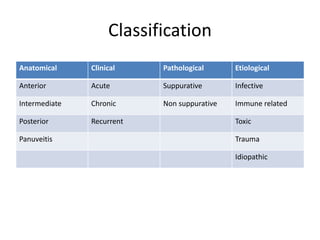
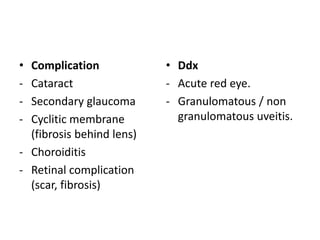
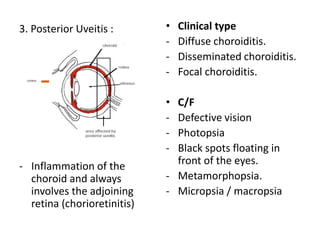
This document provides a comprehensive overview of uveal tissue inflammation, detailing the types of uveitis (anterior, intermediate, and posterior) along with their clinical features, complications, and treatments. It covers classifications based on anatomy, pathology, and etiology, including infections, immune-mediated causes, and trauma. The text also discusses diagnostic investigations and offers extensive treatment options for various uveitis-related conditions.