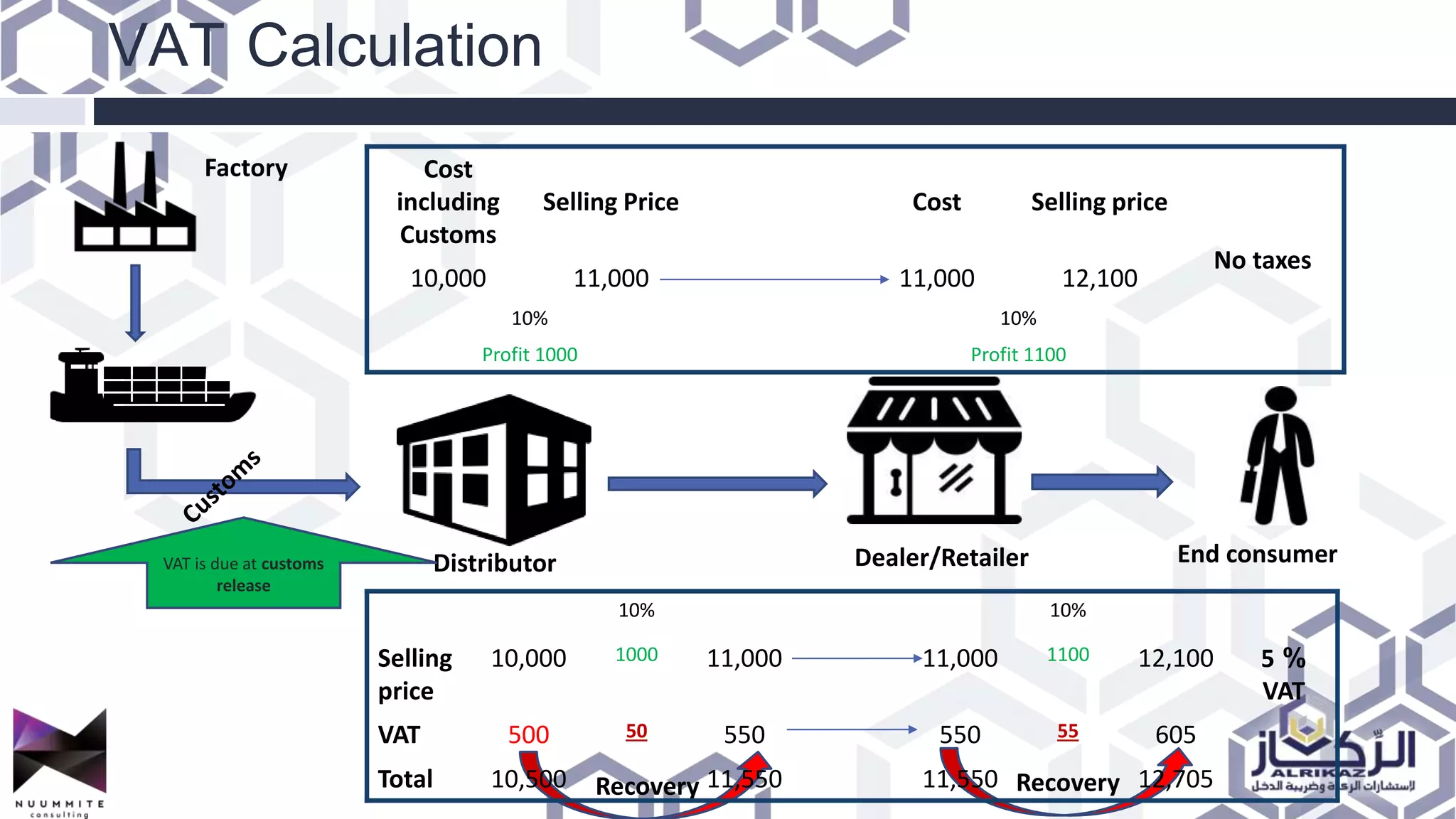
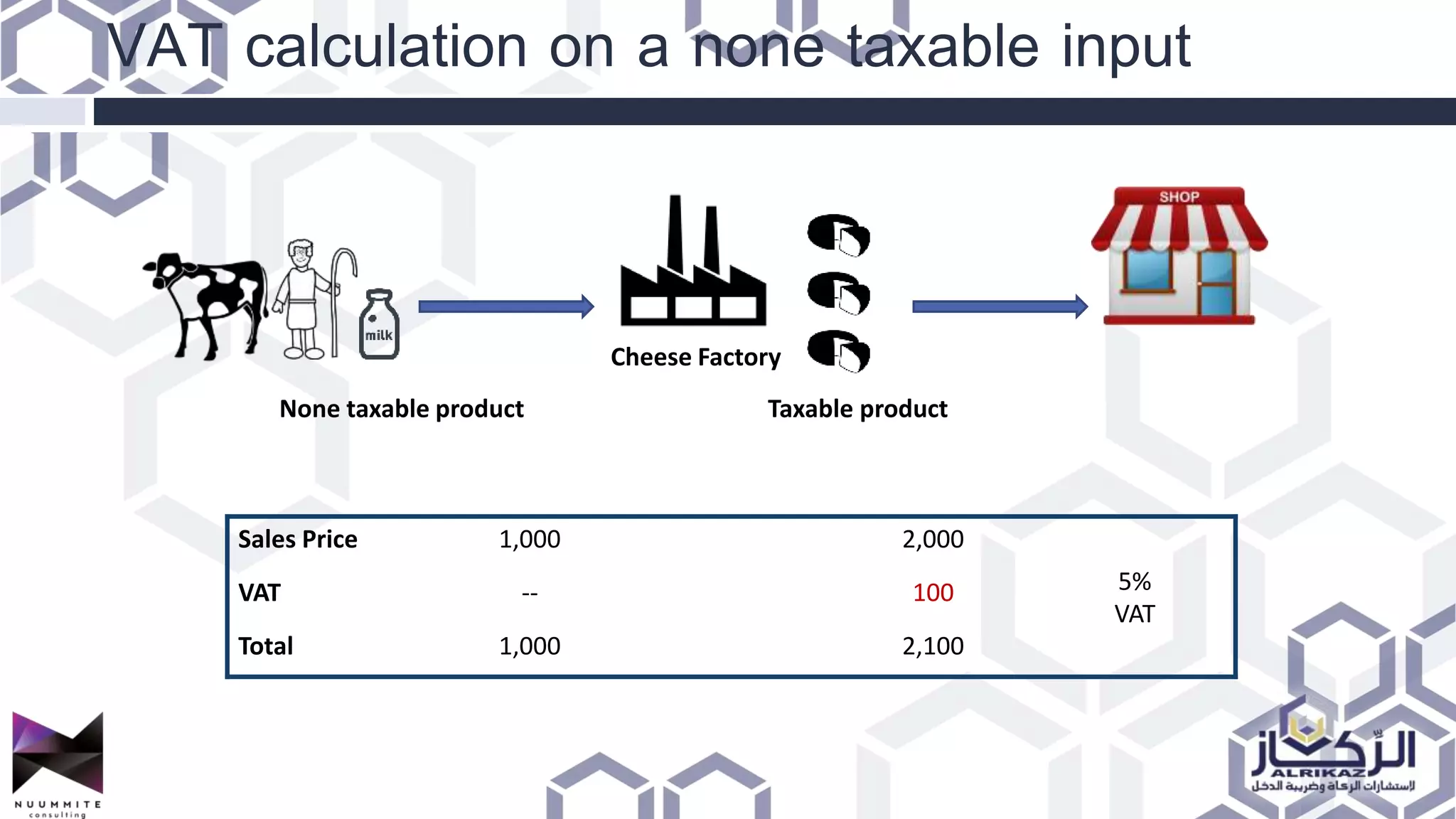
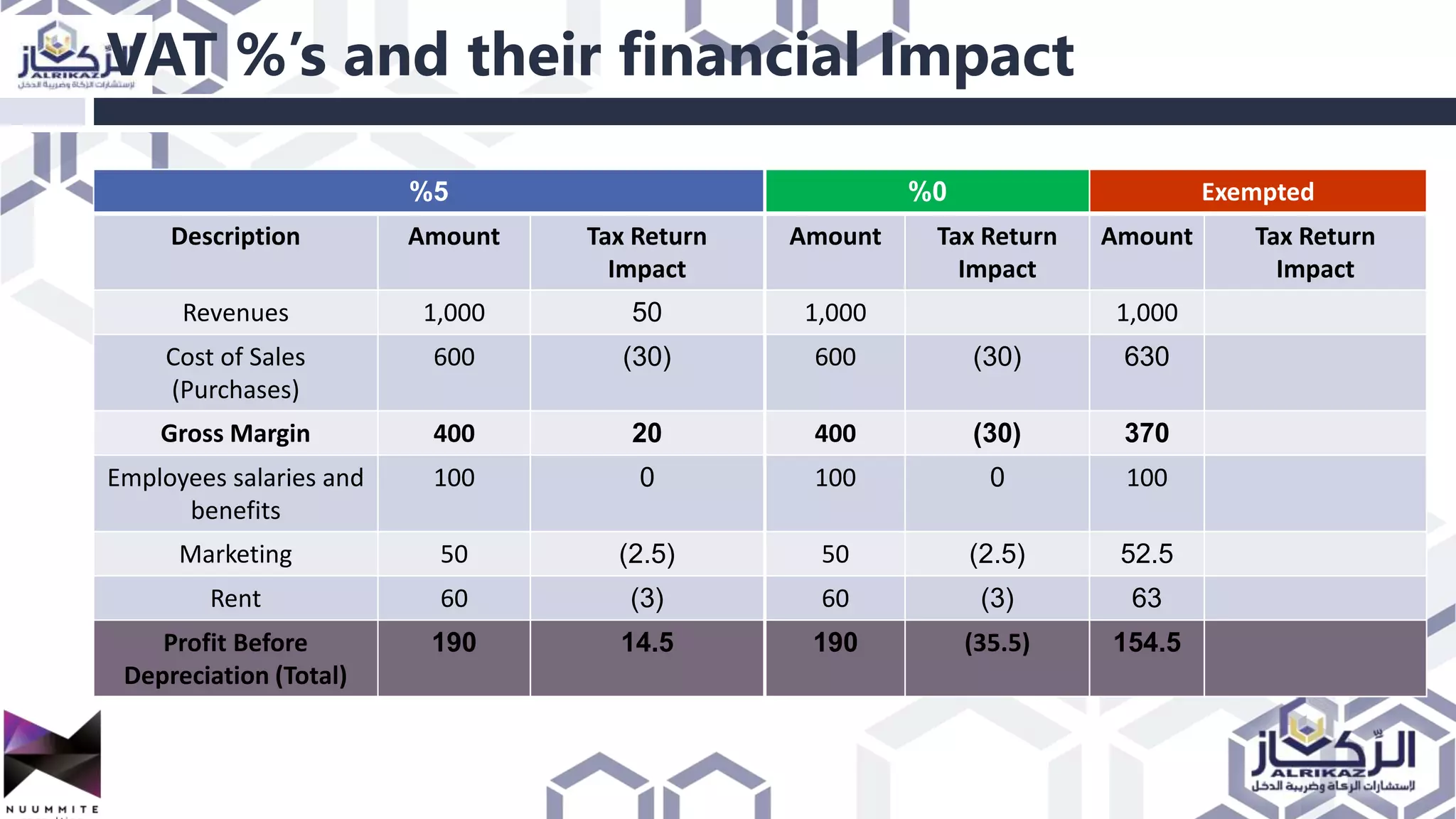
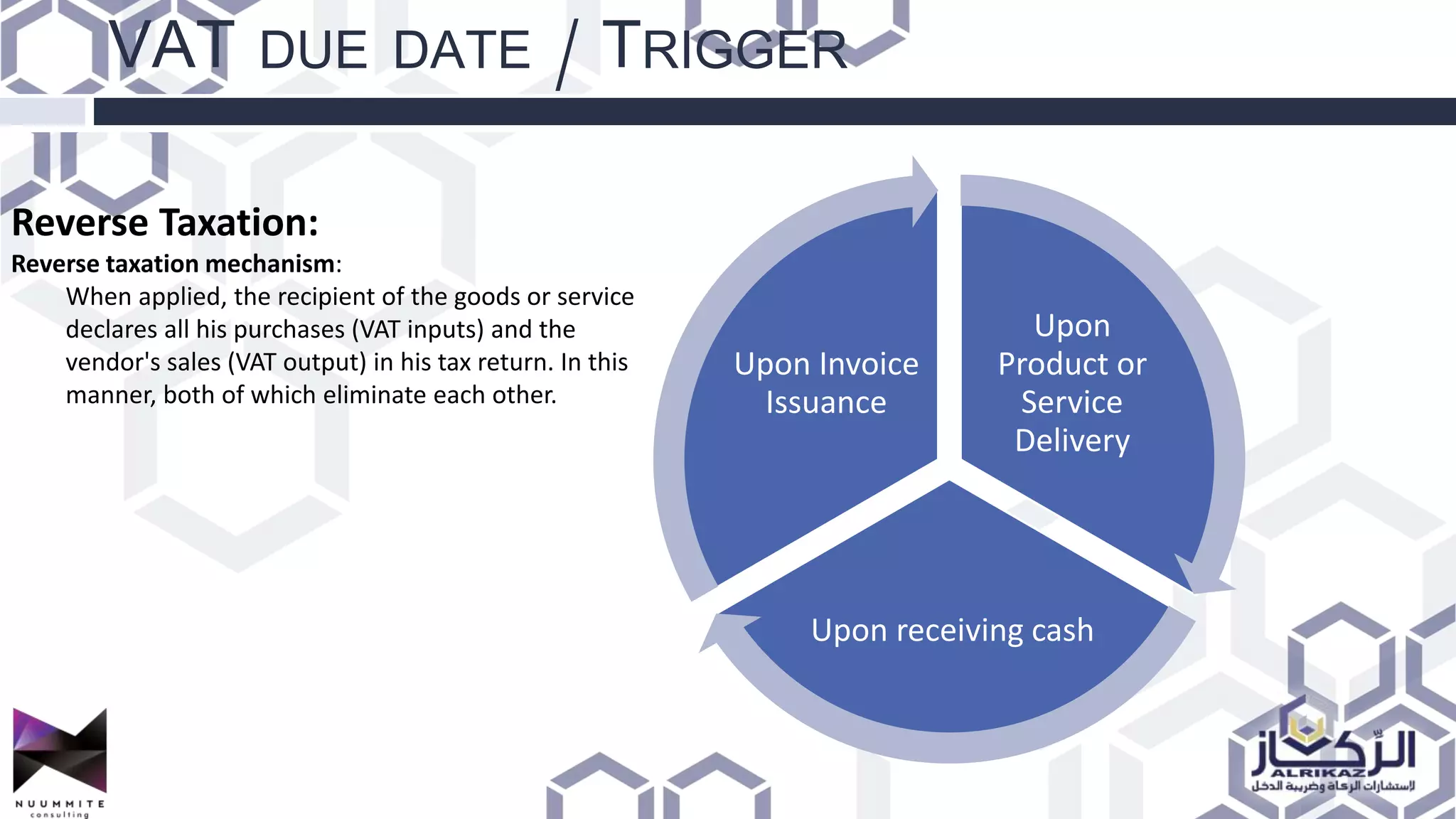
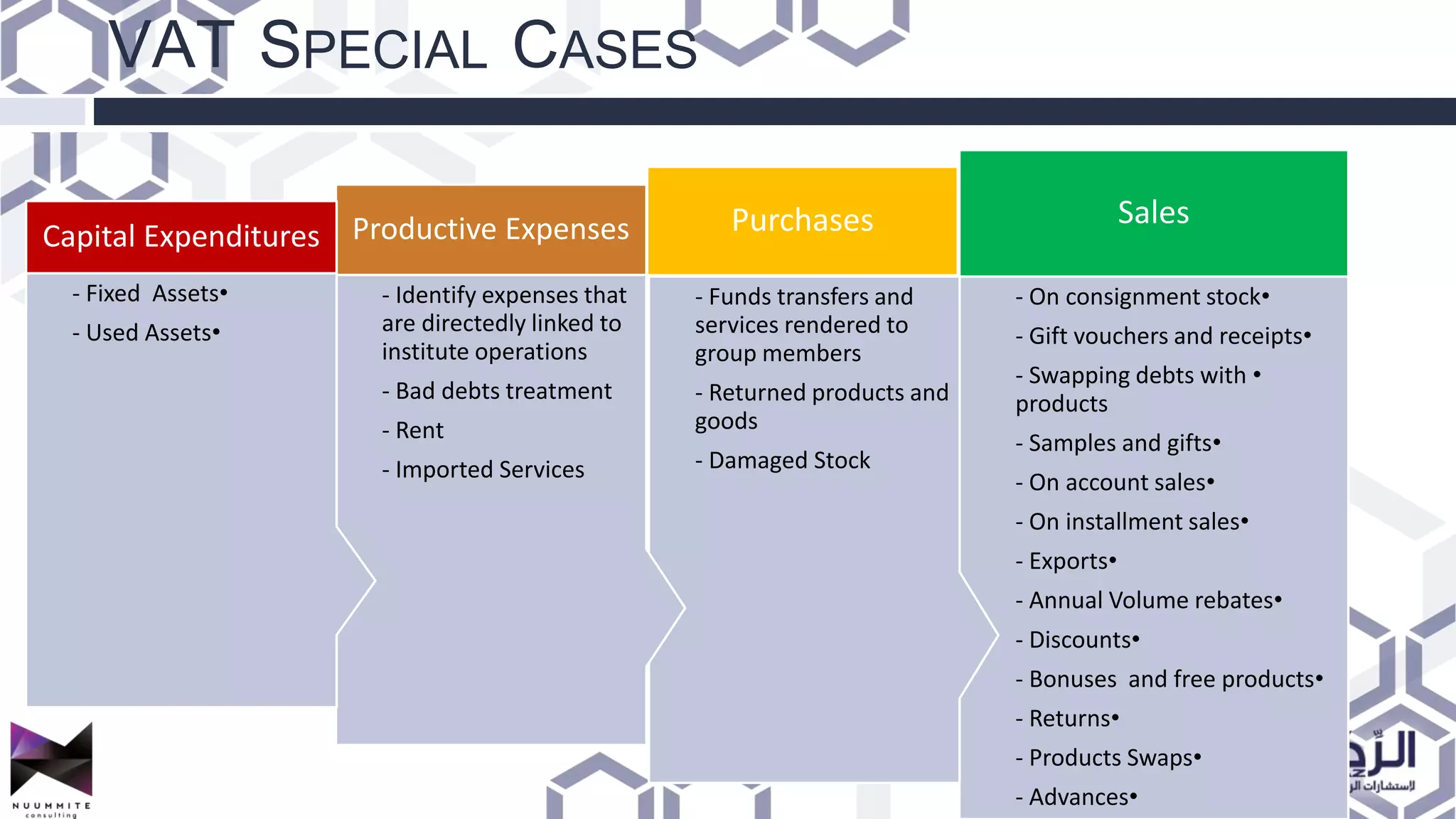
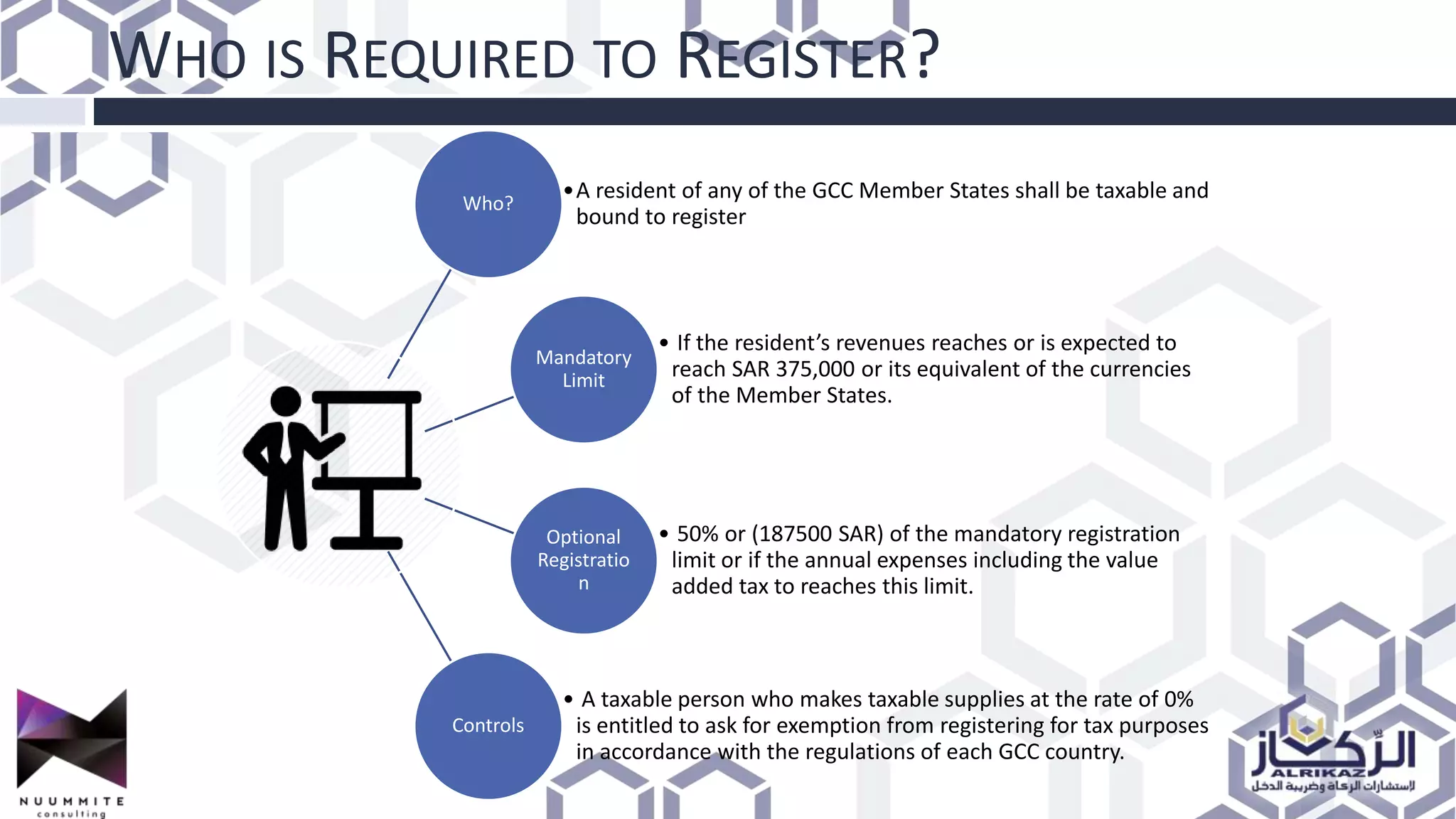
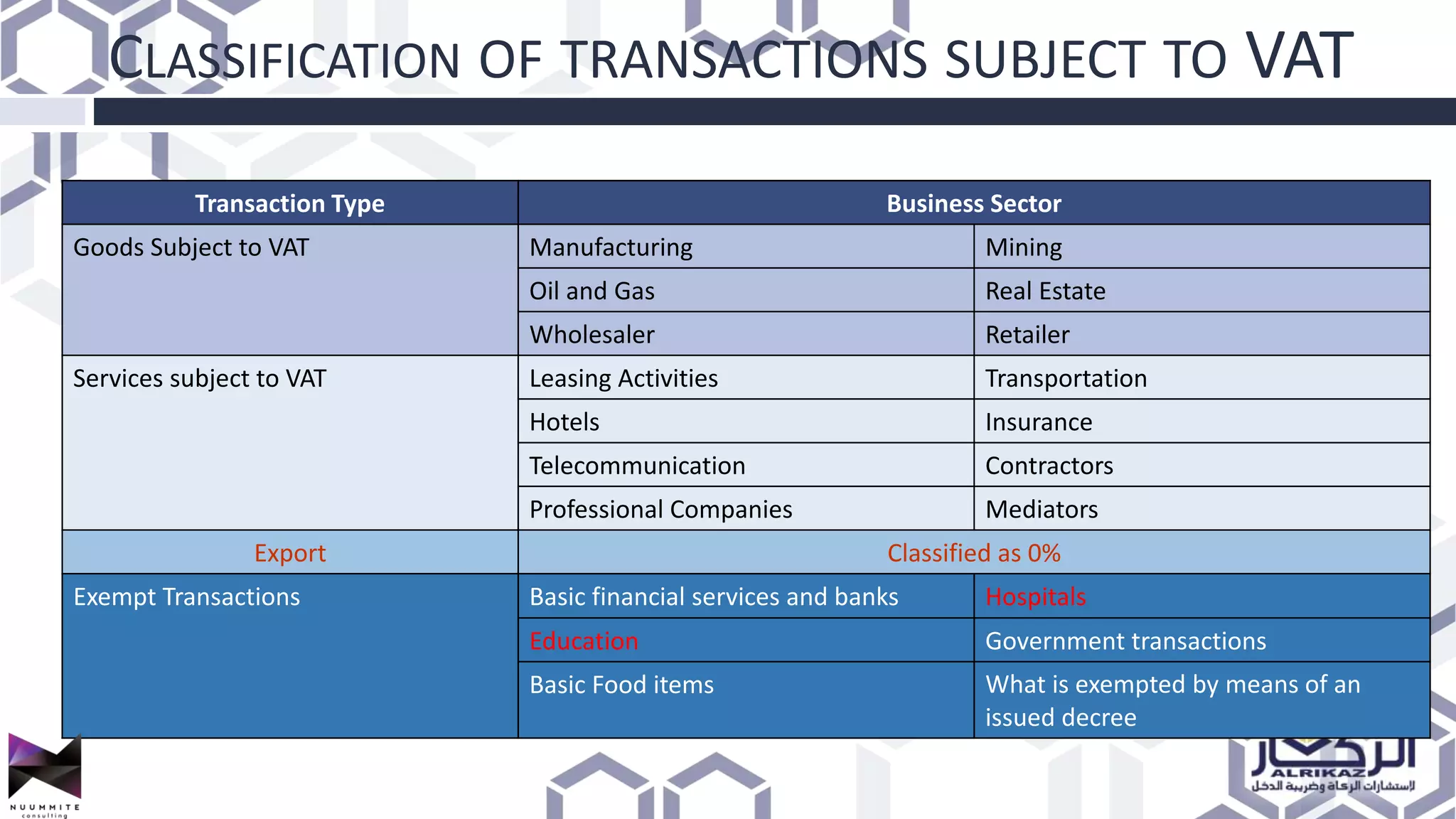
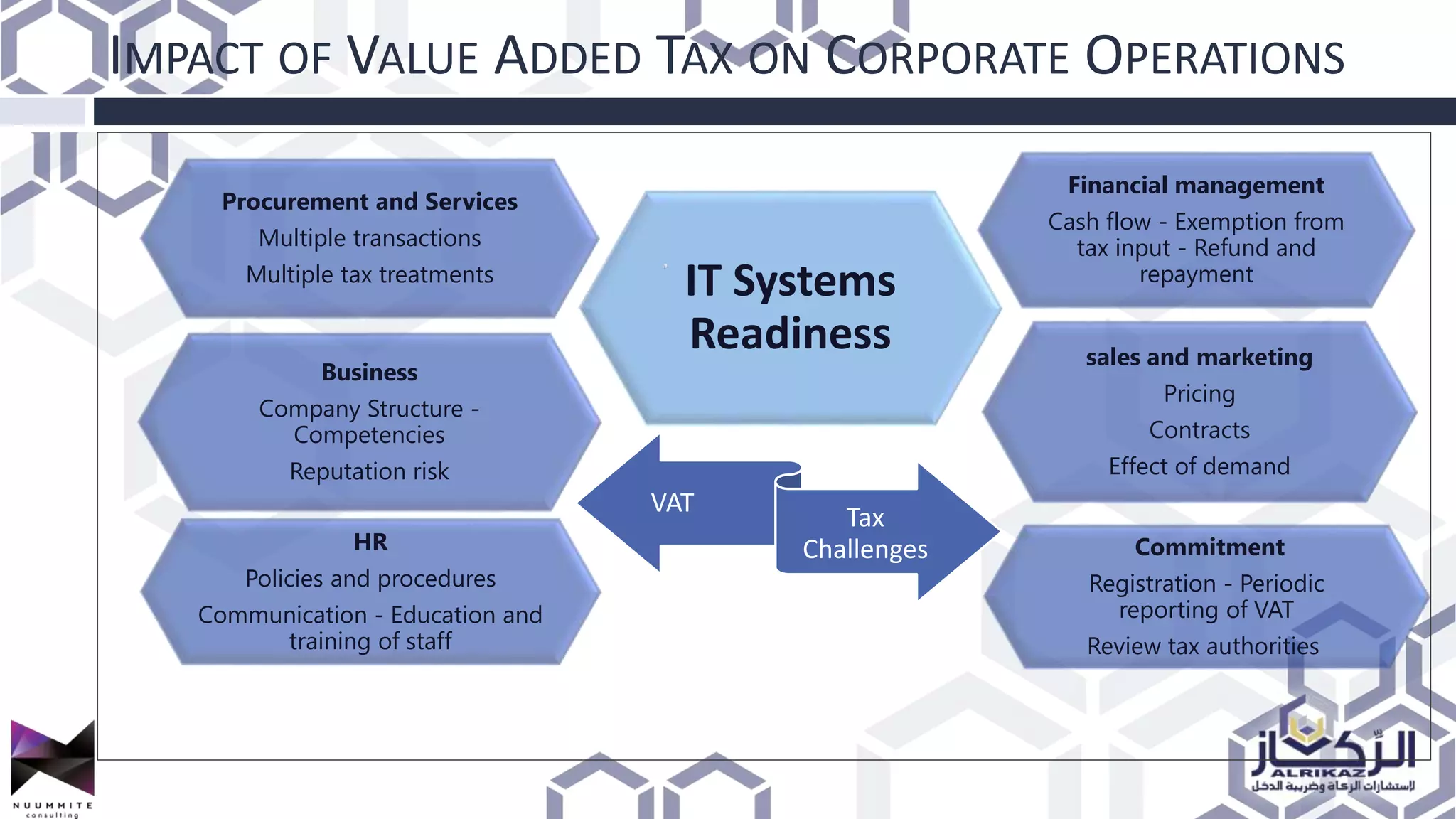
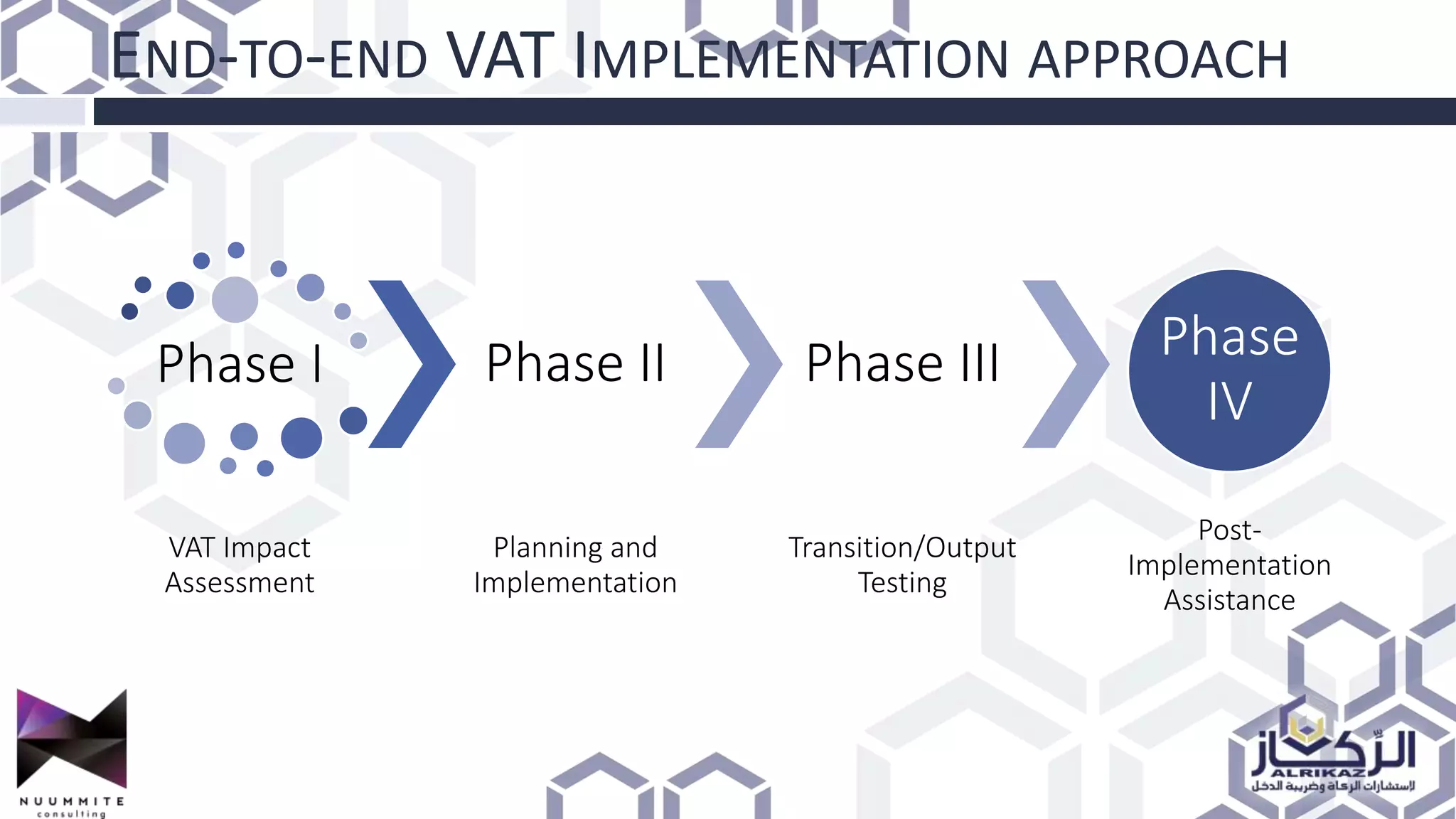
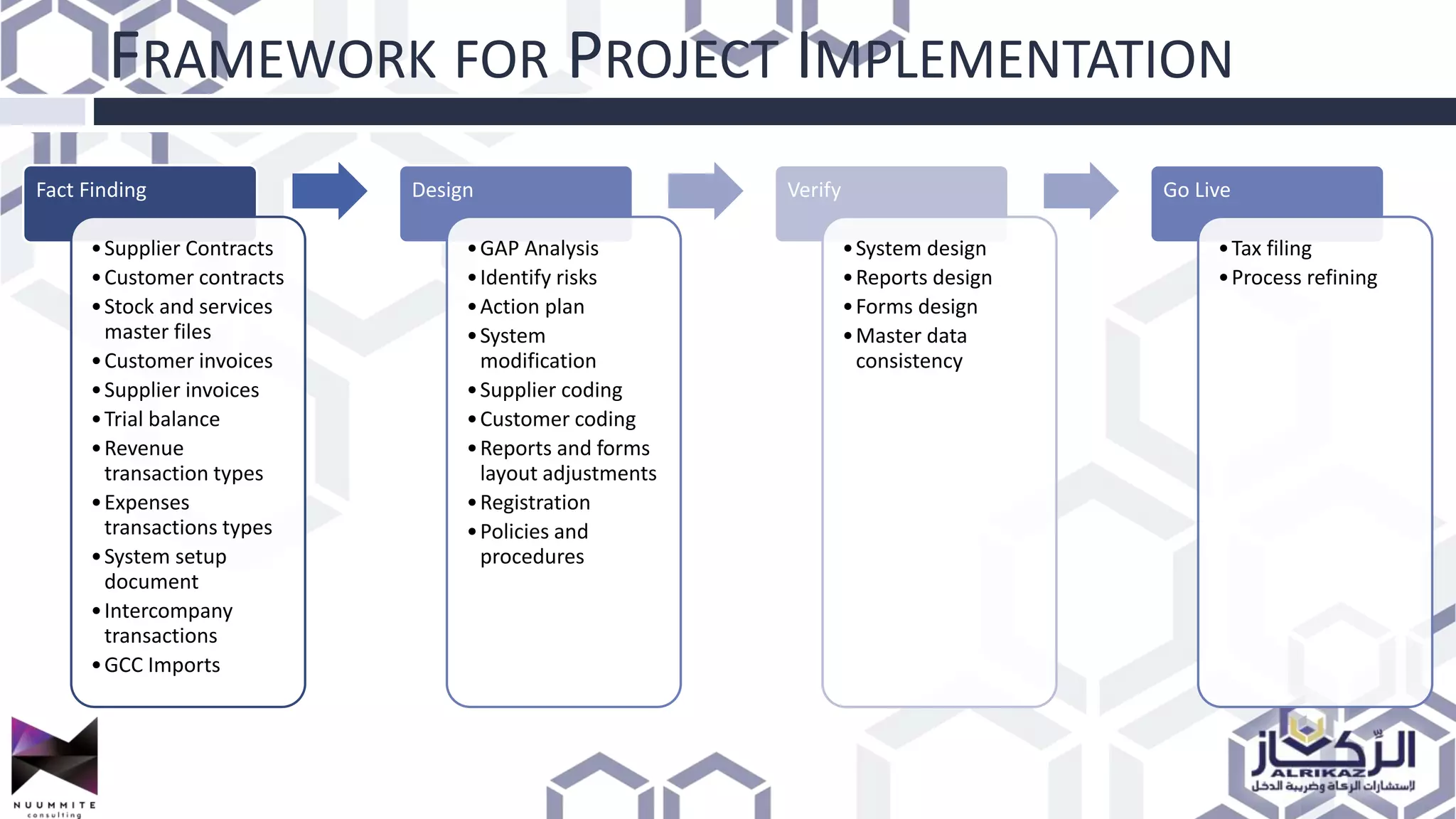
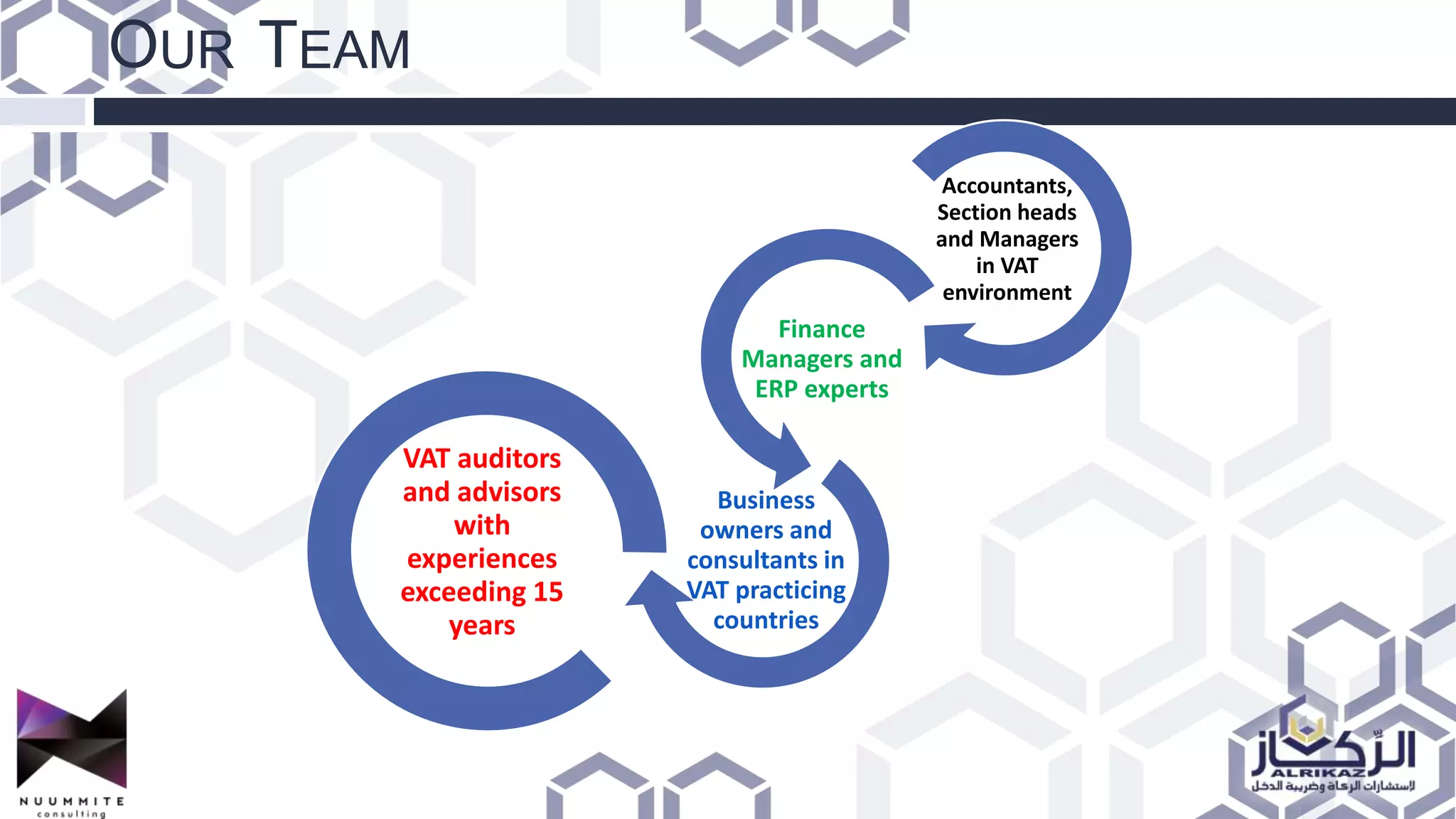
The document provides a detailed overview of value added tax (VAT) and excise tax, including definitions, calculations, and regulations applicable to GCC member states. It outlines the impact of VAT on various departments, tax record requirements, exemptions, and implementation strategies for businesses. Additionally, it discusses excise tax on goods detrimental to public health and the environment, along with the associated rates.