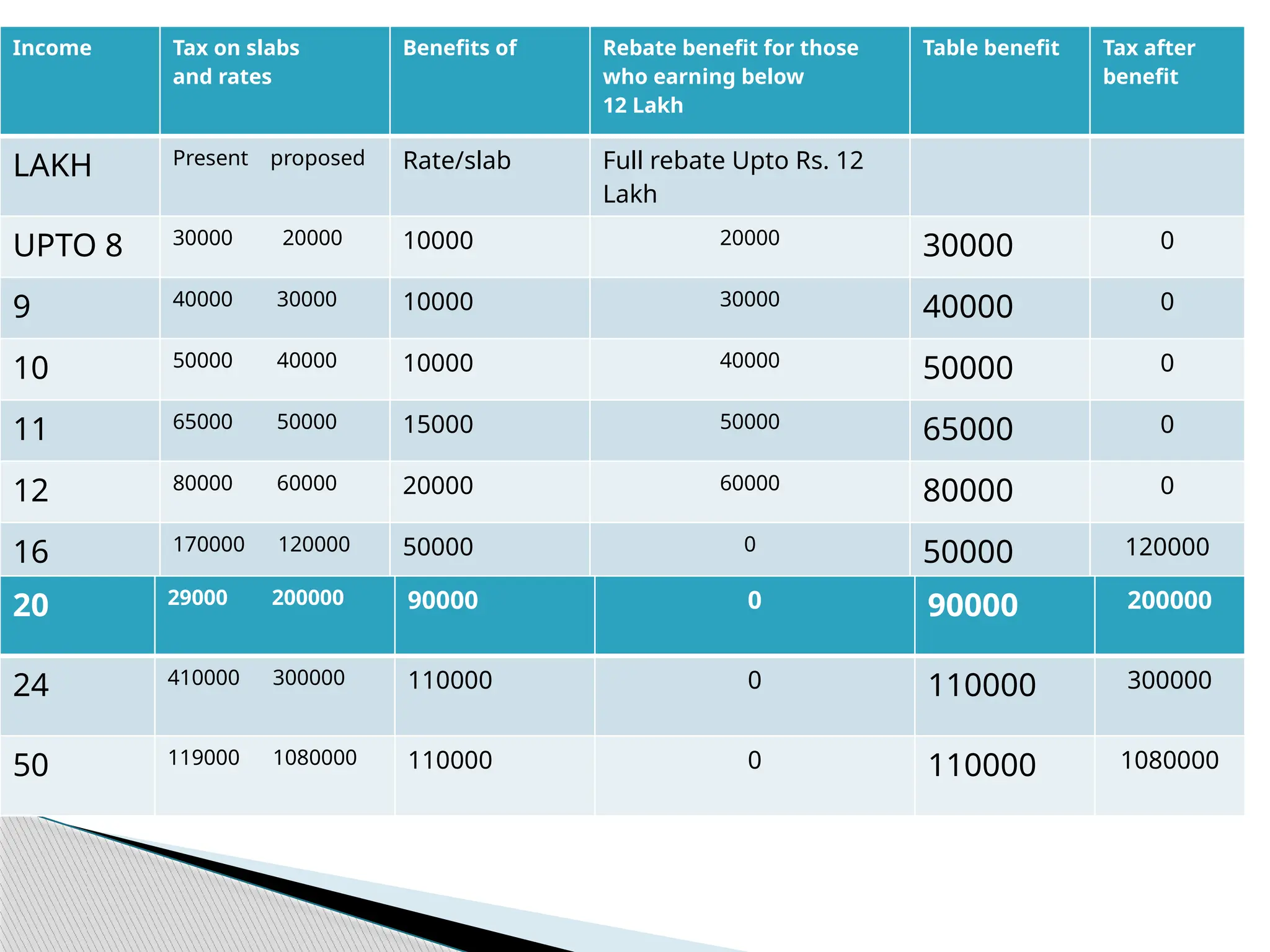
A tax payer in the new regime with an income of ₹12 lakh will get a
benefit of ₹80,000 in tax (100% of tax payable as per existng rates
will be exempt). The effective income tax rate will be 0%.
A person having income of ₹16 lakh will get a benefit of ₹50,000 in
tax. [The effective income tax rate payable will be just 7.5%]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonbudget2025-26-250202103930-c1f173ac/75/PRESENTATION-ON-BUDGET-2025-26-pptx-to-help-and-understand-the-budget-5-2048.jpg)
![ A person having income of ₹18 lakh will get a benefit of ₹70,000 in
tax. [The effective income tax rate payable will be just 8.8%]
A person having income of ₹20 lakh will get a benefit of ₹90,000 in
tax. [The effective income tax rate payable will be just 10%].
A person with an income of ₹25 lakh gets a benefit of ₹1,10,000. [The
effective tax rate will be just 13.2%]
A person with an income of ₹50 lakh also gets a benefit of ₹1,10,000.
[The effective tax rate will be just 21.6%]
As a result of these proposals, revenue of about ₹ 1 lakh crore in
direct taxes will be forgone.
Illustration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonbudget2025-26-250202103930-c1f173ac/75/PRESENTATION-ON-BUDGET-2025-26-pptx-to-help-and-understand-the-budget-6-2048.jpg)