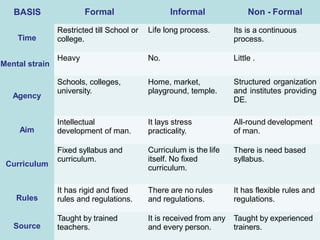
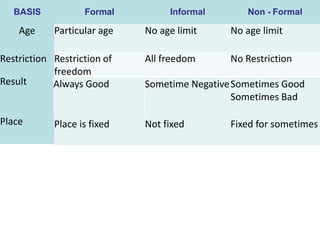
Formal education refers to pre-planned education in institutions like schools and colleges, with a set curriculum, timetable, and trained teachers. Informal education occurs incidentally through daily life experiences with family and community without a curriculum or teachers. Non-formal education occurs outside of formal schools and is intentionally planned without rigid rules, serving identified groups of any age through flexible programming. All three types - formal, informal, and non-formal - have merits and should be integrated to provide comprehensive education.